Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) and its effects on tumor angiogenesis and relapse-free survival (RFS) after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
Expression of CEACAM1 and CD34 was immunohistochemically detected in HCC specimens from 97 patients. Microvessel density (MVD) was determined by counting CD34-positive endothelial cells. Statistical analyses were performed to determine the effects of CEACAM1 on clinicopathologic factors, tumor angiogenesis, and RFS.
Results
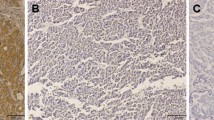
CEACAM1 expression was detected in 91 HCC specimens; 53 cases showed membranous expression and 38 cases showed cytoplastic expression. CEACAM1 cytoplastic expression was significantly associated with tumor size, number of tumors, vascular invasion, satellite nodules, Edmondson–Steiner grade, TNM stage, and MVD (p < 0.05 for all). Moreover, CEACAM1 cytoplastic expression was significantly associated with poorer RFS. The 3-year RFS of patients with CEACAM1 cytoplastic expression was significantly lower than that of those with CEACAM1 membranous expression (26.3 vs. 52.8%, p = 0.005). Cox analysis revealed that CEACAM1 cytoplastic expression was an independent prognostic factor for 3-year RFS (p = 0.031).
Conclusion
CEACAM1 expression was common in HCC, and CEACAM1 cytoplastic expression was closely associated with tumor progression, angiogenesis, and poorer RFS, indicating that cytoplastic CEACAM1 might be a predictor of relapsing phenotype and a possible novel target of antiangiogenic therapy for patients with HCC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang JP, Yan J, Xu J et al (2009) Increased intratumoral IL-17-producing cells correlate with poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J Hepatol 50(5):980–989
Zhao Y, Wang X, Wang T et al (2011) Acetylcholinesterase, a key prognostic predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma, suppresses cell growth and induces chemosensitization. Hepatology 53(2):493–503
Thompson JA, Grunert F, Zimmermann W (1991) Carcinoembryonic antigen gene family: molecular biology and clinical perspectives. J Clin Lab Anal 5(5):344–366
Beauchemin N, Draber P, Dveksler G et al (1999) Redefined nomenclature for members of the carcinoembryonic antigen family. Exp Cell Res 252(2):243–249
Hammarstrom S (1999) The carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) family: structures, suggested functions and expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin Cancer Biol 9(2):67–81
Cruz PV, Wakai T, Shirai Y et al (2005) Loss of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 expression is an adverse prognostic factor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 104(2):354–360
Oliveira-Ferrer L, Tilki D, Ziegeler G et al (2004) Dual role of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 in angiogenesis and invasion of human urinary bladder cancer. Cancer Res 64(24):8932–8938
Phan D, Cheng CJ, Galfione M et al (2004) Identification of Sp2 as a transcriptional repressor of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 in tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 64(9):3072–3078
Ebrahimnejad A, Streichert T, Nollau P et al (2004) CEACAM1 enhances invasion and migration of melanocytic and melanoma cells. Am J Pathol 165(5):1781–1787
Laack E, Nikbakht H, Peters A et al (2002) Expression of CEACAM1 in adenocarcinoma of the lung: a factor of independent prognostic significance. J Clin Oncol 20(21):4279–4284
Tanaka K, Hinoda Y, Takahashi H et al (1997) Decreased expression of biliary glycoprotein in hepatocellular carcinomas. Int J Cancer 74(1):15–19
Borscheri N, Roessner A, Röcken C (2001) Canalicular immunostaining of neprilysin (CD10) as a diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol 25(10):1297–1303
Hixson DC, Allison JP, Chesner JE et al (1983) Characterization of a family of glycoproteins associated with the bile canalicular membrane of normal hepatocytes but not expressed by two transplantable rat hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res 43(8):3874–3884
Hixson DC, McEntire KD, Obrink B (1985) Alterations in the expression of a hepatocyte cell adhesion molecule by transplantable rat hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res 45(8):3742–3749
Zhou CJ, Qu X, Yang YM et al (2009) CEACAM1 distribution and its effects on angiogenesis and lymph angiogenesis in oral carcinoma. Oral Oncol 45:883–886
Sun HC, Tang ZY, Li XM et al (1999) Microvessel density of hepatocellular carcinoma: its relationship with prognosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 125(7):419–426
Sotiriou C, Wirapati P, Loi S et al (2006) Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: understanding the molecular basis of histologic grade to improve prognosis. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(4):262–272
Llovet JM, Di Bisceglie AM, Bruix J et al (2008) Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(10):698–711
Sundberg U, Beauchemin N, Obrink B (2004) The cytoplasmic domain of CEACAM1-L controls its lateral localization and the organization of desmosomes in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 117(7):1091–1104
Tilki D, Irmak S, Oliveira-Ferrer L et al (2006) CEA-related cell adhesion molecule-1 is involved in angiogenic switch in prostate cancer. Oncogene 25(36):4965–4974
Zhou CJ, Liu B, Zhu KX et al (2009) The different expression of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) and possible roles in gastric carcinomas. Pathol Res Pract 205(7):483–489
Yang XR, Xu Y, Yu B et al (2010) High expression levels of putative hepatic stem/progenitor cell biomarkers related to tumour angiogenesis and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 59(7):953–962
Müller MM, Singer BB, Klaile E et al (2005) Transmembrane CEACAM1 affects integrin-dependent signaling and regulates extracellular matrix protein-specific morphology and migration of endothelial cells. Blood 105(10):3925–3934
Ergün S, Kilik N, Ziegeler G et al (2005) CEA-related cell adhesion molecule 1: a potent angiogenic factor and a major effector of vascular endothelial growth factor. Mol Cell 5(2):311–320
Volpert O, Luo W, Liu TJ et al (2002) Inhibition of prostate tumor angiogenesis by the tumor suppressor CEACAM1. J Biol Chem 277(38):35696–35702
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J (2003) Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 362(9399):1907–1917
Disclosure
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Yang, Y., Ma, C. et al. CEACAM1 Cytoplastic Expression is Closely Related to Tumor Angiogenesis and Poorer Relapse-free Survival After Curative Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J Surg 35, 2259–2265 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-011-1119-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-011-1119-2