Abstract
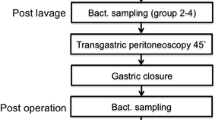
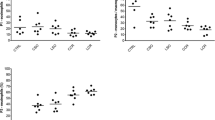
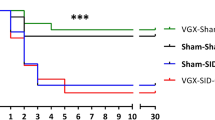
Gram-negative sepsis due to fecal peritonitis is a hazardous disease with a high percentage having a lethal course. The inflammatory effects are induced by endotoxin release. We performed this study to evaluate the potential of direct intraperitoneal application of an endotoxin inhibitor in a laparoscopic peritonitis model in rats. The human feces specimen was prepared, and a standard fecal specimen (0.5 ml/kg b.w.) was applied via minilaparotomy. The rats were randomized to two studies. First, rats were randomized to three groups to define the survival time: (1) rats without further manipulation; (2) rats with laparoscopic lavage using NaCl; (3) rats with laparoscopic lavage using endotoxin inhibitor. Second, rats underwent the same procedure used in the first part of the study and an additional group with only NaCl lavage without peritonitis was randomized. To evaluate the immunologic or biochemical effects, animals were killed at a standard time of 20 hours until the postmortem examination was established. Interleukins 6 and 10 (IL-6, IL-10), malondialdehyde, and protein carbonyl group levels in plasma and particularly in peritoneal fluid were assayed. The first part of the experiment showed significantly increased survival after endotoxin inhibitor lavage. In the second part, administration of endotoxin inhibitor intraperitoneally caused a significant reduction of IL-6 in the peritoneal fluid, in contrast to that in the other groups. Laparoscopic application of endotoxin inhibitor intraperitoneally thus produced a beneficial effect on survival and reduction of IL-6 in peritoneal fluid. Hence, it is possible to influence the inflammation cascade by causing intraperitoneal endotoxin inhibition.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
MH Ackerman (1994) ArticleTitleThe systemic inflammatory response, sepsis, and multiple organ dysfunction: new definitions for an old problem Crit. Care Nurs. Clin. North Am. 6 243–250 Occurrence Handle7946185
RC Bone RA Balk AM Fein et al. (1995) ArticleTitleA second large controlled clinical study of E5, a monoclonal antibody to endotoxin: results of a prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial; The E5 Sepsis Study Group Crit. Care Med. 23 994–1006 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00003246-199506000-00003 Occurrence Handle7774238
JF Dhainaut A Tenaillon M Hemmer et al. (1998) ArticleTitleConfirmatory platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist trial in patients with severe gram-negative bacterial sepsis: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial; BN Sepsis Investigator Group. Crit Care med 52021 26 1963–1971
SM Opal CJ Fisher SuffixJr JF Dhainaut et al. (1997) ArticleTitleConfirmatory interleukin-1 receptor antagonist trial in severe sepsis: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial; the Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Sepsis Investigator Group Crit. Care Med. 25 1115–1124 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00003246-199707000-00010 Occurrence Handle9233735
S Jacobs S Sobki C Morais et al. (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of pentaglobin and piperacillin on survival in a rat model of fecal peritonitis: importance of intervention timings Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 44 88–95 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1399-6576.2000.440116.x Occurrence Handle10669278
RL Greenman RM Schein MA Martin et al. (1991) ArticleTitleA controlled clinical trial of E5 murine monoclonal IgM antibody to endotoxin in the treatment of gram-negative sepsis; the XOMA Sepsis Study Group J. A. M. A. 266 1097–1102 Occurrence Handle1865542
CA Jacobi HU Zieren R Sabat et al. (1997) ArticleTitleComparison of local and systemic inflammation after laparotomy or laparoscopy in the rat sepsis model Langenbecks Arch. Chir. 382 9–13
M Pross HU Schulz T Manger et al. (1999) ArticleTitlePeritonitismodelle an der Ratte unter besonderer Berucksichtigung laparoskopischer Therapieoptionen Zentralbl. Chir. 124 743–748 Occurrence Handle10488547
H Buss TP Chan KB Sluis et al. (1997) ArticleTitleProtein carbonyl measurement by a sensitive ELISA method Free Radic. Biol. Med. 23 361–366 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0891-5849(97)00104-4 Occurrence Handle9214571
CA Jacobi J Ordemann B Bohm et al. (1997) ArticleTitleDoes laparoscopy increase bacteremia and endotoxemia in a peritonitis model? Surg Endosc. 11 235–238 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004649900333 Occurrence Handle9079599
SE Attwood J McGrath AD Hill et al. (1992) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic approach to Meckel’s diverticulectomy Br. J. Surg. 79 211 Occurrence Handle1532525
C Bloechle A Emmermann T Strate et al. (1998) ArticleTitleLaparoscopic vs open repair of gastric perforation and abdominal lavage of associated peritonitis in pigs Surg. Endosc. 12 212–218 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004649900637 Occurrence Handle9502698
WP Geis HC Kim (1995) ArticleTitleUse of laparoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with surgical abdominal sepsis Surg. Endosc. 9 178–182 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00191962 Occurrence Handle7597589
JY Lau SY Lo EK Ng et al. (1998) ArticleTitleA randomized comparison of acute phase response and endotoxemia in patients with perforated peptic ulcers receiving laparoscopic or open patch repair Am. J. Surg. 175 325–327 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0002-9610(98)00006-3 Occurrence Handle9568663
PW Perdue KK Kazarian J Nevola et al. (1994) ArticleTitleThe use of local and systemic antibiotics in rat fecal peritonitis J. Surg. Res. 57 360–365 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jsre.1994.1155 Occurrence Handle8072283
TE Albertson EA Panacek RD MacArthur et al. (2003) ArticleTitleMulticenter evaluation of a human monoclonal antibody to Enterobacteriaceae common antigen in patients with gram-negative sepsis Crit. Care Med. 31 419–427 Occurrence Handle10.1097/01.CCM.0000045564.51812.3F Occurrence Handle12576946
J Riese C Denzel M Zowe et al. (1999) ArticleTitleProduction of chemokines by the human peritoneum Zentralbl. Chir. 124 206–209 Occurrence Handle10327576
K Yoshizawa M Naruto N Ida (1996) ArticleTitleInjection time of interleukin-6 determines fatal outcome in experimental endotoxin shock J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 16 995–1000 Occurrence Handle8974000
A Woltmann M Schult T Schiedeck (1999) ArticleTitlePeritoneal lavage in standardized peritonitis models Zentralbl. Chir. 124 195–198 Occurrence Handle10327574
R Herwig B Glodny C Kuhle (2002) ArticleTitleEarly identification of peritonitis by peritoneal cytokine measurement Dis. Colon Rectum 45 514–521 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10350-004-6231-z Occurrence Handle12006934
L Martineau PN Shek (2000) ArticleTitlePeritoneal cytokine concentrations and survival outcome in an experimental bacterial infusion model of peritonitis Crit. Care Med. 28 788–794 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00003246-200003000-00030 Occurrence Handle10752831
HA Bock (1998) ArticleTitlePathophysiology of acute renal failure in septic shock: from prerenal to renal failure Kidney Int. Suppl. 64 15–18
TS Blackwell JW Christman (1996) ArticleTitleSepsis and cytokines: current status Br. J. Anaesth. 77 110–117 Occurrence Handle8703620
M Navasa A Follo X Filella (1998) ArticleTitleTumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis: relationship with the development of renal impairment and mortality Hepatology 27 1227–1232 Occurrence Handle10.1002/hep.510270507 Occurrence Handle9581675
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Kultusministerium Sachsen-Anhalt grant 2355A/0085H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhn, R., Schubert, D., Tautenhahn, J. et al. Effect of Intraperitoneal Application of an Endotoxin Inhibitor on Survival Time in a Laparoscopic Model of Peritonitis in Rats. World J. Surg. 29, 766–770 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-7409-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-7409-9