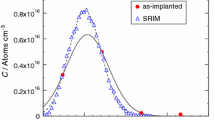
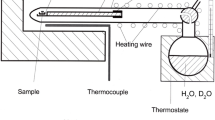
Abstract
We measured the ion conductivity of single-crystal alkali feldspar originating from two different locations in the Eifel/Germany, named Volkesfeld and Rockeskyller sanidine and having potassium site fractions \(C_\mathrm{K}\) of 0.83 and 0.71, respectively. The dc conductivities resulting from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy over the temperature range of 300–900 \(^{\circ }\hbox {C}\) show a weak composition dependence but pronounced differences between the b-direction [\(\perp (010)\)] and \(c^{*}\)-direction [\(\perp (001)\)] of the monoclinic feldspar structure. Conductivity activation energies obtained from the observed linear Arrhenius plots are close to 1.2 eV in all cases, which is closely similar to the activation energies of the \(^{22}\mathrm{Na}\) tracer diffusivity in the same crystals. Taking into account literature data on K tracer diffusion and diffusion correlation effects, the present results point to a predominance of the interstitialcy mechanism over the vacancy mechanism in mass and charge transport on the alkali sublattice in potassium-rich alkali feldspar.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
After submission of the manuscript, the mass density of RK feldspar has been determined as \(2.56\, \hbox {g cm}^{-3}\). The difference with the density of VF feldspar is \(<\)1 %.
The dc conductivity is simply denoted as \(\sigma _{}\) (which has to be distinguished from the frequency-dependent complex conductivity). We refrained from using ‘dc’ as index to \(\sigma ^{\prime }\) in order to avoid bulky variables and double indices.
References
Abart R, Petrishcheva E, Wirth R, Rhede D (2009) Exsolution by spinodal decomposition II: perthite formation during slow cooling of anatexites from Ngoronghoro, Tanzania. Am J Sci 309:450–475
Behrens H, Johannes W, Schmalzried H (1990) On the mechanisms of cation diffusion processes in ternary feldspars. Phy Chem Miner 17:62–78
Beran A (1986) A model of water allocation in alkali feldspar derived from infrared-spectroscopic investigations. Phys Chem Miner 13:306–310
Cherniak D (2010) Cation diffusion in feldspars. Rev Mineral Geochem 72:691–733
Christoffersen R, Yund R, Tullis J (1983) Interdiffusion of K and Na in alkali feldspars: diffusion couple experiments. Am Mineral 68:1126–1133
Demtröder K (2011) Untersuchung zur Al/Si-Ordnung an Sanidin Megakristallen aus der Eifel. Master’s thesis, Ruhr-Universität Bochum
Foland KA (1974) Alkali diffusion in orthoclase. Geochem Transp Kinet 634:77–98
Fredericks WJ (1975) Diffusion in alkali halides. In: Nowick AS, Burton JJ (eds) Diffusion in solids - recent developments. Academic Press, New York, pp 381–444
Giletti B, Semet M, Kasper R (1974) Self-diffusion of potassium in low albite using an ion microprobe. Geol Soc Am Abstr Program 6:754
Hu H, Li H, Lidong D, Shuangming S, Chengming Z (2011) Electrical conductivity of albite at high temperatures and high pressures. Am Mineral 96:1821–1827
Hu H, Li H, Lidong D, Shuangming S, Chengming Z (2013) Electrical conductivity of alkali feldspar solid solutions at high temperatures and high pressures. Phys Chem Miner 40:51–62
Imre AW, Voss S, Mehrer H (2002) Ionic transport in 0.2[xNa2O·(1-x)Rb2O]\(\cdot \)0.8B\(_2\)O\(_3\) mixed-alkali glasses. Phys Chem Chem Phys 4:3219–3224
Johnson EA, Rossman GR (2013) The diffusion behavior of hydrogen in plagioclase feldspar at 800–1000 \(^\circ\) C: implications for re-equilibration of hydroxyl in volcanic phenocrysts. Am Mineral 98:1779–1787
Jones A, Islam M, Mortimer M, Palmer D (2004) Alkali ion migration in albite and K-feldspar. Phys Chem Miner 31:313–320
Kasper R (1975) Cation and oxygen diffusion in albite. PhD thesis, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island
Kroll H, Ribbe PH (1983) Lattice parameters, composition and Al, Si order in alkali feldspars. Rev Mineral Geochem 2:57–100
Kronenberg AK, Yund RA, Rossman GR (1996) Stationary and mobile hydrogen defects in potassium feldspar. Geochim et Cosmochim Acta 60:4075–4094
Manning JR (1968) Diffusion kinetics for atoms in crystals. Van Nostrand, Princeton
Maury R (1968a) Conductibilite electrique des tectosilicates. I. methode et resultats experimentaux. Bulletin de la Societe Francaise de Mineralogie et Cristallographie 91:267–278
Maury R (1968b) Conductibilite electrique des tectosilicates. II. Discussion des resultats. Bulletin de la Societe Francaise de Mineralogie et Cristallographie 91:355–366
Mehrer H (2007) Diffusion in solids. Springer, Berlin
Murch GE, Dyre JC (1989) Correlation effects in ionic conductivity. CRC Crit Rev Solid State Mater Sci 14:345–365
Nazarov AV, Gurov K (1979) Calculation of non-equilibrium vacancies in the phenomenological theory of mutual diffusion. Phys Met Metall 45:185–188
Neusser G, Abart R, Fischer F, Harlov D, Norberg N (2012) Experimental Na/K exchange between alkali feldspar and an NaCl–KCl salt melt: chemically induced fracturing and element partitioning. Contrib Mineral Petrol 164:341–358
Petrishcheva E, Abart R (2009) Exsolution by spinodal decomposition I: evolution equation for binary mineral solutions with anisotropic interfacial energy. Am J Sci 309:431–449
Petrishcheva E, Abart R (2012) Exsolution by spinodal decomposition in multicomponent mineral solutions. Acta Mater 60:5481–5493
Petrishcheva E, Abart R, Schaeffer A, Habler G, Rhede D (2014) Sodium–potassium interdiffusion in potassium-rich alkali feldspar I: full diffusivity tensor at 850 °C. Am J Sci 314:1284–1299
Petrović R (1972) Alkali ion diffusion in alkali feldspars. Ph.D thesis, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut
Schaeffer AK, Petrishcheva E, Habler G, Abart R, Rhede D, Giester G (2014) Sodium–potassium interdiffusion in potassium-rich alkali feldspar II: composition- and temperature-dependence obtained from cation exchange experiments. Am J Sci 314:1300–1318
Schreuer J, Demtröder K, Sondergeld P, Dehn S (2010) Anomalous elastic behaviour of hydrous sanidine megacrysts from the Eifel, Germany. In: Friederich W (ed) Lithospheric deformation - turning observations into models, Abstract volume. Sprockhövel, pp 117–118
Spear F (1994) Metamorphic phase equilibria and pressure–temperature–time paths. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington
Stephenson PCL, Sholl CA (1994) Tracer correlation factor and atomic displacements due to the collinear interstitialcy mechanism. Philos Mag A 69:57–64
Tyburczy JA, Fisler DK (1995) Electrical properties of minerals and melts. In: Ahrens TJ (ed) Mineral physics and crystallography: a handbook of physical constants. American Geophysical Union, Washington, pp 185–208
Wilangowski F (2013) Tracer diffusion of sodium in a potassium-rich feldspar. Master’s thesis, University of Münster, Germany
Wilangowski F, Stolwijk NA (2015a) Monte carlo simulation of diffusion and ionic conductivity in a simple cubic random AB alloy by the interstitialcy mechanism. J Phys Condens Matter 27(505):401
Wilangowski F, Stolwijk NA (2015b) Vacancy-related diffusion correlation effects in a simple cubic random alloy and on the Na–K sublattice of alkali feldspar. Philos Mag 95:2277–2293
Wilangowski F, Divinski S, Abart R, Stolwijk NA (2015) Radiotracer experiments and monte carlo simulation of sodium diffusion in alkali feldspar: evidence against the vacancy mechanism. Defect Diffus Forum 363:79–84
Yang X, Keppler H, McCammon C, Ni H (2012) Electrical conductivity of orthopyroxene and plagioclase in the lower crust. Contrib Mineral Petrol 163:33–48
Zhang BH, Shan SM, Wu XP (2015) Modeling H, Na, and K diffusion in plagioclase feldspar by relating point defect parameters to bulk properties. Phys Chem Miner. doi:10.1007/s00269-015-0782-5
Acknowledgments
Gerald Giester is gratefully acknowledged for orienting single-crystal fragments on an X-ray goniometer, and Andreas Wanger is thanked for preparation of perfectly suited samples. The authors thank Michael Hackmann for taking preliminary measurements on single-crystal alkali feldspar and Frank Berkemeier for providing platinum deposition by magnetron sputtering. We are indebted to Anne Schäffer, Conny Cramers and Arno Knieschewski for helpful discussions. Financial support by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Maanaoui, H., Wilangowski, F., Maheshwari, A. et al. Ionic conductivity in gem-quality single-crystal alkali feldspar from the Eifel: temperature, orientation and composition dependence. Phys Chem Minerals 43, 327–340 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-015-0797-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-015-0797-y