Abstract
Background
Despite increasingly radical surgery for esophageal carcinoma, many patients still develop tumor recurrence after operation. This study was designed to evaluate the recurrence pattern of squamous cell carcinoma in the middle thoracic esophagus after modified Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed data of 196 patients who underwent modified Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy with two-field lymph node dissection from January 1997 to January 2001. Recurrence was classified as locoregional or hematogenous recurrence. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify risk factors of postoperative recurrence.
Results
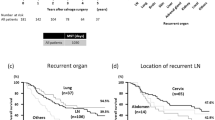
The overall 3-year and 5-year survival rates in all patients were 53% and 31%, respectively. Recurrence was recognized in 96 patients (48.9%) in the 3 years after operation. The median time to tumor recurrence was 12.2 months. The pattern of recurrence was locoregional in 52 patients (mainly mediastinal in 41, single cervical/supraclavicular in 8), hematogenous in 44 patients (simultaneous locoregional and hematogenous in 10; mainly liver, bone, or lung in 39). The locoregional recurrence rate was significantly lower in patients with postoperative radiotherapy than that in patients without postoperative radiotherapy (p = 0.02). Logistic regression analysis showed that T3 (p = 0.032), N1 (p = 0.003), and postoperative radiotherapy (p = 0.022) were independent risk factors for tumor locoregional recurrence.
Conclusions
About one half of the patients would develop recurrent disease within 3 years after modified Ivor-Lewis esophagectomy with two-field lymph node dissection, and most of them had mediastinal lymph node, liver, bone, or lung metastasis. Postoperative radiotherapy was beneficial in the control of locoregional recurrence.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Dresner SM, Griffin SM. Pattern of recurrence following radical oesophagectomy with two-field lymphadenectomy. Br J Surg 2000;87:1426–1433
Nakagawa S, Kanda T, Kosugi S, et al. Recurrence pattern of squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus after extended radical esophagectomy with three-field lymphadenectomy. J Am Coll Surg 2004;198:205–211
Hulscher JB, van Sandick JW, Tijssen JG, et al. The recurrence pattern of esophageal carcinoma after transhiatal resection. J Am Coll Surg 2000;191:143–148
Sobin LH, Wittekind C, editors. UICC TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, 5th ed, New York, Wiley-Liss 1997
Korst RJ, Rusch VW, Venkatraman E, et al. Proposed revision of the staging classification for esophageal cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1998;115:660–669
Wang Z, Liu XY, Liu FY, et al. A study of correlation between early postoperative relapse with lymph node micrometastasis in patients with N0 esophageal cancer. Zhong hua wai ke za zhi 2004;42:68–71. Chinese
Komukai S, Nishimaki T, Watanabe H, et al. Significance of immunohistochemically demonstrated micrometastases to lymph nodes in esophageal cancer with histologically negative nodes. Surgery 2000;127:40–46
Akiyama H, Tsurumaru M, Udagawa H, et al. Radical lymph node dissection for cancer of the thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg 1994;220:364–372
Law S, Wong J. Two-field dissection is enough for esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus 2001;14:98–103
Fujita H, Kakegawa T, Yamana H, et al. Mortality and morbidity rates, post-operative course, quality of life and prognosis after extended radical lymphadenectomy for esophageal cancer. Comparison of three-field lymphadenectomy with two field lymphadenectomy. Ann Surg 1995;222:654–662
Griffin SM, Shaw IH, Dresner SM. Early complications after Ivor Lewis subtotal esophagectomy with two-field lymphadenectomy: risk factors and management. J Am Coll Surg 2002;194:285–297
Xiao ZF, Yang ZY, Miao YJ, et al. Influence of number of metastatic lymph nodes on survival of curative resected thoracic esophageal cancer patients and value of radiotherapy: report of 549 cases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005;62:82–90
Ajani J, Bekaii-Saab T, Boston B, et al. NCCN practice guidelines for esophageal cancer (Version 1.2005). Retrieved from National Comprehensive Cancer Network Website: http://www.nccn.org
Visbal AL, Allen MS, Miller DL, et al. Ivor Lewis esophagogastrectomy for esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 2001;71:1803–1808
Stilidi I, Davydov M, Bokhyan V, et al. Subtotal esophagectomy with extended 2–field lymph node dissection for thoracic esophageal cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2003;23:415–420
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Wang, Z., Liu, Xy. et al. Recurrence Pattern of Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Middle Thoracic Esophagus after Modified Ivor-Lewis Esophagectomy. World J Surg 31, 1108–1115 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0551-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0551-1