Abstract
Introduction
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are gaining recognition as an important immunological biomarker with therapeutic potential in breast cancer. In this cohort study conducted on patients with advanced breast cancer treated with primary systemic therapy (PST), the TILs concentration was correlated with response to PST and survival outcomes.
Methods
Patients with primary breast cancer treated with PST between 2016 and 2020 were included in this study, approved by IEC, and registered on ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05250336). Tumor core biopsies obtained prior to starting treatment from 489 patients were assessed for the proportion of stromal TILs by standardized method and categorized into low (0–10% immune cells), intermediate (11–59%), and high (≥ 60%) TILs. TIL concentration and complete pathological response (pCR), disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival (OS) were correlated.
Results
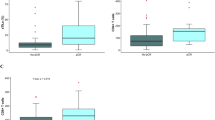
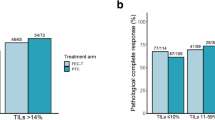
Of the 489 patients, 372 matched the eligibility criteria for assessment of TILs and made the final study cohort. Among these, 135 were luminal, 129 HER2-enriched, and 108 triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC). Proportions of patients with high TILs were greater in TNBC (15.7%) and HER2-enriched (9.3%), compared to luminal cancers (4.4%). High TIL concentration was correlated with higher pCR in all subtypes. A pCR was achieved in 33.3, 50, and 52.9% of high TIL patients in luminal, HER2-enriched, and TNBC subtypes, respectively (p < 0.05). High TILs were linked to longer DFS and OS in TNBC and HER2-enriched breast cancers.
Conclusion
In this first study of its kind from a low- and middle-income country, high TILs concentration was found to be a predictor of response to PST across all breast cancer subtypes. TILs concentration was found predictive of better DFS and OS in TNBC and HER2-enriched cancers. Prognostic role of TILs in luminal cancers was not so apparent.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pages F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B et al (2009) In situ cytotoxic and memory T cells predict outcome in patients with early-stage colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(35):5944–5951
Hwang WT, Adams SF, Tahirovic E et al (2012) Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T cells in ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis. Gynecol Oncol 124(2):192–198
Dieu-Nosjean MC, Antoine M, Danel C et al (2008) Long-term survival for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with intratumoral lymphoid structures. J Clin Oncol 26(27):4410–4417
Ruffell B, Au A, Rugo HS et al (2012) Leukocyte composition of human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:2796–2801
Becht E, Giraldo NA, Lacroix L et al (2016) Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol 17:218
Hussein MR, Hassan HI (2006) Analysis of the mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltrate in the normal breast, benign proliferative breast disease, in situ and infiltrating ductal breast carcinomas: preliminary observations. J Clin Pathol 59(9):972–977
Hornychova H, Melichar B, Tomsova M et al (2008) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer Invest 26:1024–1031
Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C et al (2006) Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol 24:5373–5380
Wesolowski R, Carson WE (2014) Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes-the next step in assessing outcome and response to treatment in patients with breast cancer. J Carcinog Mutagen 5(6):199
Liu S, Foulkes WD, Leung S et al (2014) Prognostic significance of FOXP3+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer depends on estrogen receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 expression status and concurrent cytotoxic T-cell infiltration. Breast Cancer Res 16:432
Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F et al (2013) Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy: BIG 02–98. J ClinOncol 31:860–867
West NR, Milne K, Truong PT et al (2011) Tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes predict response to anthracycline-based chemotherapy in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 13:R126
Issa-Nummer Y, Darb-Esfahani S, Loibl S et al (2013) Prospective validation of immunological infiltrate for prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in HER2-negative breast cancer: a substudy of the neoadjuvant GeparQuinto trial. PLoS ONE 8:e79775
Denkert C, Loibl S, Noske A et al (2010) Tumor associated lymphocytes as an independent predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:105–113
Stanton SE, Disis ML (2016) Clinical significance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer. J Immunother Cancer 18(4):59
Ahn SG, Jeong J, Hong S, Jung WH (2015) Current issues and clinical evidence in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer. J Pathol Transl Med 49(5):355–363
Luen SJ, Savas P, Fox SB et al (2017) Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and the emerging role of immunotherapy in breast cancer. Pathology 49(2):141–155
Agarwal G, Sonthineni C, Mishra A et al (2018) Surgical outcomes of primary versus post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy breast conservation surgery: a comparative study from a developing country. World J Surg 42(5):1364–1374
Agarwal G, Rajan S, Gambhir S et al (2016) A comparative validation of primary surgical versus post-neo-adjuvant chemotherapy sentinel lymph node biopsy for stage III breast cancers. World J Surg 40(7):1583–1589
Agarwal G, Ramakant P (2008) Breast cancer care in India: the current scenario and the challenges for the future. Breast care 3(1):21–27
Simos D, Clemons M, Ginsburg OM et al (2014) Definition and consequences of locally advanced breast cancer. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care 8(1):33–38
Tsang JYS, Tse GM (2020) Molecular classification of breast cancer. Adv Anat Pathol 27(1):27–35
Salgado R, Denkert C, Demaria S et al (2015) The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: recommendations by an international TILs working group 2014. Ann Oncol 26:259–271
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Darb-Esfahani S et al (2018) Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: a pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol 19(1):40–50
Ingold Heppner B, Untch M, Denkert C et al (2016) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes: a predictive and prognostic biomarker in neoadjuvant-treated HER2-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 22:5747–5754
Denkert C, von Minckwitz G, Brase JC et al (2015) Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with or without carboplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive and triple-negative primary breast cancers. J Clin Oncol 33:983–991
Gao G, Wang Z, Qu X, Zhang Z (2020) Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 20(1):179
Agarwal G, Nanda G, Lal P et al (2016) Outcomes of triple-negative breast cancers compared with non-TNBC: does the survival vary for all stages? World J Surg 40(6):1362–1372
Mao Y, Qu Q, Chen X et al (2016) The prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 11(4):e0152500
Liu S, Lachapelle J, Leung S et al (2012) CD8+ lymphocyte infiltration is an independent favorable prognostic indicator in basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 14(2):R48
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by an intramural research grant from the Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India (A-12-PGI/IMP/79/2018 to Dr. Gaurav Agarwal). The funding source had no role in the design of this study and did not have any role during its execution, analyses, interpretation of the data, writing assistance, or decision to submit results. The authors thank all the investigators and collaborators who contributed to this study.
Funding
Supported by SGPGI Intramural research grant (A-12-PGI/IMP/79/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
Institutional ethics committee clearance reference no. 2018–177-IMP-EXP-4.
Informed consent for participants
Waiver of consent approved by ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, G., Vishvak Chanthar, K.M.M., Katiyar, S. et al. Predictive and Prognostic Role of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer Treated with Primary Systemic Therapy. World J Surg 47, 1238–1246 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-023-06912-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-023-06912-x