Abstract
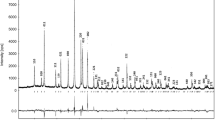
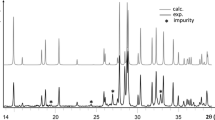
Single crystals of Li-aegirine LiFe3+Si2O6 were synthesized at 1573 K and 3 GPa, and a polycrystalline sample suitable for neutron diffraction was produced by ceramic sintering at 1223 K. LiFe3+Si2O6 is monoclinic, space group C2/c, a=9.6641(2) Å, b= 8.6612(3) Å, c=5.2924(2) Å, β=110.12(1)∘ at 300 K as refined from powder neutron data. At 229 K Li-aegirine undergoes a phase transition from C2/c to P21 /c. This is indicated by strong discontinuities in the temperature variation of the lattice parameters, especially for the monoclinic angle β and by the appearance of Bragg reflections (hkl) with h+k≠2n. In the low-temperature form two non-equivalent Si-sites with 〈SiA–O〉=1.622 Å and 〈SiB–O〉=1.624 Å at 100 K are present. The bridging angles of the SiO4 tetrahedra O3–O3–O3 are 192.55(8)° and 160.02(9)° at 100 K in the two independent tetrahedral chains in space group P21 /c, whereas it is 180.83(9)° at 300 K in the high-temperature C2/c phase, i.e. the chains are nearly fully expanded. Upon the phase transition the Li-coordination changes from six to five. At 100 K four Li–O bond lengths lie within 2.072(4)–2.172(3) Å, the fifth Li–O bond length is 2.356(4) Å, whereas the Li–O3 A bond lengths amount to 2.796(4) Å. From 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopic measurements between 80 and 500 K the structural phase transition is characterized by a small discontinuity of the quadrupole splitting. Temperature-dependent neutron powder diffraction experiments show first occurrence of magnetic reflections at 16.5 K in good agreement with the point of inflection in the temperature-dependent magnetization of LiFe3+Si2O6. Distinct preordering phenomena can be observed up to 35 K. At the magnetic phase transition the unit cell parameters exhibit a pronounced magneto-striction of the lattice. Below T N Li-aegirine shows a collinear antiferromagnetic structure. From our neutron powder diffraction experiments we extract a collinear antiferromagnetic spin arrangement within the a–c plane.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 April 2000 / Accepted: 29 January 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Redhammer, G., Roth, G., Paulus, W. et al. The crystal and magnetic structure of Li-aegirine LiFe3+Si2O6: a temperature-dependent study. Phys Chem Min 28, 337–346 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690100159
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690100159