Abstract
Background
Hyaluronidase is used as a reversal agent for hyaluronic acid fillers and to increase the diffusion of other medications after infiltration. Cases of hyaluronidase allergy have been described in the literature since 1984. However, it is still frequently misdiagnosed. This review aims to summarize the current literature to describe the clinical picture of hyaluronidase allergy and identify any risk factors associated with its development, as well as provide recommendations for management in plastic surgery.
Methods
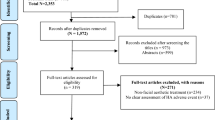
A digital search of PubMed, Scopus, and Embase databases was performed by two reviewers following the PRISMA guidelines. This search identified 247 articles.
Results
Two hundred forty-seven articles were identified, and 37 of them met the eligibility criteria. One hundred six patients with a mean age of 54.2 years were included in these studies. History of allergy to other substances (timothy grass, egg white, horse serum, penicillin, insect bites, wasp venom, thimerosal, potassium, histamine, phenylmercuric acetate, and nickel) and allergic diseases (asthma, dermatitis, atopy, rhinitis) was reported. A large portion of the patients with a history of repeated exposure (2–4) experienced the symptoms with their second injection. Nonetheless, there was no significant association between time to allergy development and the number of exposures (P = 0.3). Treatment with steroids +/− antihistamines resulted in the rapid and predominantly complete reversal of the symptoms.
Conclusions
Prior injections or sensitization by insect/wasp venom might be the primary factor associated with hyaluronidase allergy development. The time between the repeated injections is not a likely contributor to the presentation.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee Y, Jeon YJ, Kang S et al (2022) Social media use and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic in young adults: a meta-analysis of 14 cross-sectional studies. BMC Public Health 22:995
Arab K, Barasain O, Altaweel A, et al. (2019) Influence of Social Media on the Decision to Undergo a Cosmetic Procedure. Plast Reconstr Surg—Glob Open. 7, https://journals.lww.com/prsgo/Fulltext/2019/08000/Influence_of_Social_Media_on_the_Decision_to.2.aspx
The Aesthetic Society. Aesthetic plastic surgery National Databank Statistics 2020–2021
Ortiz AE, Ahluwalia J, Song SS, et al. (2020) Analysis of US food and drug administration data on soft-tissue filler complications. Dermatol Surg. 46, https://journals.lww.com/dermatologicsurgery/Fulltext/2020/07000/Analysis_of_U_S__Food_and_Drug_Administration_Data.19.aspx
Ortiz-Perez S, Fernandez E, Molina JJ et al (2011) Two cases of drug-induced orbital inflammatory disease. Orbit 30:37–39
Kim MS, Youn S, Na CH et al (2015) Allergic reaction to hyaluronidase use after hyaluronic acid filler injection. J Cosmet Laser Ther 17:283–285
Olaiya OR, Forbes D, Humphrey S et al (2021) Hyaluronidase for treating complications related to HA fillers: a national plastic surgeon survey. Plast Surg. https://doi.org/10.1177/22925503211019618
Kang SY, Lee SY, Kim JC et al (2022) Delayed hypersensitivity of hyaluronidase: a case report. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.18133. (Epub ahead of print 10 April 2022)
Taylor IS, Pollowitz JA (1984) A little-known phenomenon: allergic reaction to hyaluronidase. Ophthalmology 91:1003
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ 339:b2535
Kim J-H, Choi G-S, Ye Y-M et al (2009) Acute urticaria caused by the injection of goat-derived hyaluronidase. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 1:48–50
Wu L, Liu X, Jian X et al (2018) Delayed allergic hypersensitivity to hyaluronidase during the treatment of granulomatous hyaluronic acid reactions. J Cosmet Dermatol 17:991–995
Ebo DG, Goossens S, Opsomer F et al (2005) Flow-assisted diagnosis of anaphylaxis to hyaluronidase. Allergy 60:1333–1334
Andre P, Fléchet M (2008) Angioedema after ovine hyaluronidase injection for treating hyaluronic acid overcorrection. J Cosmet Dermatol 7:136–138
Lee A, Grummer SE, Kriegel D, et al. (2010) Hyaluronidase. Dermatol Surg. 36, https://journals.lww.com/dermatologicsurgery/Fulltext/2010/07000/Hyaluronidase.1.aspx
Quantock CL, Goswami T (2007) Death potentially secondary to sub-Tenon’s block. Anaesthesia 62:175–177
Quhill F, Bowling B, Packard RB (2004) Hyaluronidase allergy after peribulbar anesthesia with orbital inflammation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 30, https://journals.lww.com/jcrs/Fulltext/2004/04000/Hyaluronidase_allergy_after_peribulbar_anesthesia.46.aspx
Minning CA Jr (1994) Hyaluronidase allergy simulating expulsive choroidal hemorrhage. Arch Ophthalmol 112:585–586
Kirby B, Butt A, Morrison AM et al (2001) Type I allergic reaction to hyaluronidase during ophthalmic surgery. Contact Dermat 44:44–45
Agrawal A, McLure HA, Dabbs TR (2003) Allergic reaction to hyaluronidase after a peribulbar injection. Anaesthesia 58:493–494
Rajalakshmi AR, Kumar MA (2016) Hyaluronidase hypersensitivity: a rare complication of peribulbar block. Indian J Ophthalmol. 64, https://journals.lww.com/ijo/Fulltext/2016/64020/Hyaluronidase_hypersensitivity__A_rare.15.aspx
Park S, Lim LT (2014) Orbital inflammation secondary to a delayed hypersensitivity reaction to sub-Tenon’s hyaluronidase. Semin Ophthalmol 29:57–58
Lyall DAM, McQueen M, Ramaesh K et al (2012) A sting in the tale: cross reaction hypersensitivity to hyaluronidase. Eye 26:1490–1490
Borchard K, Puy R, Nixon R (2010) Hyaluronidase allergy: a rare cause of periorbital inflammation. Australas J Dermatol 51:49–51
Feighery C, McCoy EP, Johnston PB et al (2007) Delayed hypersensitivity to hyaluronidase (HyalaseTM) used during cataract surgery. Contact Dermat 57:343–343
Patil B, Agius-Fernandez A, Worstmann T (2005) Hyaluronidase allergy after peribulbar anesthesia with orbital inflammation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 31, https://journals.lww.com/jcrs/Fulltext/2005/08000/Hyaluronidase_allergy_after_peribulbar_anesthesia.13.aspx
Gupta A, Moharana B, Saini R et al (2022) Pretreatment with systemic corticosteroid can mask early symptoms of hypersensitivity reaction to hyaluronidase following peribulbar block. BMJ Case Rep 15:e247208
Park AR, Kim WM, Heo BH (2015) Delayed allergic reaction to secondary administrated epidural hyaluronidase. Korean J Pain 28:153–155
Kim TW, Lee JH, Yoon KB et al (2011) Allergic reactions to hyaluronidase in pain management—A report of three cases-. Korean J Anesthesiol 60:57–59
Delaere L, Zeyen T, Foets B et al (2009) Allergic reaction to hyaluronidase after retrobulbar anaesthesia: a case series and review. Int Ophthalmol 29:521–528
Szépfalusi Z, Nentwich I, Dobner M et al (1997) IgE-mediated allergic reaction to hyaluronidase in paediatric oncological patients. Eur J Pediatr 156:199–203
Raichura ND, Alam MS, Jaichandran VV et al (2018) Hyaluronidase allergy mimicking orbital cellulitis. Orbit 37:149–153
Leibovitch I, Tamblyn D, Casson R et al (2006) Allergic reaction to hyaluronidase: a rare cause of orbital inflammation after cataract surgery. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 244:944–949
Escolano F, Parés N, Gonzalez I et al. (2005) Allergic reaction to hyaluronidase in cataract surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol EJA. 22, https://journals.lww.com/ejanaesthesiology/Fulltext/2005/09000/Allergic_reaction_to_hyaluronidase_in_cataract.16.aspx
Dieleman M, Bettink-Remeijer MW, Jansen J et al (2012) High incidence of adverse reactions to locoregional anaesthesia containing hyaluronidase after uneventful ophthalmic surgery. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 90:e245–e246
Ahluwalia HS, Lukaris A, Lane CM (2003) Delayed allergic reaction to hyaluronidase: a rare sequel to cataract surgery. Eye 17:263–266
Musa F, Srinivasan S, King CM et al. (2006) Raised intraocular pressure and orbital inflammation: a rare IgE-mediated allergic reaction to sub-Tenon’s hyaluronidase. J Cataract Refract Surg. 32, https://journals.lww.com/jcrs/Fulltext/2006/01000/Raised_intraocular_pressure_and_orbital.51.aspx
Halliday L, Sia PI, Durkin S et al (2018) Atypical case of hyaluronidase allergy with orbital compartment syndrome and visual loss. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 46:563–564
Mayor R, Gautam P, Agarwal M et al (2016) Hyaluronidase sensitivity: our experience. Indian J Ophthalmol 64:789–790
Griffiths E, Siew L, Pillai P et al (2015) Hyaluronidase—a sting in the tale? Wiley, Blackwell
Proceedings of the RAMI section of ophthalmology meeting, Friday 7th April 2017 in the Killashee House Hotel, Naas. Ir J Med Sci 1971–2018; 187: 7–10
Eberhart AH, Weiler CR, Erie JC (2004) Angioedema related to the use of hyaluronidase in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol 138:142–143
Vartanian AJ, Frankel AS, Rubin MG (2005) Injected hyaluronidase reduces restylane-mediated cutaneous augmentation. Arch Facial Plast Surg 7:231–237
Murray G, Convery C, Walker L et al (2021) Guideline for the safe use of hyaluronidase in aesthetic medicine, including modified high-dose protocol. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 14:E69–E75
Bailey SH, Fagien S, Rohrich RJ (2014) Changing role of hyaluronidase in plastic surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 133, https://journals.lww.com/plasreconsurg/Abstract/2014/02000/Changing_Role_of_Hyaluronidase_in_Plastic_Surgery.16.aspx
Sharma DSC, Lahiri MA (2021) Use of hyaluronidase in plastic surgery: a review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 74:1610–1614
Landau M (2015) Hyaluronidase caveats in treating filler complications. Dermatol Surg 41(Suppl 1):S347–S353
Hoesly PM, Tolaymat LM, Sluzevich JC et al (2018) Pretibial myxedema successfully treated with intralesional hyaluronidase. JAAD Case Rep 4:874–876
Riedl M, Lumry W, Li H et al (2016) Subcutaneous administration of human C1 inhibitor with recombinant human hyaluronidase in patients with hereditary angioedema. Allergy Asthma Proc 37:489–500
Wasserman RL, Melamed I, Kobrynski L et al (2016) Recombinant human hyaluronidase facilitated subcutaneous immunoglobulin treatment in pediatric patients with primary immunodeficiencies: long-term efficacy, safety and tolerability. Immunotherapy 8:1175–1186
Youssef Z, Pennefather PM, Watts MT (2005) Orbital cellulitis vs allergic reaction to hyaluronidase as the cause of periorbital oedema. Eye 19:691–692
Varma D, Metcalfe TW (2003) Orbital cellulitis after peribulbar anaesthesia for cataract surgery. Eye 17:105–107
Kempeneers A, Dralands L, Ceuppens J (1992) Hyaluronidase induced orbital pseudotumor as complication of retrobulbar anesthesia. Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol 243:159–166
Zamora-Alejo K, Moore S, Leatherbarrow B et al (2013) Hyaluronidase toxicity: a possible cause of postoperative periorbital inflammation. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 41:122–126
Jin C, Focke M, Léonard R et al (2010) Reassessing the role of hyaluronidase in yellow jacket venom allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 125:184-190.e1
Keller EC, Kaminer MS, Dover JS (2014) Use of hyaluronidase in patients with bee allergy. Dermatol Surg. 40, https://journals.lww.com/dermatologicsurgery/Fulltext/2014/10000/Use_of_Hyaluronidase_in_Patients_With_Bee_Allergy.14.aspx
Dunn A, Heavner J, Racz G et al (2010) Hyaluronidase: a review of approved formulations, indications and off-label use in chronic pain management. Expert Opin Biol Ther 10:127–131
Knowles S, Printz M, Kang D et al (2021) Safety of recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20 for subcutaneous drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 18:1–13
Trocchi G, Pirrotta L, Scala E et al (2020) A prospective pilot study to evaluate the use of hyaluronidase in patients with hymenoptera venom allergy. Aesthet Med 6:13–18
Decates T, Kadouch J, Velthuis P et al (2021) Immediate nor delayed type hypersensitivity plays a role in late inflammatory reactions after hyaluronic acid filler injections. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 14:581–589
Yocum RC, Kennard D, Heiner LS (2007) Assessment and implication of the allergic sensitivity to a single dose of recombinant human hyaluronidase injection: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Infus Nurs. 30, https://journals.lww.com/journalofinfusionnursing/Fulltext/2007/09000/Assessment_and_Implication_of_the_Allergic.9.aspx
Rosengren S, Dychter S, Printz M et al (2015) Clinical immunogenicity of rHuPH20, a hyaluronidase enabling subcutaneous drug administration. AAPS J. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-015-9782-0. (Epub ahead of print 13 May 2015)
Jung H (2020) Hyaluronidase: an overview of its properties, applications, and side effects. Arch Plast Surg 47:297–300
Acknowledgments
None
Funding
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guliyeva, G., Huayllani, M.T., Kraft, C. et al. Allergic Complications of Hyaluronidase Injection: Risk Factors, Treatment Strategies, and Recommendations for Management. Aesth Plast Surg 48, 413–439 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03348-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-023-03348-5