Abstract
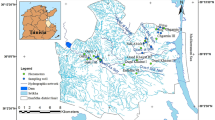
Groundwater contributes substantially to the development of arid and semi-arid regions around the globe. The present study integrates groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and irrigation around Alwar city of Rajasthan state, where agriculture is the major land use. The application for drinking was assessed by comparing the observed value with prescribed standards of WHO. Groundwater was found suitable for drinking at most of the locations. The suitability of groundwater for irrigation was determined by calculating ion-based ratios and comparing them against the suggested ratios and indices for agricultural quality. Suitability for irrigation was assessed against electrical conductivity (EC), percentage sodium (%Na), residual Na2CO3 (RSC), per cent soluble sodium (SSP), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), Mg hazard and permeability index (PI) etc., and the quality was compromised for EC, %Na and Mg Hz. Since the soil was sandy, the groundwater was found suitable for irrigation over long-term use, with the only problem of magnesium hazard. Based on the different ratios of anions and cations, silicate weathering was observed to be regulating groundwater chemistry, and the groundwater belonged to mixed CaMgCl and CaHCO3− type based on Piper’s classification and relative abundance of ions. Further, meteoric genesis classification showed that the groundwater in the study region had direct base exchange and shallow meteoric water percolation. Presence of kaolinite and quartz minerals in soil confirmed that silicate weathering is the major process controlling groundwater chemistry.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel Moneim AA (1988) Hydrogeology of the Nile Basin in Sohag Province. M.Sc.Thesis, Geology Department, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st edn. American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Arveti N, Sarma MRS, Aitkenhead-Peterson JA, Sunil K (2011) Fluoride incidence in groundwater: a case study from Talupula, Andhra Pradesh. India Environ Monit Assess 172:427–443
Bishnoi SR, Brar SPS, Kumar D (1984) Underground water quality of Dhuri block, District Sangrur, Punjab. Indian J Ecol 11(2):220–228
Bureau of Indian Standards (2012) Indian standard drinking water specifications (2nd Revision) 10500. BIS, New Delhi
Central Ground Water Board (2016) Groundwater yearbook (2014–2015) Rajasthan state. Regional Office Data Centre, Western Region Jaipur
Chitrakshi, Haritash AK (2018) Hydrogeochemical characterization and suitability appraisal of groundwater around stone quarries in Mahendragarh, India. Environ Earth Sci 77:252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7431-5
Doneen LD (1964) Water quality for agriculture. Department of Agriculture, University of California, Davis, p 4
Eaton EM (1950) Significance of carbonate in irrigation water. Soil Sci 69:123–133
Food and Agriculture Organisation (2017) Water pollution from agriculture: a global review. FAO of United Nations, Rome
Gaillardet J, Dupre B, Louvat P, Allegre CJ (1999) Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem Geol 59:3–30
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanism controlling world water chemistry. Science 17:1088–1090
Haritash AK, Kaushik CP, Kaushik A, Kansal A, Yadav AK (2008) Suitability assessment of groundwater in some villages of Rewari district in Haryana. Environ Monit Assess 145(1–3):397–406
Haritash AK, Mathur K, Singh P, Singh SK (2017) Hydrochemical characterization and suitability assessment of groundwater in Baga–Calangute stretch of Goa. India Environ Earth Sci 76:341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6679-5
Karaca O, Claudio C, Reddy KR (2017) Acid pond sediment and mine tailings contaminated with metals: physicochemical characterization and electrokinetic remediation. Environment Earth Sci 76(12). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6736-0
Kelly WP (1963) Use of saline irrigation water. Soil Sci 95:355–391
Kumar S, Lata S, Yadav J, Yadav JP (2017) Relationship between water, urine and serum fluoride and fluorosis in school-children of Jhajjar District, Haryana, India. Appl Water Sci 7:3377–3384
Kumarasamy P, Alaguraja P, Deepasaraswathi M, Sekar M, Muthuveerran P, Yuvaraj D, Thirunavukkarasu A, Arthur J, Sames R (2011) Soil suitability and water quality study in Tirupur areas using geographic information system techniques. Int J Earth Sci Eng 4:85–97
Paliwal KV (1972) Irrigation with saline water. IARI Monograph No. 2 (New Series), IARI, New Delhi, p 198
Piper AM (1953) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. USGS Groundwater Note, No, p 12
Richards LA (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline-alkali soils. In: Agriculture handbook no 60. US Department of Agriculture, Washington, p 160
Sawyer CN, Mccarty PL, Parkin GF (2003) Chemistry for environmental engineering and science, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 752
US Geological Survey (2000) Classification of natural ponds and lakes. US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey, Washington, DC
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation water. USDA Circular 969, USDA, Washington DC, p 19
World Health Organization (2006) Guidelines for drinking water quality. First addendum to 3rd edn, vol. 1, World Health Organization, Geneva
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge the help of Department of Irrigation, Alwar, Rajasthan to grant permission for collection of samples; the help of Dr Ram Singh, Department of Applied Chemistry, DTU for FTIR analysis; and Dr Anita Punia (JNU, Delhi) during interpretation of results is thankfully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aggarwal, A., Soni, J., Sharma, K. et al. Hydrogeochemical Assessment of Groundwater for Drinking and Agricultural Use: A Case Study of Rural Areas of Alwar, Rajasthan. Environmental Management 67, 513–521 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-020-01361-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-020-01361-x