Abstract
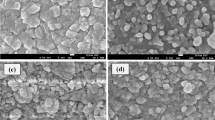
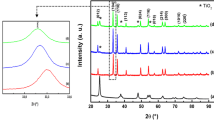
Nano-hematites, i.e., hematites with nanoparticle-, nanorod-, and nanotube-like morphologies, were synthesized via the hydrothermal method by controlling the reaction time, temperature, and reactant concentration. The nano-hematites of different crystal shapes all exhibited band gaps within the visible-light region (1.56–2.1 eV). Further, they showed weak ferromagnetic behavior, and their coercive magnetic field was larger than that of the bulk hematite. Moreover, all the nano-hematites also exhibited high photocatalytic activities during the degradation of methylene blue under visible-light irradiation. The experimental data fitted the Langmuir–Hinshelwood kinetics model very well. The nanorods had the highest photocatalytic rate constant per unit surface area, possibly owing to a higher aspect ratios; this lowers the electron–hole recombination rate. These results suggest that the crystal morphology of hematites has a significant effect on their physical and photocatalytic properties. Therefore, controlling the morphology of the materials is essential for obtaining well-tailored photocatalysts.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloyeau D, Ricolleau C, Mottet C, Oikawa T, Langlois C, Bouar YL, Braidy N, Loiseau A (2009) Size and shape effects on the order–disorder phase transition in CoPt nanoparticles. Nat Mater 8:940–946
Andersen J, Pelaez M, Guay L, Zhang ZH, Shead KO, Dionysiou DD (2013) NF-TiO2 photocatalysis of amitrole and atrazine with addition of oxidants under simulated solar light: emerging synergies, degradation intermediates, and reusable attributes. J Hazard Mater 260:569–575
Bakuzis AF, Morais PC (2001) On the origin of the surface magnetic anisotropy in manganese–ferrite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 226–230:1924–1926
Banerjee IA, Yu LT, Matsui H (2003) Cu nanocrystal growth on peptide nanotubes by biomineralization: size control of Cu nanocrystals by tuning peptide conformation. PNAS 100(25):14678–14682
Behafarid F, Ono LK, Mostafa S, Croy JR, Shafai G, Hong S, Rahman TS, Bare SR, Cuenya BR (2012) Electronic properties and charge transfer phenomena in Pt nanoparticles on c-Al2O3: size, shape, support, and adsorbate effects. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:11766–11779
Brunauer S, Deming LS, Deming WS, Teller E (1940) On a theory of the van der Waals adsorption of Gases. J Am Chem Soc 62:1723
Chen XY, Cui H, Liu P, Yang GW (2007) Shape-induced ultraviolet absorption of CuO shuttlelike nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 90:183118-1–183118-4
Chen RF, Cheng JH, Wei Y (2012) Preparation and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 microparticles with adjustable size and morphology. J Alloys Compd 520:266–271
Chen Y, Zhu LH, Feng CH, Liu J, Li C, Wen SP, Ruan SP (2013) Low temperature operating In2−xNixO3 sensors with high response and good selectivity for NO2 gas. J Alloys Compd 581:653–658
Condon JB (2006) Surface area and porosity determinations by physisorption: measurements and theory. Elsevier, Netherlands
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (2003) The iron oxides: structure, properties, reactions, occurrences and uses. Wiley, Weinheim
Cuenya BR (2010) Synthesis and catalytic properties of metal nanoparticles: size, shape, support, composition, and oxidation state effects. Thin Solid Films 518:3127–3150
Diebold U (2003) The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surf Sci Rep 48:53–229
Dormann JL, Fiorani D, Tronc E (1997) Magnetic relaxation in fine-particle system. Adv Chem Phys XCVIII:283–494
Fan HM, Ni ZH, Feng YP, Fan XF, Kuo KL, Shen ZX, Zou BS (2007) Anisotropy of electron–phonon coupling in single wurtzite CdS nanowires. Appl Phys Lett 91:171911-1–171911-4
Fan HM, Fan XF, Ni ZH, Shen ZX, Feng YP, Zou S (2008) Orientation-dependent Raman spectroscopy of single Wurtzite CdS nanowires. J Phys Chem C 112:1865–1870
Fan HM, You GJ, Li Y, Zheng Z, Tan HR, Shen ZX, Tang SH, Feng YP (2009) Shape-controlled synthesis of single-crystalline Fe2O3 hollow nanocrystals and their tunable optical properties. J Phys Chem C 113:9928–9935
Fu GT, Wu K, Jiang X, Tao L, Chen Y, Lin J, Zhou YM, Wei SH, Tang YW, Lu TH, Xia XH (2013) Polyallylamine-directed green synthesis of platinum nanocubes. Shape and electronic effect codependent enhanced electrocatalytic activity. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:3793–3802
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photocatalysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38
Gilbert B, Frandsen C, Maxey ER, Sherman DM (2009) Band-gap measurements of bulk and nanoscale hematite by soft X-ray spectroscopy. Phys Rev B 79:35108-1–35108-7
Gu JM, Li SH, Ju ML, Wang EB (2011) In situ carbon template-based strategy to fabricate ferrite hollow spheres and their magnetic property. J Cryst Growth 320:46–51
Guisbiers G, Abudukelimu G (2013) Influence of nanomorphology on the melting and catalytic properties of convex polyhedral nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 15:1431. doi:10.1007/s11051-013-1431-x
Halperin WP (1986) Quantum size effects in metal particles. Rev Modern Phys 58:533–606
Han CW, Lim SH (2009) Variation of the magnetic energy barrier with the cell shape of nanostructured magnetic thin films. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:045006-1–045006-5
Hoffmann MR, Martin ST, Choi W, Bahnemann DW (1995) Environmental applications of semiconductor photocatalysis. Chem Rev 95:69–96
Hosseini SA, Niaei A, Salari D, Nabavi SR (2012) Nanocrystalline AMn2O4 (A = Co, Ni, Cu) spinels for remediation of volatile organic compounds—synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance. Ceram Int 38:1655–1661
Kamali S, Shahmiri N, Garitaonandia JS, Ångström J, Sahlberg M, Ericsson T, Häggström L (2013) Effect of mixing tool on magnetic properties of hematite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. Thin Solid Films 534:260–264
Kawahara T, Yamada K, Tada H (2006) Visible light photocatalytic decomposition of 2-naphthol by anodic-biased α-Fe2O3 film. J Colloid Interface Sci 294:504–507
Khuspe GD, Sakhare RD, Navale ST, Chougule MA, Kolekar YD, Mulik RN, Pawar RC, Lee CS, Patil VB (2013) Nanostructured SnO2 thin films forNO2 gas sensing applications. Ceram Int 39:8673–8679
Leslie-Pelecky DL, Rieke RD (1996) Magnetic properties of nanostructured materials. Chem Mater 8:1770–1783
Li LP, Li GS, Smith RL Jr, Inomata H (2000) Microstructural evolution and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4 nanocrystals dispersed in amorphous silica. Chem Mater 12:3705–3714
Linic S, Christopher P, Xin HL, Marimuthu A (2013) Catalytic and photocatalytic transformations on metal nanoparticles with targeted geometric and plasmonic properties. Acc Chem Res 46(8):1890–1899
Lowell S, Shields JE, Thomas MA, Thommes M (2004) Characterization of porous solids and powders: surface area, pore size and density. Kluwer, Netherlands
Ma XX, Tao HQ, Feng LZ, Cheng L, Shi XZ, Li YG, Guo L, Liu Z (2012) Magnetically targeted drug delivery, photothermal therapy, and magnetic resonance imaging. Nano Res 5(3):199–212
Mahmoodi NM, Arami M, Limaee NY, Tabrizi NS (2006) Kinetics of heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of reactive dyes in an immobilized TiO2 photocatalytic reactor. J Colloid Interface Sci 295:159–164
Mazor LP, Dakwar GR, Popov M, Kolusheva S, Shames A, Linder C, Greenberg S, Heldman E, Stepensky D, Jelinek R (2013) Bolaamphiphilic vesicles encapsulating iron oxide nanoparticles: new vehicles for magnetically targeted drug delivery. Int J Pharm 450:241–249
Miller JS, Calabrese JC, Rommelmann H, Chittipeddi SR, Zhang JH, Reiff WM, Epstein AJ (1987) Ferromagnetic behavior of [Fe(C5Me5)2]·+[TCNE]·−: structural and magnetic characterization of decamethylferrocenium tetracyanoethenide, [Fe(CSMe5)2]·+[TCNE]·+· MeCN, and decamethylferrocenium pentacyanopropenide, [Fe(C5Me5)2]·+ [C3(CN5)]−. J Am Chem Soc 109:769–781
Murphy AB (2007) Band-gap determination from diffuse reflectance measurements of semiconductor films, and application to photoelectrochemical water-splitting. Solar Energy Mater Solar Cells 91:1326–1337
Ni XM, Zheng Z, Xiao XK, He L (2010) Silica-coated iron nanoparticles: shape-controlled synthesis, magnetism and microwave absorption properties. Mater Chem Phys 120:206–212
Pradhan GK, Parida KM (2011) Fabrication, growth mechanism, and characterization of γ-Fe2O3 Nanorods. Appl Mater Interface 3:317–323
Priya MH, Madras G (2006) Kinetics of photocatalytic degradation of phenols with multiple substituent groups. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 179:256–262
Rubio D, Casanueva JF, Nebot E (2013) Improving UV seawater disinfection with immobilized TiO2: study of the viability of photocatalysis (UV254/TiO2) as seawater disinfection technology. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 271:16–23
Schuler E, Gustavsson AK, Hertenberger S, Satt K (2013) Solar photocatalytic and electrokinetic studies of TiO2/Ag nanoparticle suspensions. Sol Energy 96:220–226
Shahroosv H, Ghorbani-asl M (2013) Solution-based synthetic strategies for Eu doped ZnO nanoparticle with enhanced red photoluminescence. J Lumin 144:223–229
Silva MF, Oliveira LAS, Ciciliati MA, Silva LT, Pereira BS, Hechenleitner AAW, Oliveira DMF, Pirota KR, Ivashita FF, Paesano A Jr, Pastor JM, Perez-Landazabal JI, Pineda EAG (2013) Nanometric particle size and phase controlled synthesis and characterization of γ-Fe2O3 or (α + γ)-Fe2O3 by a modified sol–gel method. J Appl Phys 114:104311-1–104311-7
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA, Rouquerol J, Siemieniewska T (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619
Sohn YS, Smith YR, Misra M, Subramanian VR (2008) Electrochemically assisted photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange using anodized titanium dioxide nanotubes. Appl Catal B Environ 84:372–378
Song HJ, Li N, Yu SL (2010) Template-free synthesis of γ-Fe2O3 microcubes and their magnetic property. Micro Nano Lett 5(4):200–202
Sudarsanam P, Katta L, Thrimurthulu G, Reddy BM (2013) Vapor phase synthesis of cyclopentanone over nanostructured ceria–zirconia solid solution catalysts. J Ind Eng Chem 19:1517–1524
Teja AS, Koh PY (2009) Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater 55:22–45
Townsend TK, Sabio EM, Browning ND, Osterloh FE (2011) Photocatalytic water oxidation with suspended alpha-Fe2O3 particles-effects of nanoscaling. Energy Environ Sci 4:4270–4275
Wang ZK, Lim HS, Liu HY, Ng HC, Kuok MH (2005) Spin waves in nickel nanorings of large aspect ratio. Phys Rev Lett 94:137208-1–137208-4
Wang JM, Li C, Zhuang H, Zhang JH (2013) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and inactivation of gram-negative bacteria by TiO2 nanoparticles in aqueous suspension. Food Control 34:372–377
Wu W, Xiao XH, Zhang SF, Zhou JA, Fan LX, Ren F, Jiang CZ (2010) Large-scale and controlled synthesis of iron oxide magnetic short nanotubes: shape evolution, growth mechanism, and magnetic properties. J Phys Chem C 114:16092–16103
Xu WL, Bony BA, Kim CR, Baeck JS, Chang YM, Bae JE, Kim TJ, Lee GH (2013) Mixed lanthanide oxide nanoparticles as dual imaging agent in biomedicine. Sci Rep 3:3210–3219
Yang Y, Wu QY, Guo YH, Hu CW, Wang EB (2005) Efficient degradation of dye pollutants on nanoporous polyoxotungstate–anatase composite under visible-light irradiation. J Mol Catal A Chem 225:203–212
Yarahmadi SS, Wijayantha KGU, Tahir AA, Vaidhyanathan B (2009) Nanostructured γ-Fe2O3 electrodes for solar driven water splitting: effect of doping agents on preparation and performance. J Phys Chem C 113:4768–4778
Zhang LY, Zhang YF (2009) Fabrication and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanowire arrays in different diameters. J Magn Magn Mater 321:L15–L20
Zhang ZA, Yuan YA, Shi GY, Fang YJ, Liang LH, Ding HC, Jin LT (2007) Photoelectrocatalytic activity of highly ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays electrode for azo dye degradation. Environ Sci Technol 41:6259–6263
Zhang XT, Wan JQ, Chen KZ, Wang SX (2013) Controlled synthesis of spherical and cubic magnetite nanocrystal clusters. J Cryst Growth 372:170–174
Zhao ZH, Zhou ZJ, Bao JF, Wang ZY, Hu J, Chi XQ, Ni KY, Wang RF, Chen XY, Chen Z, Gao JH (2013) Octapod iron oxide nanoparticles as high performance T2 contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Nat Commun 4:2266. doi:10.1038/ncomms3266
Zhong JY, Cao CB (2010) Nearly monodisperse hollow Fe2O3 nanoovals: synthesis, magnetic property and applications in photocatalysis and gas sensors. Sens Actuators B 145:651–656
Zhou WZ (2010) Reversed crystal growth: implications for crystal engineering. Adv Mater 22:3086–3092
Zhu WC, Cui XL, Wang L, Liu T, Zhang Q (2011) Monodisperse porous pod-like hematite: hydrothermal formation, optical absorbance, and magnetic properties. Mater Lett 65:1003–1006
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Prof. Wei-The Jiang of the Department of Earth Sciences for the help with XRD measurements. We thank the Instrument Center of National Cheng Kung University for the SQUID measurement. We sincerely thank the National Science Council for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y.H., Lin, C.C. Effect of nano-hematite morphology on photocatalytic activity. Phys Chem Minerals 41, 727–736 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-014-0686-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-014-0686-9