Abstract
Background
The use of double-lumen endobronchial tubes (DLTs) is necessary for differential lung ventilation during pulmonary lobectomy. However, when used with conventional extubation procedures, coughing is more likely and is associated with an increased risk for parenchymal air leak along the staple line and possible subsequent lung injury. We examined the prevalence of coughing-associated air leaks at extubation and the efficacy of using supraglottic airways (SGAs) to prevent air leaks with post-lobectomy extubation.
Methods
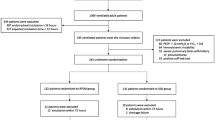
This study included 150 patients with pulmonary emphysema diagnosed using preoperative computed tomography, who underwent pulmonary lobectomy between April 2010 and March 2015. The patients were chronologically enrolled in two groups: the DLT group (60 patients) from April 2010 to August 2012, and the SGA group (90 patients) from September 2012 to March 2015. (Note: the DLT group only included cases without air leak present just prior to extubation). Data were collected on specific patient characteristics and operative and postoperative factors.
Results
Coughing at extubation occurred in 15 (25.0 %) of 60 DLT patients, and parenchymal air leaks developed in 10 (66.7 %) of these 15. Comparison of groups revealed the SGA group was significantly lower for the following: patients with coughing at extubation (P < 0.001), coughing-associated air leaks at extubation (P < 0.001), air leaks >7 days (P = 0.006), reoperation due to air leaks (P = 0.013), and duration of chest tube drainage (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
The SGA is effective for preventing air leaks associated with coughing during conventional DLT extubation in post-lobectomy patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brunelli A, Varela G, Refai M et al (2010) A scoring system to predict the risk of prolonged air leak after lobectomy. Ann Thorac Surg 90:204–209
Varela G, Jimenez MF, Novoa N et al (2005) Estimating hospital costs attributable to prolonged air leak in pulmonary lobectomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 27:329–333
Stix MS, Borromeo CJ, Sciortino GJ et al (2001) Learning to exchange an endotracheal tube for a laryngeal mask prior to emergence. Can J Anaesth 48:795–799
Goddard PR, Nicholson EM, Laszlo G et al (1982) Computed tomography in pulmonary emphysema. Clin Radiol 33:379–387
Macchiarini P, Wain J, Almy S et al (1999) Experimental and clinical evaluation of a new synthetic, absorbable sealant to reduce air leaks in thoracic operations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 117:751–758
Asai T, Koga K, Vaughan RS (1998) Respiratory complications associated with tracheal intubation and extubation. Br J Anaesth 80:767–775
Kim ES, Bishop MJ (1998) Cough during emergence from isoflurane anesthesia. Anesth Analg 87:1170–1174
Cooper JD, Trulock EP, Triantafillou AN et al (1995) Bilateral pneumectomy (volume reduction) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 109:106–119
Sullivan EA (2011) Lung volume reduction. In: Slinger PD (ed) Principles and practice of anesthesia for thoracic surgery. Springer Science + Business Media Inc., New York, pp 511–521
Marshall MB, Deeb ME, Bleier JI et al (2002) Suction vs water seal after pulmonary resection: a randomized prospective study. Chest 121:831–835
Alphonso N, Tan C, Utley M et al (2005) A prospective randomized controlled trial of suction versus non-suction to the under-water seal drains following lung resection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 27:391–394
Brain AI (1983) The laryngeal mask—a new concept in airway management. Br J Anaesth 55:801–805
Dob DP, Shannon CN, Bailey PM (1999) Efficacy and safety of the laryngeal mask airway vs Guedel airway following tracheal extubation. Can J Anaesth 46:179–181
Stix MS, Borromeo CJ, Sciortino GJ et al (2001) Learning to exchange an endotracheal tube for a laryngeal mask prior to emergence. Can J Anaesth 48:795–799
Koga K, Asai T, Vaughn RS et al (1998) Respiratory complications associated with tracheal extubation. Timing of tracheal extubation and use of the laryngeal mask during emergence from anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 53:540–544
Pennant JH, White PF (1993) The laryngeal mask airway. Its uses in anesthesiology. Anesthesiology 79:144–163
Joshi GP, Morrison SG, Gajraj NM et al (1994) Hemodynamic changes during emergence from anesthesia: use of the laryngeal mask airway vs endotracheal tube. Anesth Analg 78:S185
George SL, Blogg CE (1994) Role of the LMA in tracheal extubation? Br J Anaesth 72:610
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishibashi, H., Kobayashi, M., Takasaki, C. et al. Efficacy of Supraglottic Airway for Preventing Lung Injury Associated with Coughing at Extubation after Pulmonary Lobectomy. World J Surg 40, 1892–1898 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-016-3522-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-016-3522-1