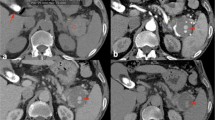
Abstract
Splenic pseudoaneurysms following chronic pancreatitis can rarely become a source of life-threatening bleeding by rupturing into various regions or components, including pseudocysts, the abdominal cavity, the gastrointestinal tract, and the pancreatic duct. In such cases, prompt diagnosis and therapy are warranted. We report herein the case of a 52-year-old man in whom a splenic pseudoaneurysm ruptured into the colon via a fistula with an abscess cavity, causing massive bleeding, which was successfully managed by trans-catheter arterial embolization (TAE).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
White AF, Baum S, Buranasiri S (1976) Aneurysms secondary to pancreatitis. Am J Roentgenol 127:393–396
Burke JW, Erickson SJ, Kellum CD, et al. (1986) Pseudoaneurysms complicating pancreatitis: Detection by CT. Radiology 161:447–450
Vujic I (1989) Vascular complications of pancreatitis. Radiol Clin North Am 27:81–91
Boudghene F, L’Hermine C, Bigot JM (1993) Arterial complications of pancreatitis: Diagnostic and therapeutic aspects in 104 cases. J Vasc Intervent Radiol 4:551–558
Stanley JC, Frey CF, Miller TA, et al. (1976) Major arterial hemorrhage: a complication of pancreatic pseudocysts and chronic pancreatitis. Arch Surg 111:435–440
Stabile BE, Wilson SE, Debas HT (1983) Reduced mortality from bleeding pseudocysts and pseudoaneurysms caused by pancreatitis. Arch Surg 118:45–51
Memis A, Parildar M (2001) Interventional radiological treatment in complications of pancreatitis. Eur J Radiol 43:219–228
Takahashi T, Shimada K, Kobayashi N, et al. ((2001) Migration of steel-wire coils into the stomach after transcatheter arterial embolization for a bleeding splenic artery pseudoaneurysm: Report of a case. Surg Today 31:458–462
Uflacker R, Diehl JC (1982) Successful embolization of a bleeding splenic artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to necrotizing pancreatitis. Gastrointest Radiol 7:379–382
Stosslein F, Zimmermann L, Bulang T (1998) Embolization treatment of bleeding complications in pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 5:344–347
McDermott VG, Shlansky-Goldberg R, Cope C (1994) Endovascular management of splenic artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 17:179–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwama, Y., Sugimoto, K., Zamora, C.A. et al. Transcatheter Embolization of Splenic Artery Pseudo-Aneurysm Rupturing into Colon After Post-Operative Pancreatitis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 29, 133–136 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-0061-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-004-0061-1