Abstract
Background
In addition to symptom relief, the crucial objective of reduction mammoplasty is to achieve a stable and esthetically pleasing postoperative breast shape. However, the morphological changes in breasts following reduction mammoplasty have not been comprehensively understood. In this study, we applied three-dimensional (3D) scanning technology for long-term follow-up monitoring of breast morphological changes to discern their changing trends. Our goal was to provide a reliable basis for assessing postoperative effects and determining follow-up time points.
Methods
This prospective study included patients undergoing vertical-scar reduction mammoplasty. We utilized a combination of linear measurements and 3D scanning to measure various parameters, including breast volume, breast volume distribution, nipple position, and scar length at various time points: pre-surgery, immediately post-surgery, 3-month postoperative, 6-month postoperative, and 1-year postoperative.
Results
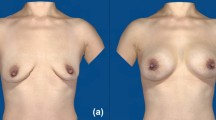
A total of 115 patients were enrolled in this study. Throughout the initial 3 months of postoperative follow-up, there was a gradual reduction in breast volume, which tended to stabilize from 3 to 12 months. The nipple position showed a gradual shift both laterally, inferiorly, and posteriorly. The volume of the lower and lateral part of the breast increased gradually. Notably, at 1 year after surgery, the scar length was approximately 6.3% shorter compared to the immediate postoperative measurement.
Conclusions
Our 3D analysis unveiled comprehensive changes in breast morphology: The overall breast volume shifted laterally and inferiorly, the nipple position moved laterally, inferiorly, and posteriorly, and there was a significant reduction in scar length. Concurrently, breast volume exhibited a gradual decrease and stabilization after 3 months, establishing it as a suitable follow-up point for assessing postoperative results. Additionally, surgical plans can be formulated based on the overall trend of changes in breast volume and distribution, combined with methods such as three-dimensional scanning, to enhance surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to authors www.springer.com/00266.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nichols LM, Oranges CM, Tremp M et al (2021) Management of symptomatic breast hypertrophy and reduction mammaplasty. Rev Med Suisse 17(743):1177–1181
Pérez-Panzano E, Gascón-Catalán A, Sousa-Domínguez R et al (2017) Reduction mammaplasty improves levels of anxiety, depression and body image satisfaction in patients with symptomatic macromastia in the short and long term. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol 38(4):268–275
American Society of Plastic Surgeons (2020) Plastic surgery statistics report. https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2020/plastic-surgery-statistics-full-report-2020
Rinker B (2013) Lowering revision rates in medial pedicle breast reduction by the selective addition of “inverted-T” technique. Aesthet Plast Surg 37(2):341–348
Kemaloğlu CA, Özocak H (2018) Comparative outcomes of inferior pedicle and superomedial pedicle technique with wise pattern reduction in gigantomastic patients. Ann Plast Surg 80(3):217–222
Xue AS, Wolfswinkel EM, Weathers WM et al (2013) Breast reduction in adolescents: indication, timing, and a review of the literature. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 26(4):228–233
Wampler AT, Powelson IA, Homa K et al (2021) BREAST-Q outcomes before and after bilateral reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 147(3):382e–390e
Gfrerer L, Mattos D, Mastroianni M et al (2015) Assessment of patient factors, surgeons, and surgeon teams in immediate implant-based breast reconstruction outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg 135(2):245e–252e
Yang J, Zhang R, Shen J et al (2015) The three-dimensional techniques in the objective measurement of breast aesthetics. Aesthet Plast Surg 39(6):910–915
Kovacs L, Eder M, Zimmermann A et al (2012) Three-dimensional evaluation of breast augmentation and the influence of anatomic and round implants on operative breast shape changes. Aesthet Plast Surg 36(4):879–887
Ji K, Luan J, Liu C et al (2014) A prospective study of breast dynamic morphological changes after dual-plane augmentation mammaplasty with 3D scanning technique. PLoS ONE 9(3):e93010
Becker H (2012) The role of three-dimensional scanning technique in evaluation of breast asymmetry. Plast Reconstr Surg 130(6):893e–894e
Li XR, Zeng L, Hong WJ et al (2023) Three-dimensional evaluation of results after dual-plane breast augmentation with and without internal suture mastopexy. Aesthet Plast Surg 47(4):1303–1311
Eder M, Klöppel M, Müller D et al (2013) 3-D analysis of breast morphology changes after inverted T-scar and vertical-scar reduction mammaplasty over 12 months. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 66(6):776–786
Liu Y, Luan J (2023) Breast morphological changes after transaxillary dual-plane augmentation with smooth round implants: a prospective study. Aesthet Plast Surg 47(3):966–978
Tong OLH, Chamson-Reig A, Yip LCM et al (2020) Structured-light surface scanning system to evaluate breast morphology in standing and supine positions. Sci Rep 10(1):14087
Chen L, Sun J, Mu D et al (2020) What makes a difference? three-dimensional morphological study of parameters that determine breast aesthetics. Aesthet Plast Surg 44(2):315–322
Kovacs L, Eder M, Hollweck R et al (2006) New aspects of breast volume measurement using 3-dimensional surface imaging. Ann Plast Surg 57(6):602–610
Liu C, Luan J, Mu L et al (2010) The role of three-dimensional scanning technique in evaluation of breast asymmetry in breast augmentation: a 100-case study. Plast Reconstr Surg 126(6):2125–2132
Lee HY, Hong K, Kim EA (2004) Measurement protocol of women’s nude breasts using a 3D scanning technique. Appl Ergon 35(4):353–359
Swanson E (2012) A measurement system for evaluation of shape changes and proportions after cosmetic breast surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 129(4):982–992
Eder M, Waldenfels FV, Sichtermann M et al (2011) Three-dimensional evaluation of breast contour and volume changes following subpectoral augmentation mammaplasty over 6 months. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64(9):1152–1160
Liu C, Luan J, Ji K et al (2012) Measuring volumetric change after augmentation mammaplasty using a three-dimensional scanning technique: an innovative method. Aesthet Plast Surg 36(5):1134–1139
Ahmad J, Lista F (2008) Vertical scar reduction mammaplasty: the fate of nipple-areola complex position and inferior pole length. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(4):1084–1091
Sun J, Mu D, Liu C et al (2016) Scar assessment after breast augmentation surgery with axillary incision versus inframammary fold incision: long-term follow-up in chinese patients. Aesthet Plast Surg 40(5):699–706
Suga H, Shiraishi T, Takushima A (2020) Scar assessment after breast reconstruction: risk factors for hypertrophy and hyperpigmentation in asian patients. Ann Plast Surg 85(3):229–232
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
All participants have given informed consent in writing prior to inclusion in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1 (MP4 11266 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Lin, Y., Zhang, X. et al. 3D Analysis of Breast Morphological Changes after Vertical-Scar Reduction Mammoplasty: A Prospective Study. Aesth Plast Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-03985-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-024-03985-4