Abstract
Background
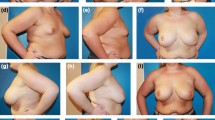
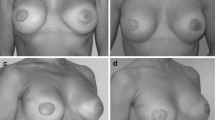
The correction of tuberous breast deformity with fat grafting has gained popularity in recent years, but it remains unclear whether this new technique can produce patient satisfaction levels comparable to those achieved with implant-based correction.
Methods
This study aimed to compare patients’ satisfaction and quality of life using the BREAST-Q questionnaire after correction of tuberous breast deformity with fat grafting and implants. Twenty-four patients (36 breasts) were included in our study. Thirteen patients (15 breasts) had a correction with lipofilling (mean 2.67 interventions) and 11 patients (21 breasts) had an implant-based correction (mean 1 intervention).
Results
Both fat and implant treatments showed statistically significant improvements in breast satisfaction (p value=0.001, 0.002, respectively), psychosocial (p value=0.003, 0.003, respectively), and sexual satisfaction (p value=0.008, 0.002, respectively) between the pre-treatment and post-treatment stages. However, the only statistically significant differences between the treatments were observed in the physical condition pre-treatment (p value=0.008) and sexual condition post-treatment (p value=0.030). The outcome of both treatments was not statistically different. Furthermore, the outcome exhibited a statistically significant positive linear relationship with breast satisfaction for both treatments.
Conclusions
This study suggests that lipofilling can achieve breast and outcome satisfaction comparable to that of implants, although this parity in results comes at the cost of more interventions. These preliminary results lend support to the notion that, as surgeons have access to two equally effective techniques, it is crucial to provide appropriate guidance to patients to ensure their satisfaction.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rees TD, Aston SJ (1976) The tuberous breast. Clin Plast Surg 3(2):339–347
DeLuca-Pytell DM, Piazza RC, Holding JC, Snyder N, Hunsicker LM, Phillips LG (2005) The incidence of tuberous breast deformity in asymmetric and symmetric mammaplasty patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 116(7):1894–9
Zambacos GJ, Mandrekas AD (2006) The incidence of tuberous breast deformity in asymmetric and symmetric mammaplasty patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(7):1667
Klinger M, Caviggioli F, Giannasi S, Bandi V, Banzatti B, Veronesi A et al (2016) The prevalence of tuberous/constricted breast deformity in population and in breast augmentation and reduction mammaplasty patients. Aesthet Plast Surg 40(4):492–496
Papadopoulos S, Colpaert SDM, Goulis DG, Nigdelis MP, Grimbizis GF, Tio J et al (2021) Treating anisomastia and tuberous breast with fat grafting: technique and evaluation of outcomes using BREAST-Q surveys. Aesthet Plast Surg 45:2729–2741
Costagliola M, Atiyeh B, Rampillon F (2013) Tuberous breast: revised classification and a new hypothesis for its development. Aesthet Plast Surg 37(5):896–903
Mandrekas AD, Zambacos GJ (2010) Aesthetic reconstruction of the tuberous breast deformity: a 10-year experience. Aesthet Surg J 30(5):680–692
Grolleau JL, Lanfrey E, Lavigne B, Chavoin JP, Costagliola M (1999) Breast base anomalies: treatment strategy for tuberous breasts, minor deformities, and asymmetry. Plast Reconstr Surg 104(7):2040–2048
Klinger F, Vinci V, Lozito A, Agnelli B, Lisa A, Battistini A et al (2023) Quantitative analysis of the histological features of tuberous breast. Aesthet Plast Surg 47:605–611
Lozito A, Vinci V, Talerico E, Asselta R, Di Tommaso L, Agnelli B et al (2022) Review of tuberous breast deformity: developments over the last 20 years. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 10(5):e4355
Brown MH, Somogyi RB (2015) Surgical strategies in the correction of the tuberous breast. Clin Plast Surg 42(4):531–549
Muti E (1996) Personal approach to surgical correction of the extremely hypoplastic tuberous breast. Aesthet Plast Surg 20(5):385–390
Ribeiro L, Canzi W, Buss A Jr, Accorsi A Jr (1998) Tuberous breast: a new approach. Plast Reconstr Surg 101(1):42–50
Delay E, Sinna R, Ho QC (2013) Tuberous breast correction by fat grafting. Aesthet Surg J 33(4):522–528
Serra-Renom JM, Munoz-Olmo J, Serra-Mestre JM (2011) Treatment of grade 3 tuberous breasts with Puckett’s technique (modified) and fat grafting to correct the constricting ring. Aesthet Plast Surg 35(5):773–781
Claudio Silva-Vergara C, Fontdevila J, Weshahy O (2018) Fat grafting technique, a paradigm shift in the treatment of tuberous breast. World J Plast Surg 7(1):72–77
Alvaro AI, Willet JW, Dounas GD, Jeeves A, Lodge M, Javed MU (2023) A systematic review of outcomes and complications of tuberous breast surgery. Aesthet Surg J 43:NP1001–NP1009
Persichetti P, Cagli B, Tenna S, Simone P, Marangi GF, Li VG (2005) Decision making in the treatment of tuberous and tubular breasts: volume adjustment as a crucial stage in the surgical strategy. Aesthet Plast Surg 29(6):482–488
Oroz-Torres J, Pelay-Ruata MJ, Escolan-Gonzalvo N, Jordan-Palomar E (2014) Correction of tuberous breasts using the unfolded subareolar gland flap. Aesthet Plast Surg 38(4):692–703
Papadopoulos S, Vidovic G, Neid M, Abdallah A (2018) Using fat grafting to treat breast implant capsular contracture. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 6(11):e1969
Ueberreiter K, von Finckenstein JG, Cromme F, Herold C, Tanzella U, Vogt PM (2010) BEAULI–a new and easy method for large-volume fat grafts. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 42(6):379–385
Taha S, Saller MM, Haas E, Farkas Z, Aszodi A, Giunta R et al (2020) Adipose-derived stem/progenitor cells from lipoaspirates: a comparison between the Lipivage200-5 liposuction system and the body-jet liposuction system. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 73(1):166–175
Yin S, Luan J, Fu S, Wang Q, Zhuang Q (2015) Does water-jet force make a difference in fat grafting? In vitro and in vivo evidence of improved lipoaspirate viability and fat graft survival. Plast Reconstr Surg 135(1):127–138
Khouri RK, Rigotti G, Cardoso E, Khouri RK Jr, Biggs TM (2014) Megavolume autologous fat transfer: part II. Practice and techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 133(6):1369–1377
Ho Quoc C, Sinna R, Gourari A, La Marca S, Toussoun G, Delay E (2013) Percutaneous fasciotomies and fat grafting: indications for breast surgery. Aesthet Surg J 33(7):995–1001
Pusic AL, Chen CM, Cano S, Klassen A, McCarthy C, Collins ED et al (2007) Measuring quality of life in cosmetic and reconstructive breast surgery: a systematic review of patient-reported outcomes instruments. Plast Reconstr Surg. 120(4):823–37
Pusic AL, Klassen A, Cano SJ, Kerrigan CL (2007) Validation of the breast evaluation questionnaire. Plast Reconstr Surg 120(1):352–353
The BREAST-Q. Licensed through Mapi Research Trust, Lyon, France – Internet:https://eprovide.mapi-trust.org/. Accessed November 5, 2017. BREAST-Q and QScore is now distributed through this website: http://qportfolio.org/breast-q/Memorial. Owner Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center and The University of British Columbia, copyright Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center and The University of British Columbia © 2007, All rights reserved.
Mundy LR, Homa K, Klassen AF, Pusic AL, Kerrigan CL (2017) Normative data for interpreting the BREAST-Q: augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 139(4):846–853
WHO Consultatoin on Obesity, World Health Organization (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 894:1–253.
Derder M, Whitaker IS, Boudana D, Marchac A, Hivelin M, Mattar N et al (2014) The use of lipofilling to treat congenital hypoplastic breast anomalies: preliminary experiences. Ann Plast Surg 73(4):371–377
Gutierrez-Ontalvilla P, Naidu NS, Blanco EL, Brito EC, Ruiz-Valls A (2020) Autologous fat grafting with percutaneous fasciotomy and reduction of the nipple-areolar complex for the correction of tuberous breast deformity in teenagers. Aesthet Plast Surg 44:264–269
Klit A, Siemssen PA, Gramkow CS (2015) Treatment of congenital unilateral hypoplastic breast anomalies using autologous fat grafting: a study of 11 consecutive patients. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 68(8):1106–1111
Kolker AR, Collins MS (2015) Tuberous breast deformity: classification and treatment strategy for improving consistency in aesthetic correction. Plast Reconstr Surg 135(1):73–86
Tenna S, Cagli B, Brunetti B, Barone M, Persichetti P (2017) Management of tuberous breast deformities: review of long-term outcomes and patient satisfaction with BREAST-Q. Aesthet Plast Surg 41(6):1249–1258
Brault N, Stivala A, Guillier D, Moris V, Revol M, Francois C et al (2017) Correction of tuberous breast deformity: a retrospective study comparing lipofilling versus breast implant augmentation. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 70(5):585–595
Deschler A, Stroumza N, Pessis R, Azuelos A, Atlan M (2020) Primary breast augmentation with autologous fat grafting alone: evaluation of patient satisfaction using the BREAST-Q. Aesthet Surg J 40(11):1196–1204
Papadopoulos S, Colpaert SDM, Goulis DG, Nigdelis MP, Grimbizis GF, Tio J et al (2021) Fat grafting and auto-augmentation mastopexy after breast implant removal: technique and evaluation of outcomes using BREAST-Q. Aesthet Surg J. 41(6):NP388–NP401
Alderman AK, Bauer J, Fardo D, Abrahamse P, Pusic A (2014) Understanding the effect of breast augmentation on quality of life: prospective analysis using the BREAST-Q. Plast Reconstr Surg 133(4):787–795
Coriddi M, Angelos T, Nadeau M, Bennett M, Taylor A (2013) Analysis of satisfaction and well-being in the short follow-up from breast augmentation using the BREAST-Q, a validated survey instrument. Aesthet Surg J 33(2):245–251
Jawanrudi P, Bender R, Pennig D, Taskin B, Schaller S, Al-Malat T et al (2022) Evaluation of quality of life (BREAST-Q) and scar quality (POSAS) after breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 10(5):e4313
Papadopoulos S, Colpaert SDM, Tio J, Vidovic G, Grimbizis GF, Abdallah A (2022) Treating pain and fat necrosis after breast cancer surgery with fat grafting: Is one session enough? Aesthet Plast Surg 46(6):2677–2688
Nahabedian MY (2021) Large-volume autologous fat grafting to the breast. Aesthet Surg J 41:S16–S24
Chang CS, Lanni MA, Mirzabeigi MN, Bucky LP (2022) Large-volume fat grafting: identifying risk factors for fat necrosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 150(5):941e-e949
Sun Z, Zhao H (2022) Thoughts on mega volume fat grafting for breast augmentation. Aesthet Surg J 42(11):NP697–NP8
Martin Ginis KA, McEwan D, Bassett RL (eds) (2013) Physical activity and body image. Routledge, New York
Miller L, Warner V, Wickramaratne P, Weissman M (1999) Self-esteem and depression: ten year follow-up of mothers and offspring. J Affect Disord 52(1–3):41–49
Stice E, Whitenton K (2002) Risk factors for body dissatisfaction in adolescent girls: a longitudinal investigation. Dev Psychol 38(5):669–678
Polivy J, Herman CP (2002) Causes of eating disorders. Annu Rev Psychol 53:187–213
Bassett-Gunter R, McEwan D, Kamarhie A (2017) Physical activity and body image among men and boys: a meta-analysis. Body Image 22:114–128
Funding
All authors have nothing to disclose. No funding was received for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Papadopoulos, S., Colpaert, S.D.M., Vidovic, G. et al. Correction of the Tuberous Breast with Fat Grafting and Implant: Techniques, Evaluation with BREAST-Q, and Preliminary Results. Aesth Plast Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-04032-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-04032-y