Abstract
Objectives
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is an option for ultrafiltration for patients with end-stage renal disease. Once placed, PD catheters may malfunction often due to omental wrapping. Omental procedures such as omentectomy and omentopexy may reduce this risk. This investigation aims to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature on the role of omental procedures on PD catheter insertions.
Methods
Following protocol registration on PROSPERO (CRD42020218950), a systematic review was performed in accordance with the Cochrane Collaboration. A literature search was performed in February 2021 across Medline, EMBASE, Scopus, and Cochrane Library. Records with patients who underwent PD catheter insertion with and without omental manipulation were included. The records underwent screening, full-text review, and data extraction. Study qualities were assessed using RoBINS-I and RoB2. Effect estimates were extracted as risk ratios and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) were pooled using inverse variance method with random-effect model.
Results
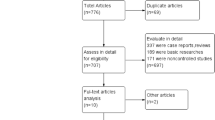
Of 510 records identified, 15 studies were included in the meta-analysis (1 RCT, 2 prospective, 12 retrospective). With omental procedures, there was decreased the likelihood of failure requiring removal of PD catheter (RR 0.47, 95% CI 0.38, 0.58) and PD catheter obstruction (RR 0.23, 95% CI 0.14, 0.39); there was no difference in likelihood of catheter malposition or migration (RR 0.87, 95% CI 0.23, 3.29) or peritonitis (RR 0.74, 95% CI 0.40, 1.35).
Conclusion
Based on the current low to moderate quality of evidence, omental manipulation at the time of PD catheter insertion confers benefits of decreased obstruction and failure requiring removal.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PD:
-
Peritoneal Dialysis
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
References
Nayak Karopadi A, Mason G, Rettore E, Ronco C (2014) The role of economies of scale in the cost of dialysis across the world: a macroeconomic perspective. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29:885–892
Karopadi AN, Mason G, Rettore E, Ronco C (2013) Cost of peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis across the world. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:2553–2569
Mehrotra R, Devuyst O, Davies SJ, Johnson DW (2016) The current state of peritoneal dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:3238–3252
Ludlow MJ, George CR, Hawley CM, Mathew TH, Agar JW, Kerr PG, Lauder LA (2011) How Australian nephrologists view home dialysis: results of a national survey: home dialysis survey. Nephrology 16:446–452
Wang V, Maciejewski ML, Coffman CJ, Sanders LL, Lee SD, Hirth R, Messana J (2017) Impacts of geographic distance on peritoneal dialysis utilization: refining models of treatment selection. Health Serv Res 52:35–55
Jansen MA, Hart AA, Korevaar JC, Dekker FW, Boeschoten EW, Krediet RT (2002) Predictors of the rate of decline of residual renal function in incident dialysis patients. Kidney Int 62:1046–1053
Bargman JM, Thorpe KE, Churchill DN, CANUSA Peritoneal Dialysis Study Group (2001) Relative contribution of residual renal function and peritoneal clearance to adequacy of dialysis: a reanalysis of the CANUSA study. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2158–62
Jheng JS, Chang CT, Huang CC (2012) Omental wrapping of peritoneal dialysis catheter. Kidney Int 82:827
Nicholson ML, Burton PR, Donnelly PK (1991) The orle of omentectomy in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int 11(4):330–332
Ladd AP, Breckler FD, Novotny NM (2011) Impact of primary omentectomy on longevity of peritoneal dialysis catheters in children. Am J Surg 201(3):401–404
Lewis M, Webb N, Smith T, Roberts D (1995) Routine omentectomy is not required in children undergoing chronic peritoneal dialysis. Adv Perit Dial 11:293–295
Radtke J, Schild R, Reismann M et al (2018) Obstruction of peritoneal dialysis catheter is associated with catheter type and independent of omentectomy: a comparative data analysis from a transplant surgical and a pediatric surgical department. J Ped Surg 53(4):640–643
Reissman P, Shiloni E, Kluger Y, Berlatzky Y (1989) Routine omentectomy during Tenckhoff catheter insertion for peritoneal dialysis. Harefuah 117(12):427–430
Chen G, Wang P, Liu H et al (2014) Greater omentum folding in the open surgical placement of peritoneal dialysis catheters: a randomized controlled study and systemic review. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29(3):687–697
Crabtree JH, Fishman A (2003) Selective performance of prophylactic omentopexy during laparoscopic implantation of peritoneal dialysis catheters. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 13(3):180–184
Higgins JPT , Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, Welch V (2019) The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 6, updated 2019; Available at https://methods.cochrane.org/bias/resources/rob-2-revised-cochrane-risk-bias-tool-randomized-trials accessed July 2019
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg 88:105906
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC et al (2016) ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 355:i4919
The Cochrane Collaboration (2014) Review manager (RevMan) [Computer program]. Version 5. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, Copenhagen
Martinez-Mier G, Luna-Castillo M, Ortiz-Enriquez JJ et al (2012) Factors associated with early peritoneal dialysis catheter replacement in Veracruz. Mexico Nefrologia 32(3):353–358
Cribbs RK, Greenbaum LA, Heiss KF (2010) Risk factors for early peritoneal dialysis catheter failure in children. J Pediatr Surg 45(3):585–589
Krezalek MA, Bonamici N, Lapin B et al (2016) Laparoscopic peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion using rectus sheath tunnel and selective omentopexy significantly reduces catheter dysfunction and increases peritoneal dialysis longevity. Surgery 160(4):924–935
Finan PJ, Gillou PJ (1985) Experience with surgical implantation of catheters for continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 67(3):190–192
LaPlant MB, Saltzman DA, Segura BJ, Acton RD, Feltis BA, Hess DJ (2018) Peritoneal dialysis catheter placement, outcomes and complications. Pediatr Surg Int 34(11):1239–1244
Macchini F, Valade A, Ardissino G et al (2006) Chronic peritoneal dialysis in children: catheter related complications. A single centre experience. Pediatr Surg Int. 22(6):524–528
Nicholson ML, Burton PR, Donnelly PK et al (1991) The role of omentectomy in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int 11(4):330–332
Numanoglu A, Rasche L, Roth MA et al (2008) Laparoscopic insertion with tip suturing, omentectomy, and ovariopexy improves lifespan of peritoneal dialysis catheters in children. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech 18(2):302–305
Phan J, Stanford S, Zaritsky JJ, Duegarte DA (2013) Risk factors for morbidity and mortality in pediatric patients with peritoneal dialysis catheters. J Pediatr Surg 48(1):197–202
Pumford N, Cassey J, Uttley WS (1994) Omentectomy with peritoneal catheter placement in acute renal failure. Nephron 68(3):327–328
Sahpazova EM, Kuzmanovska DB (2010) Our experience with catheter-related complications in pediatric peritoneal dialysis in R. Macedonia Perit Dial Int 30(SUPPL. 2):S175
Washburn KK, Currier H, Salter KJ, Brandt ML (2004) Surgical techniques for peritoneal dialysis catheter placement in the pediatric patient: a North American survey. Adv Perit Dial 20:218–221
Wallace EL, Fissel RB, Golper TA et al (2016) Catheter insertion and perioperative practices within the ISPD North American Research Consortium. Perit Dial Int 36(4):382–386
Debray TPA, Moons KGM, Riley RD (2018) Detecting small-study effects and funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analysis of survival data: a comparison of new and existing tests. Res Synth Methods 9(1):41–50
Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA et al (2011) GRADE guidelines: 1 Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol 64(4):383–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.04.026 (Epub 2010 Dec 31. PMID: 21195583)
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix A
Appendix A
Embase search strategy
1 | exp peritoneal dialysis/ |
2 | CAPD.mp. or exp continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis/ |
3 | exp omentum/or oment*.mp |
4 | exp omentectomy/ |
5 | tenckhoff.mp |
6 | exp peritoneal dialysis catheter/or exp catheter/or exp dialysis catheter/ |
7 | 1 or 2 |
8 | 3 or 4 |
9 | 5 or 6 |
10 | 7 and 8 and 9 |
Medline search strategy
1 | exp Peritoneal Dialysis/ |
2 | CAPD.mp. or exp Peritoneal Dialysis, Continuous Ambulatory/ |
3 | exp Omentum/or oment*.mp |
4 | omentectomy.mp |
5 | Tenckhoff.mp |
6 | exp Catheters/ |
7 | 1 or 2 |
8 | 3 or 4 |
9 | 5 or 6 |
10 | 7 and 8 and 9 |
Scopus search strategy
( TITLE-ABS-KEY ( peritoneal AND dialysis OR pd OR capd OR continuous AND ambulatory AND peritoneal AND dialysis) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY ( oment* OR omentectomy OR omentum) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY ( tenckhoff OR catheter*)).
Cochrane search strategy
Peritoneal Dialysis in Title Abstract Keyword OR PD in Title Abstract Keyword OR Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis in Title Abstract Keyword OR CAPD in Title Abstract Keyword AND Catheter* in Title Abstract Keyword AND (oment*) in Title Abstract Keyword—(Word variations have been searched).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.K., Lolas, M., Keefe, D.T. et al. Omental Procedures During Peritoneal Dialysis Insertion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J Surg 46, 1183–1195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-021-06413-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-021-06413-9