Abstract
Background
Reduction mammoplasty (RM) remains one of the most common plastic surgeries worldwide. Many different techniques have been described in the literature, each with its advantages and limitations. Nipple-areolar complex necrosis remains a daunting complication, regardless of the chosen surgical approach.
Objective
We describe the senior author’s (HYK) unique reduction mammoplasty technique, employing the infero-central (IC) pedicle throughout the last two decades.
Patients and Methods
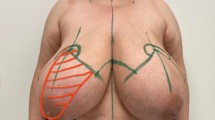
A retrospective chart review of 520 patients undergoing breast reduction was performed. After exclusion criteria, 360 were included in the study. These patients underwent RM with the IC technique, with stabilization of the breast mound and plication of the inferior pole dermis to prevent bottoming out. Demographics, operative data, and complications were recorded. Pre- and postoperative photographs were evaluated by a specialists’ panel. The BREAST-Q questionnaire was utilized to assess satisfaction rates.
Results
BREAST-Q questionnaire-satisfaction with breast score was 84.19, and outcome score was 91.67. Aesthetic outcome evaluation, reviewed by four plastic surgeons, yielded a high score in all parameters (1.64–2; range 0–2). On a per-breast basis for all patients, the following complications were analyzed: dehiscence (3.61%), infection (2.22%), hematoma (1.66%), superficial wound healing problems (1.38%), seroma (0.83%), skin flap ischemia (1.52%), hypertrophic scar (1.38%), fat necrosis (0.97%), and partial nipple ischemia (0.27%).
Conclusion
Infero-central mound technique can be applied to breast reductions of nearly all sizes, allowing for consistently satisfactory aesthetic outcomes for most patients. Due to robust vascularity of the pedicle, complication rates are kept at a minimum. IC mound technique is an essential tool in the plastic surgeon’s armamentarium.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.










Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
American Society of Plastic Surgeons (2018) Cosmetic plastic surgery statistics. Available at, https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2019/plastic-surgery-statistics-report-2019.pdf
Hall-Findlay EJ, Shestak KC (2015) Breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 136(4):531e–544e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000001622
DeLong MR, Chang I, Farajzadeh M et al (2020) the central mound pedicle: a safe and effective technique for reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 146(4):725–733. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000007173
Hall-Findlay EJ (1999) A simplified vertical reduction mamma- plasty: shortening the learning curve. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:748–759
Matarasso A (2002) Suction mammaplasty: the use of suction lipectomy alone to reduce large breasts. Clin Plast Surg 29(433–443):vii
Ramirez OM (2002) Reduction mammaplasty with the “owl” incision and no undermining. Plast Reconstr Surg 109:512–522
Hidalgo DA, Elliot LF, Palumbo S, Casas L, Hammond D (1999) Current trends in breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:806–815
Landau AG, Hudson DA (2008) Choosing the superomedial pedicle for reduction mammaplasty in gigantomastia. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:735–739
Okoro SA, Barone C, Bohnenblust M, Wang HT (2008) Breast reduction trend among plastic surgeons: a national survey. Plast Reconstr Surg 122:1312–1320
Robbins TH (1977) A reduction mammoplasty with the areola-nipple based on an inferior dermal pedicle. Plast Reconstr Surg 59:64–67
Courtiss E, Goldwyn R (1977) Reduction mammaplasty by the inferior pedicle technique. Plast Reconstr Surg 59:500–507
Pennington DG (2006) Improving the results of inferior pedicle breast reduction using pedicle suspension and plication. Aesthetic Plast Surg 30(4):390–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0040-9
Balch CR (1981) The central mound technique for reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 67:305–311
Kaplan H (2021) The infero-central mound reduction mammoplasty with inferior pole plication, A single surgeon, 20-year experience. Tel-Aviv Breast Meeting Tel-Aviv. 10–12 November, 2021
Pusic AL, Klassen A, Scott A, Klok J et al (2009) Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: the BREAST-Q. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:345–353
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Centre (2012) The BREAST-Q. Available at: https://webcore.mskcc.org/breastq/get-bq. html. Accessed November 13
Lowery JC, Wilkins EG, Kuzon WM, Davis JA (1996) Evaluations of aesthetic results in breast reconstruction: an analysis of reliability. Ann Plast Surg 36(6):601–606
Lassus C (1970) A technique for breast reduction. Int Surg 53:69–72
Pitanguy I (1967) Surgical treatment of breast hypertrophy. Br J Plast Surg 20:78–85
Nahabedian MY, Inneligan P, Inliu DZ (2018) Plastic surgery, 4th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 136–145
Lotsch F (1923) Uber hangebrustplastik. Zentralbi chir 50:1241–1244
Wise RJ, Gannon JP, Hill JR (1963) Further experience with reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 32:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-196307000-00002
McKissock PK (1972) Reduction mammaplasty with a vertical der- mal flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 49:245–252
Marchac D, de Olarte G (1982) Reduction mammaplasty and correction of ptosis with a short inframammary scar. Plast Reconstr Surg 69:45–55
Lejour M, Abboud M, Declety A, Kertesz P (1990) Reduction of mammaplasty scars: from a short inframammary scar to a ver-tical scar (in French). Ann Chir Plast Esthet 35:369–379
Georgiade NG, Serafin D, Morris R et al (1979) Reduction mammaplasty utilizing an inferior pedicle nipple-areolar flap. Ann Plast Surg 3:211–218
Wang D, Xiong S, Ai T et al (2021) The use of DCE-MRI to evaluate the blood supply to the nipple-areola complex: a study in 245 asian women. Aesthet Surg J 41(6):NP346–NP354. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa406
Würinger E, Mader N, Posch E, Holle J (1998) Nerve and vessel supplying ligamentous suspension of the mammary gland. Plast Reconstr Surg 101(6):1486–1493. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199805000-00009
Lugo LM, Prada M, Kohanzadeh S, Mesa JM, Long JN, de la Torre J (2013) Surgical outcomes of gigantomastia breast reduction superomedial pedicle technique: a 12-year retrospective study. Ann Plast Surg 70(5):533–537
Nahabedian MY, McGibbon BM, Manson PN (2000) Medical pedicle reduction mammaplasty for severe mammary hypertrophy. Plast Reconstr Surg 1(05):896–904
Abramo AC (2012) A superior vertical dermal pedicle for the nipple areola: an alternative for severe breast hypertrophy and ptosis. Aesthetic Plast Surg 36:134–139
Kalliainen LK, ASPS Health Policy Committee (2012) ASPS clinical practice guideline summary on reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 130(4):785–789
Cunningham BL, Gear AJ, Kerrigan CL, Collins ED (2005) Analysis of breast reduction complications derived from the BRAVO study. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(6):1597–1604
Abramson DL, Pap S, Shifteh S, Glasberg SB (2005) Improving long-term breast shape with the medial pedicle wise pattern breast reduction. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(7):1937–1943. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000165085.23537.a7
Beer GM, Spicher I, Cierpka KA, Meyer VE (2004) Benefits and pitfalls of vertical scar breast reduction. Br J Plast Surg 57(1):12–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0040-9
Jaspars JJ, Posma AN, van Immerseel AA, Gittenberger-de Groot AC (1997) The cutaneous innervation of the female breast and nipple-areola complex: implications for surgery. Br J Plast Surg 50(4):249–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0007-1226(97)91155-3
Hunt SC, Sun Y, Azad S (2022) A simplified approach to breast reduction using the medial pedicle. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 4:ojac019. https://doi.org/10.1093/asjof/ojac019
Jørgensen MG, Albertsdottir E, Dalaei F et al (2021) Age and body mass index affect patient satisfaction following reduction mammoplasty: a multicenter study using BREAST-Q. Aesthet Surg J 41(6):NP336–NP345. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa395
Bustos SS, Molinar V, Kuruoglu D et al (2021) Inferior pedicle breast reduction and long nipple-to-inframammary fold distance: how long is safe? J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 74(3):495–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2020.08.123
Funding
This study has no funding. No funding was received for this work from any of the following organizations: National Institutes of Health (NIH); Wellcome Trust; Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI); RCUK; and other(s). Dr. Kaplan has nothing to disclose. No funding was received for this article. Dr. Shachar has nothing to disclose. No funding was received for this article. Dr. Rysin has nothing to disclose. No funding was received for this article. None of the authors has a financial interest in any of the products, devices, or drugs mentioned in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HK provided substantial contributions to: 1) conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation of data; 2) drafting the article; 3) final approval of the version to be published; 4) agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work. RR substantially contributed to: 1) conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation of data; 2) drafting the article; 3) final approval of the version to be published; 4) agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work. YS provided substantial contributions to: 1) conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data; 2) drafting the article; 3) final approval of the version to be published; 4) agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable, none needed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Video 1 Initial flap dissection (MP4 22299 KB)
Video 2 Flap elevation (MP4 41610 KB)
Video 3 Flap undermining (MP4 3818 KB)
Video 4 Breast mound resection (MP4 58176 KB)
Video 5 Inferior pedicle measurement (MP4 5969 KB)
Video 6 Inferior pedicle plication (MP4 11143 KB)
Video 7 Superior pole fixation suture (MOV 29248 KB)
Video 8 Flap re-draping (MP4 9339 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaplan, H.Y., Rysin, R. & Shachar, Y. The Infero-Central Mound Reduction Mammoplasty: A Single Surgeon, 20-year Experience. Aesth Plast Surg 48, 914–924 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03442-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03442-8