Abstract
Introduction
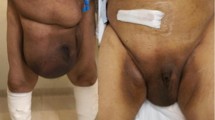
Large incisional hernias with loss of domain (LIHLD) of the abdominal wall remain a therapeutic challenge due to the difficulty of replacing the contents of the hernia sac into the peritoneal cavity. Preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum (PPP) is a valuable option. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the feasibility of peritoneal catheter insertion under ultrasound guidance for PPP and to compare the morbidity and mortality of this new technique to previously used techniques in our department.
Methods
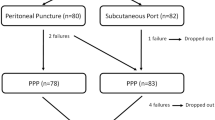
Medical records were reviewed retrospectively from February 1989 to April 2013 in a single institution. Three different techniques of PPP were evaluated: surgical subcutaneous implantable port (SIP), surgical peritoneal dialysis catheter (PDC), and radiologic multipurpose drainage catheter (MDC). Collected data included patients’ age, sex, body mass index, medical and surgical history, hernia location, PPP technique, length of hospitalization, volume of air injected, morbidity and mortality linked to PPP, and the procedure of hernia repair.
Results
Thirty-seven patients with a mean age of 63.1 years were evaluated. Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum was performed using SIP, PDC, and MDC for 14, 11, and 12 patients, respectively. Overall morbidity related to the technique was seen in 36 % of SIP, 27 % of PDC, and 0 % of MDC. One patient from the SIP group died on the 3rd postoperative day due to septic shock following aspiration pneumonia. No postoperative mortality in the other groups was observed.
Conclusion
The MDC is an interesting modification of the original technique and is a safe procedure. It is a minimally invasive technique with a very low risk of perforation of the viscera. Therefore, the use of a non-absorbable prosthesis with MDC technique can be offered for all patients undergoing PPP without increasing the risk of infection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Willis S, Schumpelick V (2000) Use of progressive pneumoperitoneum in the repair of giant hernias. Hernia 4(2):105–111
Goni Moreno I (1947) Chronic eventration and large hernias: preoperative treatment by progressive pneumoperitoneum-original procedure. Surgery 22:945–953
Mayagoitia JC et al (2006) Preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum in patients with abdominal-wall hernias. Hernia 10(3):213–217
Trivellini G et al (1984) Surgical treatment of large eventrations. Study of a technic adapted to disorders of respiratory compliance. Chirurgie 110(2):116–122
Munegato G, Grigoletto R, Brandolese R (2000) Respiratory mechanics in abdominal compartment syndrome and large incisional hernias of the abdominal wall. Hernia 4(4):282–285
Martínez MA, Padilla LR, Hesiquio SR, Álvarez CO, Medina RO (2002) Double lumen catheter for pneumoperitoneum in giant hernias. Report on four patients. Cir Gen 24(4):313–318
Sanclemente MCL et al (2013) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum in patients with giant hernias of the abdominal wall. Cir Esp 91(7):444–449
Braye FM, Breton P, Caillot JL (2003) Preoperative pneumoperitoneum used for tissue expansion before abdominal wall reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 50(6):649–652
Muysoms FE, Miserez M, Berrevoet F, Campanelli G, Champault GG, Chelala E, Dietz UA, Eker HH, El Nakadi I, Hauters P, Hidalgo Pascual M, Hoeferlin A, Klinge U, Montgomery A, Simmermacher RKJ, Simons MP, Smietanski M, Sommelin C, Tollens T, Vierendeels T, Kingsnorth A (2009) Classification of primary and incisional abdominal wall hernias. Hernia 13(4):407–414
Stoppa R et al (1999) Evolution of large ventral incisional hernia repair. The French contribution to a difficult problem. Hernia 3(1):1–3
Mason E (1995) Pneumoperitoneum in giant hernia. In: Nyhus LM, Condon RE (eds) Hernia, 4th edn. JB Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 515–524
Kingsnorth AN et al (2004) Open mesh repair of incisional hernias with significant loss of domain. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 86(5):363–366
Sabbagh C et al (2011) Peritoneal volume is predictive of tension-free fascia closure of large incisional hernias with loss of domain: a prospective study. Hernia 15(5):559–565
Berlemont M (1952) Pneumoperitoneum as a cure for enormous irreducible hernias. Mem Acad Chir (Paris) 78(1–3):77–78
La Meir M, Vierendeels T, Poortmans M (2002) Pneumoperitoneum in repair of giant hernias and eventrations. Acta Chir Belg 102(4):263–265
Cady B, Brooke-Cowden GL (1976) Repair of massive abdominal wall defects. Combined use of pneumoperitoneum and Marlex mesh. Surg Clin North Am 56(3):559–570
Hamer DB, Duthie HL (1972) Pneumoperitoneum in the management of abdominal incisional hernia. Br J Surg 59(5):372–375
Raynor RW, Del Guercio LR (1989) The place for pneumoperitoneum in the repair of massive hernia. World J Surg 13(5):581–585. doi:10.1007/BF01658874
Caldironi MW et al (1990) Progressive pneumoperitoneum in the management of giant incisional hernias: a study of 41 patients. Br J Surg 77(3):306–307
Barst HH (1972) Pneumoperitoneum as an aid in the surgical treatment of giant herniae. Br J Surg 59(5):360–364
Goni Moreno IG (1978) The rational treatment of hernias and voluminous chronic eventrations: preparation with progressive pneumoperitoneum. In: Nyhus LM, Condon RE (eds) Hernia, 2nd edn. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 536–560
Steichen FM (1965) A simple method for establishing, maintaining, and regulating surgically induced pneumoperitoneum in preparation for large hernia repairs. Surgery 58(6):1031–1032
McAdory RS, Cobb WS, Carbonell AM (2009) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum for hernias with loss of domain. Am Surg 75(6):504–508
Toniato A, Pagetta C, Bernante P, Piotto A, Pelizzo MR (2002) Incisional hernia treatment with progressive pneumoperitoneum and retromuscular prosthetic hernioplasty. Langenbecks Arch Surg 387(5–6):246–248
Oprea V, Matei O, Gheorghescu D, Leuca D, Buia F, Rosianu M, Dinca M (2014) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum (PPP) as an adjunct for surgery of hernias with loss of domain. Chirurgia (Bucur) 109(5):664–669
Gonda SJ, Li R (2011) Principles of subcutaneous port placement. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 14(4):198–203
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alyami, M., Passot, G., Voiglio, E. et al. Feasibility of Catheter Placement Under Ultrasound Guidance for Progressive Preoperative Pneumoperitoneum for Large Incisional Hernia with Loss of Domain. World J Surg 39, 2878–2884 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-015-3206-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-015-3206-2