Abstract
Background
Periampullary cancers, the incidence of which increases gradually with industrialization, still pose a significant challenge to clinicians and researchers. Specifically, the role of cell-cycle proteins and tumor suppressor genes in these cancers is not yet clear. Recent studies have revealed that genes and proteins related to cell cycle and apoptosis regulation may be involved in pancreatic carcinogenesis.
Methods
Tissue samples were obtained from patients with periampullary cancers who underwent surgery at the National Taiwan University Hospital without receiving previous chemotherapy or radiation therapy. All periampullary cancer tissue samples were examined by a pathologist, who was unaware of the parameters to be investigated. A total of 68 patients with periampullary cancers (29 ampulla of Vater cancers (AVCs) and 39 pancreatic ductal cancers (PDCs), including various stages and histological subtypes, were enrolled. The relevant demographic and clinicopathological information was obtained from medical records.
Results
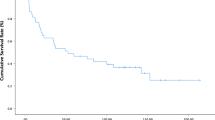
Cell-cycle proteins, including p16, Rb, cyclin D1, p53, and E2F1, were analyzed by immunohistochemical staining. Here, significant differences were noted between AVCs and PDCs with regard to the expression of cyclin D1. This corresponded to a poor prognosis in PDCs (P < 0.05); AVCs, on the other hand, showed a relatively high survival rate. There is no obvious statistical difference between the 2 groups with regard to the expression of p16, Rb, p53, and E2F1. The study also revealed that cyclin D1 plays different roles in the carcinogenesis of AVCs and PDCs.
Conclusions
The expression of cyclin D1 is more often correlated with prognosis in AVCs than in PDCs, and may serve as a biomarker for the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Sarmiento JM, Nagomey DM, Sarr MG, et al. Periampullary cancers: are there differences? Surg Clin North Am 2001;81:543–555
Bardeesy N, DePinho RA. Pancreatic cancer biology and genetics. Nat Rev Cancer 2002;2:897–909
Yamaguchi K, Enjoji M, Tsuneyoshi M. Pancreatoduodenal carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of 304 patients and immunohistochemical observation for CEA and CA19-9. J Surg Oncol 1991;47:148–154
Kim SG, Chan AO, Wu TT, et al. Epigenetic and genetic alterations in duodenal carcinomas are distinct from biliary and ampullary carcinomas. Gastroenterology 2003;124:1300–1310
Rashid A, Ueki T, Gao YT, et al. K-ras mutation, p53 overexpression, and microsatellite instability in biliary tract cancers: a population-based study in China. Clin Cancer Res 2002;8:3156–3163
Howe JR, Klimstra DS, Cordon-Cardo C, et al. K-ras mutation in adenomas and carcinomas of the ampulla of Vater. Clin Cancer Res 1997;3:129–133
Suto T, Habano W, Sugai T, et al. Infrequent microsatellite instability in biliary tract cancer. J Surg Oncol 2001;76:121–126
Sherr CJ. Cancer cell cycles. Science 1996;274:1672–1677
Shapiro GI. Cyclin-dependent kinase pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol 2006;24:1770–1783
Migaldi M, Sgambato A, Garagnani L, et al. Loss of p21Waf1 expression is a strong predictor of reduced survival in primary superficial bladder cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:3131–3138
Alle KM, Henshall SM, Field AS, et al. Cyclin D1 protein is overexpressed in hyperplasia and intraductal carcinoma of the breast. Clin Cancer Res 1998;4:847–854
Yuan J, Knorr J, Altmannsberger M, et al. Expression of p16 and lack of pRB in primary small cell lung cancer. J Pathol 1999;189:358–362
Wilentz RE, Su GH, Dai JL, et al. Immunohistochemical labeling for dpc4 mirrors genetic status in pancreatic adenocarcinomas: a new marker of DPC4 inactivation. Am J Pathol 2000;156:37–43
Wilentz RE, Geradts J, Maynard R, et al. Inactivation of the p16 (INK4A) tumor-suppressor gene in pancreatic duct lesions: loss of intranuclear expression. Cancer Res 1998;58:4740–4744
Belvedere O, Puglisi F, Di Loreto C, et al. Lack of correlation between immunohistochemical expression of E2F-1, thymidylate synthase expression and clinical response to 5-fluorouracil in advanced colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 2004;15:55–58
Wang CH, Mo LR, Lin RC, et al. A survival predictive model in patients undergoing radical resection of ampullary adenocarcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 2004;51:1495–1499
Memon MA, Shiwani MH, Anwer S. Carcinoma of the ampulla of Vater: results of surgical treatment of a single center. Hepatogastroenterology 2004;51:1275–1277
De Castro SM, Kuhlmann KF, van Heek NT, et al. Recurrent disease after microscopically radical (R0) resection of periampullary adenocarcinoma in patients without adjuvant therapy. J Gastrointest Surg 2004;8:775–784; discussion 784
Han S, Park K, Bae BN, et al. Cyclin D1 expression and patient outcome after tamoxifen therapy in estrogen receptor positive metastatic breast cancer. Oncol Rep 2003;10:141–144
Esposito I, Friess H, Buchler MW. Carcinogenesis of cancer of the papilla and ampulla: pathophysiological facts and molecular biological mechanisms. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2001;386:163–171
Gansauge S, Gansauge F, Ramadani M, et al. Overexpression of cyclin D1 in human pancreatic carcinoma is associated with poor prognosis. Cancer Res 1997;57:1634–1637
Qiao Q, Ramadani M, Gansauge S, et al. Reduced membranous and ectopic cytoplasmic expression of beta-catenin correlate with cyclin D1 overexpression and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 2001;95:194–197
Kawesha A, Ghaneh P, Andren-Sandberg A, et al. K-ras oncogene subtype mutations are associated with survival but not expression of p53, p16(INK4A), p21(WAF-1), cyclin D1, erbB-2 and erbB-3 in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 2000;89:469–474
Biankin AV, Morey AL, Lee CS, et al. DPC4/Smad4 expression and outcome in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2002;20:4531–4542
Yamazaki K, Hanami K, Nagao T, et al. Increased cyclin D1 expression in cancer of the ampulla of Vater: relevance to nuclear beta catenin accumulation and k-ras gene mutation. Mol Pathol 2003;56:336–341
Liu SC, Zhang SY, Babb JS, et al. Image cytometry of cyclin D1: a prognostic marker for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2001;10:455–459
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, MC., Chang, YT., Sun, CT. et al. Differential Expressions of Cyclin D1 Associated with Better Prognosis of Cancers of Ampulla of Vater. World J Surg 31, 1136–1142 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0032-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-006-0032-6