Abstract
Background
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is an effective treatment for benign thyroid nodules. However, it remains unclear if ablating multiple nodules in single-session offers comparable safety and efficacy to ablating single nodule. Our study compared early complication rate and 6-month nodule shrinkage between multiple-nodules ablation and single-nodule ablation by RFA.
Methods
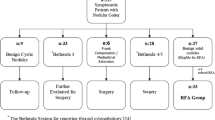
Among the 174 eligible patients undergoing RFA of one or more benign thyroid nodules, 85 (48.8%) had single-nodule ablation (group I) while 89 (51.1%) had two or three nodules ablation (group II). The 6-month nodule shrinkage of each nodule (by volume reduction ratio) (VRR) was calculated by (Baseline volume − volume at 6-month)/(Baseline volume)*100 and compared between two groups. To determine independent predictors for VRR, a multivariate analysis was done by logistic regression analysis.
Results
Patients in group II reported significantly higher pain scores during and 2-h after treatment than group I (42.31 vs. 29.66, p = 0.029 and 38.21 vs. 26.18, p = 0.037, respectively). Two vocal cord paresis occurred in each group. 3- and 6-month VRR of the largest nodule were comparable between two groups (67.39% vs. 63.89%, p = 0.248 and 77.29% vs. 73.38%, p = 0.182). Similar 3- and 6-month VRR were observed for 2 and 3 largest nodules in group II. In multivariate analysis, total energy given per nodule volume (OR = 1.007, 95% CI = 1.001–1.012, p = 0.036) was the only independent predictor for 6-month VRR.
Conclusion
In the presence of multinodular goiter, ablating two or more nodules by RFA within one session appears to offer a comparable level of safety and efficacy to ablating single nodule.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Gharib H, Papini E, Garber JR et al (2016) AACE/ACE/AME task force on thyroid nodules. American association of clinical endocrinologists, American college of endocrinology, and associazione medici endocrinologi medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules-2016 update. Endocr Pract 22(5):622–639
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC et al (2016) 2015 American thyroid association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American thyroid association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 26:1–133
Durante C, Costante G, Lucisano G et al (2015) The natural history of benign thyroid nodules. JAMA 313(9):926–935
Chung SR, Suh CH, Baek JH, Park HS, Choi YJ, Lee JH (2017) Safety of radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules and recurrent thyroid cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Hyperth 33(8):920–930. https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2017.1337936
Negro R, Salem TM, Greco G (2016) Laser ablation is more effective for spongiform than solid thyroid nodules. A 4-year retrospective follow-up study. Int J Hyperthermia 32(7):822–828. https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2016.1212279
Lang BHH, Woo YC, Chiu KW (2019) Two-year efficacy of single-session high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) ablation of benign thyroid nodules. Eur Radiol 29(1):93–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5579-8
Papini E, Pacella CM, Solbiati LA, Achille G, Barbaro D, Bernardi S, Cantisani V, Cesareo R, Chiti A, Cozzaglio L, Crescenzi A, De Cobelli F, Deandrea M, Fugazzola L, Gambelunghe G, Garberoglio R, Giugliano G, Luzi L, Negro R, Persani L, Raggiunti B, Sardanelli F, Seregni E, Sollini M, Spiezia S, Stacul F, Van Doorne D, Sconfienza LM, Mauri G (2019) Minimally-invasive treatments for benign thyroid nodules: a Delphi-based consensus statement from the Italian minimally-invasive treatments of the thyroid (MITT) group. Int J Hyperth 36(1):376–382. https://doi.org/10.1080/02656736.2019.1575482
Lang BHH, Woo YC, Chiu KW (2018) Sequential high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) ablation in the treatment of benign multinodular goitre: an observational retrospective study. Eur Radiol 28(8):3237–3244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5333-2
Fung MMH, Lang BH (2021) A prospective study evaluating the feasibility and accuracy of very early postoperative translaryngeal ultrasonography in the assessment of vocal cord function after neck surgery. Surgery 169(1):191–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2020.03.025
Gambelunghe G, Fede R, Bini V, Monacelli M, Avenia N, D’Ajello M, Colella R, Nasini G, De Feo P (2013) Ultrasound-guided interstitial laser ablation for thyroid nodules is effective only at high total amounts of energy: results from a three-year pilot study. Surg Innov 20(4):345–350. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350612459276
Trimboli P, Deandrea M (2020) Treating thyroid nodules by radiofrequency: Is the delivered energy correlated with the volume reduction rate? A pilot study. Endocrine 69(3):682–687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02275-8
Acknowledgments
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors wrote the manuscript, researched the data and performed statistical analyses. Both authors have full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lang, B.H.H., Fung, M.M.H. Safety and Efficacy of Single-Session Radiofrequency Ablation Treatment for Benign Non-toxic Multinodular Goiter. World J Surg 46, 1704–1710 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-022-06527-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-022-06527-8



