Abstract
Background
In recent years, the increase in antibiotics usage locally has led to a worrying emergence of multi-drug resistant organisms (MDRO), with the Malaysian prevalence rate of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ranging from 17.2 to 28.1% between 1999 and 2017. A study has shown that 7% of all non-lactational breast abscesses are caused by MRSA. Although aspiration offers less morbidities compared to surgical drainage, about 20% of women infected by MRSA who initially underwent aspiration subsequently require surgical drainage. This study is conducted to determine the link between aetiology, antimicrobial resistance pattern and treatment modalities of breast abscesses.
Methods
Retrospective study of reviewing microbiology specimens of breast abscess patients treated at Universiti Malaya Medical Centre from 2015 to 2020. Data collected from microbiology database and electronic medical records were analysed using SPSS V21.
Result
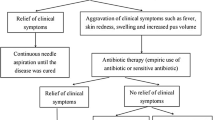
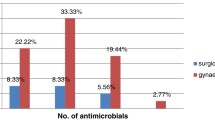
A total of 210 specimens from 153 patients were analysed. One-fifth (19.5%) of the specimens isolated were MDRO. Lactational associated infections had the largest proportion of MDR in comparison to non-lactational and secondary infections (38.5%, 21.7%, 25.7%, respectively; p = 0.23). Staphylococcus epidermidis recorded the highest number of MDR (n = 12) followed by S. aureus (n = 8). Adjusted by aetiological groups, the presence of MDRO is linked to failure of single aspirations (p = 0.554) and significantly doubled the risk of undergoing surgical drainage for resolution (p = 0.041).
Conclusion
MDR in breast abscess should be recognised as an increasing healthcare burden due to a paradigm shift of MDRO and a rise of resistance cases among lactational associated infection that were vulnerable to undergo surgical incision and drainage for resolution.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dener C, Inan A (2003) Breast abscesses in lactating women. World J Surg 27(2):130–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-002-6563-6
Egbe TO, Njamen TN, Essome H, Tendongfor N (2020) The estimated incidence of lactational breast abscess and description of its management by percutaneous aspiration at the Douala General Hospital, Cameroon. Int Breastfeed J 15(1):26
Bharat A, Gao F, Aft RL, Gillanders WE, Eberlein TJ, Margenthaler JA (2009) Predictors of primary breast abscesses and recurrence. World J Surg 33(12):2582–2586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-009-0170-8
Russell SP, Neary C, Abd Elwahab S, Powell J, O’Connell N, Power L et al (2020) Breast infections - microbiology and treatment in an era of antibiotic resistance. Surgeon 18(1):1–7
El-Tamer MB, Ward BM, Schifftner T, Neumayer L, Khuri S, Henderson W (2007) Morbidity and mortality following breast cancer surgery in women: national benchmarks for standards of care. Ann Surg 245(5):665–671
Murthy BL, Thomson CS, Dodwell D, Shenoy H, Mikeljevic JS, Forman D et al (2007) Postoperative wound complications and systemic recurrence in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 97(9):1211–1217
Al Benwan K, Al Mulla A, Rotimi VO (2011) A study of the microbiology of breast abscess in a teaching hospital in Kuwait. Med Princ Pract 20(5):422–426
Lodhi N, Khurshaidi N, Soomro R, Saleem M, Rahman SSU, Anwar S (2018) Is our choice of empirical antibiotics appropriate for patients with methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in breast abscess? Iran J Microbiol 10(6):348–353
Boccaccio C, Verdaguer Babic V, Botto L, Cervetto MM, Cetani S, Paladino S et al (2014) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolation in breast abscesses in a public maternity. Medicina (B Aires) 74(3):210–215
Branch-Elliman W, Lee GM, Golen TH, Gold HS, Baldini LM, Wright SB (2013) Health and economic burden of post-partum Staphylococcus aureus breast abscess. PLoS ONE 8(9):e73155
Tan SY, Khan RA, Khalid KE, Chong CW, Bakhtiar A (2022) Correlation between antibiotic consumption and the occurrence of multidrug-resistant organisms in a Malaysian tertiary hospital: a 3-year observational study. Sci Rep 12(1):3106
Che Hamzah AM, Yeo CC, Puah SM, Chua KH, Chew CH (2019) Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Malaysia: a review of antimicrobial resistance and characteristics of the clinical isolates 1990–2017. Antibiotics (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8030128
Ministry of Health Malaysia (2017) National Antibiotic Resistance Surveillance report
Saboo A, Bennett I (2018) Trends in non-lactation breast abscesses in a tertiary hospital setting. ANZ J Surg 88(7–8):739–744
Lam E, Chan T, Wiseman SM (2014) Breast abscess: evidence based management recommendations. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 12(7):753–762
Naeem M, Rahimnajjad MK, Rahimnajjad NA, Ahmed QJ, Fazel PA, Owais M (2012) Comparison of incision and drainage against needle aspiration for the treatment of breast abscess. Am Surg 78(11):1224–1227
Afzal S, Bashir A, Shahzad H, Masroor I, Sattar AK (2022) Ultrasound-guided percutaneous aspiration for the treatment of breast abscess at a tertiary care center in the developing world. Cureus 14(10):e30865
Chandika AB, Gakwaya AM, Kiguli-Malwadde E, Chalya PL (2012) Ultrasound guided needle aspiration versus surgical drainage in the management of breast abscesses: a Ugandan experience. BMC Res Notes 5:12
Chen CY, Anderson BO, Lo SS, Lin CH, Chen HM (2010) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections may not impede the success of ultrasound-guided drainage of puerperal breast abscesses. J Am Coll Surg 210(2):148–154
World Health Organization Western Pacific Region (2019) For the future: towards the healthiest and safest region. Report No.: RC70/INF/1
Rondas AA, Schols JM, Halfens RJ, Stobberingh EE (2013) Swab versus biopsy for the diagnosis of chronic infected wounds. Adv Skin Wound Care 26(5):211–219
Giuliano C, Patel CR, Kale-Pradhan PB (2019) A guide to bacterial culture identification and results interpretation. Pharm Ther 44(4):192–200
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2020) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute
Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG et al (2012) Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect 18(3):268–281
Ministry of Health Malaysia (2012–2016) Malaysia National Cancer Registry report
Ministry of Health Malaysia (2019) National health and morbidity survey
Ministry of Health Malaysia (2014) National antibiotic guideline - second edition
Ministry of Health Malaysia (2019) National antimicrobial guideline - third edition
Dabbas N, Chand M, Pallett A, Royle GT, Sainsbury R (2010) Have the organisms that cause breast abscess changed with time?—implications for appropriate antibiotic usage in primary and secondary care. Breast J 16(4):412–415
Leung SS (2016) Breast pain in lactating mothers. Hong Kong Med J 22(4):341–346
Bartolomé-Álvarez J, Solves-Ferriz V (2021) Microbiology of breast abscesses. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eimce.2022.05.009. (Engl Ed)
Moglad EH, Altayb HN (2022) Antibiogram prevalence of methicillin-resistant and multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus spp. in different clinical samples. Saudi J Biol Sci 29(12):103432
Rashid ZZ, Bahari N, Othman A, Jaafar R, Mohamed NA, Jabbari I et al (2013) Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Malaysian tertiary centre. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 44(1):104–108
Xu Z, Cave R, Chen L, Yangkyi T, Liu Y, Li K et al (2020) Antibiotic resistance and molecular characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis recovered from hospital personnel in China. J Glob Antimicrob Resist 22:195–201
Hagiya H, Shiota S, Sugiyama W, Otsuka F (2014) Postpartum breast abscess caused by community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Japan. Breastfeed Med 9(1):45–46
Li Y, Ma XJ, He XP (2021) Clinical characteristics of lactational breast abscess caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: hospital-based study in China. Int Breastfeed J 16(1):80
Khan MN, Vidya R, Lee RE (2006) The limited role of microbiological culture and sensitivity in the management of superficial soft tissue abscesses. Sci World J 6:1118–1123
Ding ST, He XP, Ma XJ, Zhang Y, Liu XX, Qin J (2020) Lactational breast abscesses caused by methicillin-resistant or methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus infection and therapeutic effect of ultrasound-guided aspiration. Breastfeed Med 15(7):471–474
Talari K, Goyal M (2020) Retrospective studies–utility and caveats. J R Coll Physicians Edinb 50(4):398–402
Acknowledgements
The authors have none to disclose.
Funding
The study was funded by the Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education through the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2021/STG01/UCSI/03/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.J., Lai, L.L., See, M.H. et al. Breaking the Barrier: A Study on Multi-drug Resistance in Breast Abscess at an Academic Malaysian Hospital. World J Surg 47, 2743–2752 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-023-07108-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-023-07108-z