Abstract
Background
Retroperitoneal sarcomas (RS) are a rare group of malignant soft-tissue tumors; due to the flexibility of the retroperitoneum, they generally grow to a large size before becoming symptomatic, often involving surrounding structures. Therefore, the surgeon is frequently compelled to perform large excisions. The aim of this study is to assess clinical and pathological factors affecting prognosis in patients with RS who underwent surgical treatment, comparing giant forms (size ≥ 25 cm) with smaller ones (size < 25 cm).
Methods
The hospital records of 73 consecutive patients who underwent surgical exploration for primary RS at our unit between 1984 and 2003 were reviewed. Statistical analysis of factors influencing overall and disease-free survival was performed including both the whole group of patients and only those who underwent complete surgical resection.
Results
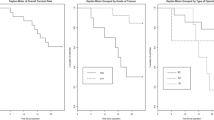
Giant RS showed a lower resectability rate than smaller forms (54.2% vs. 84.2%, P = 0.005). In the group with complete surgical excision (51 out of 73), patients with giant RS had a higher rate of adjacent organ resection compared with the smaller ones (84.2% vs. 53.1%, P = 0.023). Tumor size did not influence prognosis: after complete resection, 5-year overall survival was 60.9% and 56.3% for giant RS and smaller forms respectively, while 5-year disease-free survival was 54.3% and 48.3% for the two groups respectively. Advanced stage, incomplete gross surgical resection, higher tumor grade, non-liposarcoma histology and microscopic infiltration of margins were found to be significantly negative prognostic factors.
Conclusions
The present study confirms the importance of aggressive surgical management for RS, in order to offer these patients the best chance of long-term survival.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dalton RR, Donohue JH, Mucha P Jr, et al. Management of retroperitoneal sarcomas. Surgery 1989;106:725
Malerba M, Doglietto GB, Pacelli F, et al. Primary retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcomas: results of aggressive surgical treatment. World J Surg 1999;23:670–675
Lewis JJ, Leung D, Woodruff JM, et al. Retroperitoneal soft-tissue sarcoma. Analysis of 500 patients treated and followed at a single institution. Ann Surg 1998;228:355–365
Hassan I, Park SZ, Donohue JH, et al. Operative management of primary retroperitoneal sarcomas. A reappraisal of an institutional experience. Ann Surg 2004;239:244–250
Neuhaus SJ, Barry P, Clark MA, et al. Surgical management of primary and recurrent retroperitoneal liposarcoma. Br J Surg 2005;92:246–252
Gronchi A, Casali PG, Fiore M, et al. Retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcomas. Patterns of recurrence in 167 patients treated at a single institution. Cancer 2004;100:2448–2455
Van Dalen T, Hennipman A, Van Coevorden F, et al. Evaluation of a clinically applicable post-surgical classification system for primary retroperitoneal soft-tissue sarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2004;11:483–490
Mendenhall WM, Zlotecki RA, Hochwald SN, et al. Retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer 2005;104:669–674
Bradley JC, Caplan R. Giant retroperitoneal sarcoma: a case report and review of the management of retroperitoneal sarcomas. Am Surg 2002;68:52–56
Russo P, Kim Y, Ravindran S, et al. Nephrectomy during operative management of retroperitoneal sarcoma. Ann Surg Oncol 1997;4:421–424
Catton CN, O’Sullivan B, Kotwall C, et al. Outcome and prognosis in retroperitoneal soft tissue sarcoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1994;29(5):1005–1010
Rossi CR, Nitti D, Foletto M, et al. Management of primary sarcomas of the retroperitoneum. Eur J Surg Oncol 1993;19(4):355–360
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doglietto, G.B., Tortorelli, A.P., Papa, V. et al. Giant Retroperitoneal Sarcomas: A Single Institution Experience. World J Surg 31, 1047–1054 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0433-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0433-6