Abstract
Background
The prognosis of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains poor, particularly in patients with tumor thrombi (TT) in the major vessels.
Patients and Methods
From July 1992 to October 2004, 161 patients diagnosed as having advanced HCC with major vascular involvement were seen consecutively at our hospital. Among these patients, 32 (20%) underwent surgical resection [16 complete resection (CR), 16 reductive resection (RR)]. Eighteen patients (11%) received radiotherapy (RT), 73 (45%) underwent transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) or transcatheter arterial infusion chemotherapy (TAI), 8 (5%) with distant metastases received systemic chemotherapy, and 30 (19%) received palliative therapy.
Results
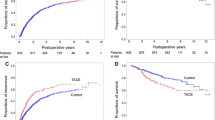
Excluding the CR group, the patients in the RR group had a higher 1-year survival rate than the other treatment groups. However, there was no significant difference in the overall survival rates of the RR, RT, and TACE/TAI groups. When we evaluated prognostic factors to clarify the indications for RR in the multidisciplinary treatment of patients with advanced HCC with TT, prothrombin activity (PA) was identified as a significant independent preoperative factor for overall survival in the RR group. The survival rate in patients with PA of ≤78% was significantly lower than that of patients with PA of >78% (P = 0.0004). The median survival time of patients with serum PA of >78% who underwent RR was 13.9 months and that of patients who underwent CR was 9.1 months, with no survival difference between the groups.
Conclusion
In advanced HCC with major vascular involvement, patients who had RR with PA of greater 78% achieved a similar survival to those who had CR. The surgeon should still proceed with RR in those patients with serum PA of >78% if CR does not seem feasible on preoperative evaluation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Makuuchi M, Kosuge T, Takayama T, et al. Surgery for small liver cancers. Semin Surg Oncol 1993;9:298–304
Imamura H, Seyama Y, Kokudo N, et al. One thousand fifty-six hepatectomies without mortality in 8 years. Arch Surg 2003;138:1198–1206
Furuse J, Iwasaki M, Yoshino M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: embolization of arterioportal shunts. Radiology 1997;204:787–790
Yamakado K, Tanaka N, Nakatsuka A, et al. Clinical efficacy of portal vein stent placement in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma invading the main portal vein. J Hepatol 1999;30:660–668
Tanaka A, Morimoto T, Yamaoka Y. Implications of surgical treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the portal vein. Hepatogastroenterology 1996;43:637–643
Fujii T, Takayasu K, Muramatsu Y, et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein thrombosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1995;10:237–240
The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients. Hepatology 1998;28:751–755
Chen SC, Hsieh MY, Chuang WL, et al. Development of portal vein invasion and its outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transcatheter arterial chemo-embolization. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1994;9:1–6
Asahara T, Itamoto T, Kayayama K, et al. Hepatic resection with tumor thrombectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the major vasculature. Hepatogastroenterology 1999;46:1862–1869
Fujii T, Takayasu K, Muramatsu Y, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal tumor thrombus: analysis of factors determining prognosis. Jpn J Clin Oncol 1993;23:105–109
Lee HS, Kim JS, Choi IJ, et al. The safety and efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and main portal vein obstruction: a prospective controlled study. Cancer 1997;79:2087–2094
Ando E, Yamashita F, Tanikawa K, et al. A novel chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombosis of the main trunk of the portal vein. Cancer 1997;79:1890–1896
Sakon M, Nagano H, Dono K, et al. Combined intraarterial 5-fluorouracil and subcutaneous interferon-α therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with tumor thrombi in the major portal branches. Cancer 2002;94:435–442
Ando E, Tanaka M, Yamashita F, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis. Cancer 2002;95:588–59
Minagawa M, Makuuchi M, Takayama T, et al. Selection criteria for hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombus. Ann Surg 2001;233:379–384
Satoh S, Ikai I, Honda G, et al. Clinicopathologic evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct thrombi. Surgery 2000;128:779–783
Poon RTP, Fan ST, Wong J. Risk factors, prevention, and management of postoperative recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 2000;232:10–24
Ikai I, Yamaoka Y, Yamamoto Y, et al. Surgical intervention for patients with stage – a hepatocellular carcinoma without lymph node metastasis. Ann Surg 1998;227:433–439
Konishi M, Ryu M, Kinoshita T, et al. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with direct removal of the tumor thrombus in the main portal vein. Hepatogastroenterology 2001;48:1421–1424
Lau H, Fan ST, Ng IOL, et al. Long term prognosis after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 1998;83:2302–2311
Fan ST, Ng IOL, Poon RTP, et al. Hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg 1999;134:1124–1130
Torzilli G, Makuuchi M, Inoue K, et al. No-mortality liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic and noncirrhotic patients. Arch Surg 1999;134:984–992
Shimada M, Takenaka K, Kawahara N, et al. Surgical treatment strategy for patients with stage ? hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery 1996;119:517–522
Tanaka A, Morimoto T, Ozaki N, et al. Extension of surgical indication for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Is it possible to prolong life span or improve quality of life? Hepatogastroenterology 1996;43:1172–11801
Wu CC, Ho WL, Lin MC, et al. Hepatic resection for bilobar multicentric hepatocellular carcinoma: Is it justified? Surgery 1998;123:270–277
Tsai TJ, Chau GY, Lui WY, et al. Clinical significance of microscopic tumor venous invasion in patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery 2000;127:603–608
Poon RTP, Fan ST, Lo CM, et al. Improving survival results after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study of 377 patients over 10 years. Ann Surg 2001;234:63–70
El-Assal ON, Yamanoi A, Soda Y, et al. Proposal of invasiveness score to predict recurrence and survival after curative hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery 1997;122:571–577
Hanazaki K, Kajikawa S, Koide N, et al. Prognostic factors after hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatitis C viral infection: univariate and multivariate analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:1243–1250
Seong J, Park HC, Han KH, et al. Clinical results and prognostic factors in radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study of 158 patients. Int J Radiation Oncology Biol Phys 2003;55:329–336
Yamada K, Izaki K, Sugimoto K, et al. Prospective trial of combined transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for portal vein tumor thrombus in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003;57:113–119
Sangro B, Herraiz M, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, et al. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in relation to treatment: a multivariate analysis of 178 patients from a single European institution. Surgery 1998;124:575–583
Chung YH, Song IH, Song BC, et al. Combined therapy consisting of intraarterial cisplatin infusion and systemic interferon-α for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with major portal vein thrombosis or distant metastasis. Cancer 2000;88:1986–1991
Yamamoto K, Takenaka K, Kawahara N, et al. Indication for palliative reduction surgery in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. The use of a remnant tumor index. Arch Surg 1997;132:120–123
Wakabayashi H, Ushiyama T, Ishimura K, et al. Significance of reduction surgery in multidisciplinary treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple intrahepatic lesions. J Surg Oncol 2003;82:98–103
Inoue K, Nakamura T, Kinoshita T, et al. Volume reduction surgery for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2004;130:362–366
Shimamura Y, Gunven P, Ishii M, et al. Debulking surgery and arterial embolization for unresectable liver cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 1993;40:10–13
Yamamoto M, Iizuka H, Matsuda M, et al. The indications for tumor mass reduction surgery and subsequent multidisciplinary treatments in stage IV hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Today 1993;23:675–681
Nagano Y, Tanaka K, Togo S, et al. Efficacy of hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinomas larger than 10 cm. World J Surg 2005;29:66–71
Shuto T, Hirohashi K, Kubo S, et al. Efficacy of major hepatic resection for large hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 1999;46:413–416
Noguchi T, Kawarada Y, Kitagawa M, et al. Clinicopathologic factors influencing the long-term prognosis following hepatic resection for large hepatocellular carcinoma more than 10cm in diameter. Semin Oncol 1997;24:S6-7–S6-13
Poon RTP, Fan ST, Lo CM, et al. Extended hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: Is it justified? Ann Surg 2002;236:602–611
Asahara T, Itamoto T, Katayama K, et al. Indications for palliative reduction surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple intrahepatic metastases. Hiroshima J Med Sci 1998;47:115–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gotohda, N., Kinoshita, T., Konishi, M. et al. New Indication for Reduction Surgery in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Major Vascular Involvement. World J. Surg. 30, 431–438 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-0250-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-0250-3