Abstract
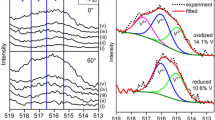
Vivianite, Fe3(PO4)2×8 H2O, (010) surfaces cleaved in an N2 gas atmosphere are examined using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Quantitative evaluation of Fe(2p 32) and O(1s) spectra show cleaved surfaces are partly oxidized. Ferric hydroxide is identified as an oxidation product. An auto-reduction-oxidation mechanism involving rupture of hydrogen bonds between the H2O ligands which hold together the sheet structure of vivianite is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: September 23, 1996/Revised, accepted: November 27, 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pratt, A. Vivianite auto-oxidation. Phys Chem Min 25, 24–27 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050082
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050082