Abstract.
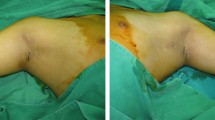
Treatment of axillary osmidrosis has been mainly concerned with surgical excision of glandular tissues and involved major surgical procedures with high morbidities and many complications. Search for a less invasive procedure for axillary osmidrosis resulted in the use of liposuction. However, there have been controversies over the efficacy of this method. The problem was that liposuction could not effectively remove the apocrine gland located in the dermis and dermosubcutaneous junction. A high rate of residual malodor and dissatisfaction were reported. The author used ultrasound-assisted lipoplasty (UAL) in the very superficial plane to remove the apocrine gland located in the dermis and dermosubcutaneous junction. The purpose of this study was to prove the efficacy of the very superficial UAL (VSUAL) for the treatment of axillary osmidrosis. From December 1998 to December 1999, 21 consecutive patients underwent UAL in their axilla for axillary osmidrosis. The follow-up period ranged from 2 to 12 months (mean: 8 months). UAL was performed in the very superficial plane with an amplitude of 40%. The very superficial UAL (VSUAL) was done mainly in a withdrawing manner with the tip of the cannula against the skin. The UAL (VSUAL) was done aggressively until the skin changed slightly erythematous. The results were assessed subjectively and objectively, and classified as excellent, good, fair, and poor. Nineteen patients were graded as excellent and one patient as good. The total satisfaction rate was 95.2%. One patient complained of residual malodor in her left axilla. There were no cases of skin necrosis, hematoma, or seroma. Histology showed partial removal of the subcutaneous layer and deep dermis, and degenerative epithelial changes in the apocrine glands in the residual deep dermis. These microscopic findings meant near-total functional ablation of the apocrine gland in the axilla comparable to ``flap-to-graft conversion'' or surgical excision of axillary skin. The UAL (VSUAL) for axillary osmidrosis has the advantages of a high success rate with minimal complications. Rapid recovery, less restriction of movement, and tiny scars were other major benefits of this technique. Therefore, UAL (VSUAL) is a viable option for treatment of axillary osmidrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S. Very Superficial Ultrasound-Assisted Lipoplasty for the Treatment of Axillary Osmidrosis. Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24, 275–279 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002660010045
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002660010045