Abstract
Background
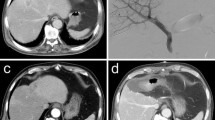
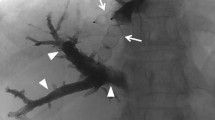
Preoperative portal vein embolization (PVE) induces shrinkage of the embolized lobe and compensatory regeneration in the non-embolized lobe, but does not always induce sufficient regeneration of the future remnant liver (FRL). We previously developed preoperative sequential PVE–hepatic vein embolization (HVE), and here we present our experience of treating 42 patients with sequential PVE–HVE.
Methods
During 8-year study period, preoperative PVE–HVE was performed on 42 patients with hepatobiliary malignancies.
Results
Primary diseases were bile duct cancers [perihilar cholangiocarcinoma (n = 33) and diffuse bile duct cancer (n = 1)], hepatocellular carcinomas (n = 4), and intrahepatic tumors [intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (n = 3) and gallbladder cancer liver invasion (n = 1)]. These patients demonstrated insufficient FRL regeneration following PVE, thus HVE was performed to induce further regeneration. No PVE–HVE procedure-associated complications occurred. In the bile duct cancer group, FRL volume was 33.9 ± 2.2 % before PVE, 38.4 ± 1.5 % before HVE, 43.7 ± 2.1 % at surgery, and 73.6 ± 8.3 % at 2 weeks after right hepatectomy. The degree of FRL hypertrophy was 13.3 % after PVE, 28.9 % after PHV–HVE, and 117.1 % at 2 weeks after right hepatectomy. All patients except one recovered uneventfully after surgery, and the 3-year patient survival rate was 45.1 %. In the HCC group, transarterial chemoembolization was initially performed and FRL regeneration following PVE–HVE occurred very slowly. Active FRL regeneration occurred in the liver tumor group, but rapid tumor growth was observed in 1 of 4 patients.
Conclusion
The sequential application of HVE following PVE safely and effectively induces further FRL regeneration in non-cirrhotic livers. Further validation using larger patient population and multicenter studies is needed to reliably widen the indications.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FRL:
-
Future remnant liver
- HVE:
-
Hepatic vein embolization
- PV:
-
Portal vein
- PVE:
-
Portal vein embolization
- RHV:
-
Right hepatic vein
- MHV:
-
Middle hepatic vein
- TLV:
-
Total liver volume
- TACE:
-
Transarterial chemoembolization
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- PHRR:
-
Parenchymal hepatic resection rate
- KGR:
-
Kinetic growth rate
References
Yokoyama Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y (2007) Mechanisms of hepatic regeneration following portal vein embolization and partial hepatectomy: a review. World J Surg 31:367–374
Yokoyama Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y (2007) Mechanism of impaired hepatic regeneration in cholestatic liver. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 14:159–166
Hwang S, Lee SG, Ko GY et al (2009) Sequential preoperative ipsilateral hepatic vein embolization after portal vein embolization to induce further liver regeneration in patients with hepatobiliary malignancy. Ann Surg 249:608–616
Gruttadauria S, Gridelli B (2007) Sequential preoperative ipsilateral portal and arterial embolization in patients with liver tumors: is it really the best approach? World J Surg 31:2427–2428
Kyokane T, Nagino M, Oda K et al (2001) An experimental study of selective intrahepatic biliary ablation with ethanol. J Surg Res 96:188–196
am Esch JS II, Knoefel WT, Klein M et al (2005) Portal application of autologous CD133 + bone marrow cells to the liver: a novel concept to support hepatic regeneration. Stem Cells 23:463–470
Munene G, Parker RD, Larrigan J et al (2013) Sequential preoperative hepatic vein embolization after portal vein embolization for extended left hepatectomy in colorectal liver metastases. World J Surg Oncol 11:134
Hwang S (2011) Right hepatectomy in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma after induction of hepatic parenchymal atrophy through subsequent portal and hepatic vein embolizations. Korean J Gastroenterol 58:162–165
Shindoh J, Truty MJ, Aloia TA et al (2013) Kinetic growth rate after portal vein embolization predicts posthepatectomy outcomes: toward zero liver-related mortality in patients with colorectal liver metastases and small future liver remnant. J Am Coll Surg 216:201–209
Lee SG, Hwang S (2005) How I do it: assessment of hepatic functional reserve for indication of hepatic resection. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 12:38–43
Higuchi R, Yamamoto M (2014) Indications for portal vein embolization in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 21:542–549
Ribero D, Curley SA, Imamura H et al (2008) Selection for resection of hepatocellular carcinoma and surgical strategy: indications for resection, evaluation of liver function, portal vein embolization, and resection. Ann Surg Oncol 15:986–992
Nagino M, Kamiya J, Nishio H et al (2006) Two hundred forty consecutive portal vein embolizations before extended hepatectomy for biliary cancer: surgical outcome and long-term follow-up. Ann Surg 243:364–372
Ko GY, Hwang S, Sung KB et al (2010) Interventional oncology: new options for interstitial treatments and intravascular approaches: right hepatic vein embolization after right portal vein embolization for inducing hypertrophy of the future liver remnant. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 17:410–412
Ko GY, Sung KB, Yoon HK et al (2003) Preoperative portal vein embolization with a new liquid embolic agent. Radiology 227:407–413
Yoo H, Ko GY, Gwon DI et al (2009) Preoperative portal vein embolization using an amplatzer vascular plug. Eur Radiol 19:1054–1061
Ku Y, Fukumoto T (2011) Hepatic vein embolization. In: Madoff DC, Makuuchi M, Nagino M, Vauthey JN (eds) Venous embolization of the liver. Radiological and surgical practice. Springer, London, pp 169–175
Ogata S, Belghiti J, Farges O et al (2006) Sequential arterial and portal vein embolizations before right hepatectomy in patients with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg 93:1091–1098
Imamura H, Shimada R, Kubota M et al (1999) Preoperative portal vein embolization: an audit of 84 patients. Hepatology 29:1099–1105
Azoulay D, Castaing D, Smail A et al (2000) Resection of nonresectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer after percutaneous portal vein embolization. Ann Surg 231:480–486
Komori K, Nagino M, Nimura Y (2006) Hepatocyte morphology and kinetics after portal vein embolization. Br J Surg 93:745–751
Kito Y, Nagino M, Nimura Y (2001) Doppler sonography of hepatic arterial blood flow velocity after percutaneous transhepatic portal vein embolization. Am J Roentgenol 176:909–912
Sofue K, Arai Y, Shimada K et al (2014) Right portal vein embolization with absolute ethanol in major hepatic resection for hepatobiliary malignancy. Br J Surg 101:1122–1128
Igami T, Ebata T, Yokoyama Y et al (2014) Portal vein embolization using absolute ethanol: evaluation of its safety and efficacy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 21:676–681
Thornton RH, Covey AM, Madoff DC (2011) Embolic materials used for portal vein embolization. In: Madoff DC, Makuuchi M, Nagino M, Vauthey JN (eds) Venous embolization of the liver. Radiological and surgical practice. Springer, London, pp 29–136
Hwang S, Lee SG, Park KM et al (2004) Hepatic venous congestion in living donor liver transplantation: preoperative quantitative prediction and follow-up using computed tomography. Liver Transpl 10:763–770
Aoki T, Kokudo N (2011) Tumor growth after portal vein embolization. In: Madoff DC, Makuuchi M, Nagino M, Vauthey JN (eds) Venous embolization of the liver. Radiological and surgical practice. Springer, London, pp 271–278
Hayashi S, Baba Y, Ueno K et al (2007) Acceleration of primary liver tumor growth rate in embolized hepatic lobe after portal vein embolization. Acta Radiol 48:721–727
Yoo H, Kim JH, Ko GY et al (2011) Sequential transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and portal vein embolization versus portal vein embolization only before major hepatectomy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 18:1251–1257
Lee SG, Song GW, Hwang S et al (2010) Surgical treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma in the new era: the Asan experience. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 17:476–489
Truant S, Scatton O, Dokmak S, e-HPBchir Study Group from the Association de Chirurgie Hépato-Biliaire et de Transplantation (ACHBT) et al (2015) Associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy (ALPPS): impact of the inter-stages course on morbi-mortality and implications for management. Eur J Surg Oncol 41:674–682
Li J, Girotti P, Königsrainer I et al (2013) ALPPS in right trisectionectomy: a safe procedure to avoid postoperative liver failure? J Gastrointest Surg 17:956–961
Hwang S, Ha TY, Song GW et al (2015) Quantified risk assessment for major hepatectomy via the indocyanine green clearance rate and liver volumetry combined with standard liver volume. J Gastrointest Surg 19:1305–1314
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, S., Ha, TY., Ko, GY. et al. Preoperative Sequential Portal and Hepatic Vein Embolization in Patients with Hepatobiliary Malignancy. World J Surg 39, 2990–2998 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-015-3194-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-015-3194-2