Abstract
Background
With the global increase in the use of injectable fillers, more cases with serious adverse events such vision loss are being reported. This article aims to review the cases of hyaluronic acid (HA) filler-related vision loss and to discuss the potential efficacy of hyaluronidase (HYASE) treatment via different given methods.
Methods
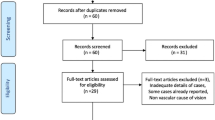
A total of 29 articles presenting 144 cases of HA filler-related vision loss were included in this study.
Results
Most cases of HA filler-related vision impairment were reported from China, followed by Korea. The majority of cases were seen in women. The nose, forehead and glabella were the most commonly injection sites. All cases had vision impairment and nearly all cases were unilateral with immediate onset of visual signs and symptoms. Ophthalmic artery occlusion (OAO) and central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) were the two most commonly involved arterial obstruction patterns featured with a very poor prognosis followed by branch retinal artery occlusion (BRAO), the most favorable involved arterial pattern for a better prognosis. HYASE given subcutaneously and intra-arterially helped with visual recovery to different degrees, while retrobulbar HYASE seemed to be less helpful.
Conclusion
Complications after HA-based filler injection are extremely rare but can cause disastrous visual impairment. HYASE given subcutaneously and intra-arterially helped with visual recovery to different extents, and the efficacy might be reinforced when performed together, while retrobulbar HYASE seemed to be less helpful. However, to accurately access the efficacy of HYASE via different administration methods, further randomized controlled trials are needed.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Thulesen J (2020) Iatrogenic vision loss following aesthetic treatment with hyaluronic acid-containing filler: every injector should be prepared. Dermatol Ther 33(6):e13913. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.13913 (Published Online First: 2020/07/01)
Crowley JS, Kream E, Fabi S et al (2021) Facial rejuvenation with fat grafting and fillers. Aesthet Surg J 41(Suppl 1):S31-s38. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjab014 (Published Online First: 2021/05/19)
Ozturk CN, Li Y, Tung R et al (2013) Complications following injection of soft-tissue fillers. Aesthet Surg J 33(6):862–877. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820x13493638 (Published Online First: 2013/07/05)
Wang Y, Massry G, Holds JB (2021) Complications of periocular dermal fillers. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 29(2):349–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2021.02.001 (Published Online First: 2021/04/29)
Gilbert E, Hui A, Meehan S et al (2012) The basic science of dermal fillers: past and present part II: adverse effects. J Drugs Dermatol 11(9):1069–1077 (Published Online First: 2012/11/09)
Sharma DSC, Lahiri MA (2021) Use of hyaluronidase in plastic surgery: a review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 74(7):1610–1614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2021.03.125 (Published Online First: 2021/05/25)
Park KH, Kim YK, Woo SJ et al (2014) Iatrogenic occlusion of the ophthalmic artery after cosmetic facial filler injections: a national survey by the Korean Retina Society. JAMA Ophthalmol 132(6):714–723. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2013.8204 (Published Online First: 2014/03/29)
Kwon SG, Hong JW, Roh TS et al (2013) Ischemic oculomotor nerve palsy and skin necrosis caused by vascular embolization after hyaluronic acid filler injection: a case report. Ann Plast Surg 71(4):333–334. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0b013e31824f21da (Published Online First:2012/12/04)
Chesnut C (2018) Restoration of visual loss with retrobulbar hyaluronidase injection after hyaluronic acid filler. Dermatol Surg 44(3):435–437. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000001237
Hu XZ, Hu JY, Wu PS et al (2016) Posterior Ciliary Artery Occlusion Caused by Hyaluronic Acid Injections Into the Forehead: A Case Report. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(11):e3124. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000003124 (Published Online First: 2016/03/18)
Zhu GZ, Sun ZS, Liao WX et al (2017) Efficacy of retrobulbar hyaluronidase injection for vision loss resulting from hyaluronic acid filler embolization. Aesthet Surg J 38(1):12–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjw216 (Published Online First: 2017/03/24)
Goodman GJ, Clague MD (2016) A rethink on hyaluronidase injection, intraarterial injection, and blindness: Is there another option for treatment of retinal artery embolism caused by intraarterial injection of hyaluronic acid? Dermatol Surg 42(4):547–549. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000000670
Thanasarnaksorn W, Cotofana S, Rudolph C et al (2018) Severe vision loss caused by cosmetic filler augmentation: case series with review of cause and therapy. J Cosmet Dermatol 17(5):712–718. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12705 (Published Online First: 2018/07/15)
Ramesh S, Fiaschetti D, Goldberg RA (2018) Orbital and ocular ischemic syndrome with blindness after facial filler injection. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 34(4):e108–e110. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000001104 (Published Online First: 2018/03/17)
Sharudin SN, Ismail MF, Mohamad NF et al (2019) Complete recovery of filler-induced visual loss following subcutaneous hyaluronidase injection. Neuroophthalmology 43(2):102–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/01658107.2018.1482358 (Published Online First: 2019/07/18)
Bae IH, Kim MS, Choi H et al (2018) Ischemic oculomotor nerve palsy due to hyaluronic acid filler injection. J Cosmet Dermatol 17(6):1016–1018. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12498 (Published Online First: 2018/04/03)
Kim A, Kim SH, Kim HJ et al (2016) Ophthalmoplegia as a complication of cosmetic facial filler injection. Acta Ophthalmol 94(5):e377–e379. https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.12893 (Published Online First: 2015/09/27)
Lee JI, Kang SJ, Sun H (2017) Skin necrosis with oculomotor nerve palsy due to a hyaluronic acid filler injection. Arch Plast Surg 44(4):340–343. https://doi.org/10.5999/aps.2017.44.4.340 (Published Online First: 2017/07/22)
Shi H, Liang L-l, Cui Z-h (2018) Ophthalmic Artery Occlusion After Cosmetic Facial Filler Injections. JAMA Ophthalmology 136(6):e180764–e180864. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2018.0764
Chen YC, Wu HM, Chen SJ et al (2018) Intra-arterial thrombolytic therapy is not a therapeutic option for filler-related central retinal artery occlusion. Facial Plast Surg 34(3):325–329. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1621730 (Published Online First: 2018/01/30)
Oh BL, Jung C, Park KH et al (2014) Therapeutic intra-arterial hyaluronidase infusion for ophthalmic artery occlusion following cosmetic facial filler (hyaluronic acid) injection. Neuroophthalmology 38(1):39–43. https://doi.org/10.3109/01658107.2013.830134 (Published Online First:2014/01/28)
Wibowo A, Kapoor KM, Philipp-Dormston WG (2019) Reversal of post-filler vision loss and skin ischaemia with high-dose pulsed hyaluronidase injections. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(5):1337–1344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01421-6 (Published Online First:2019/06/27)
Kim YK, Jung C, Woo SJ et al (2015) Cerebral angiographic findings of cosmetic facial filler-related ophthalmic and retinal artery occlusion. J Korean Med Sci 30(12):1847–1855. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.12.1847 (Published Online First: 2015/12/30)
Jolly R, Bhalla M, Zakir R et al (2021) Visual loss from dermal fillers. Eur J Ophthalmol 31(2):NP102–NP105. https://doi.org/10.1177/1120672119855856 (Published Online First: 2019/06/13)
Zhang L, Pan L, Xu H et al (2019) Clinical observations and the anatomical basis of blindness after facial hyaluronic acid injection. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(4):1054–1060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01374-w (Published Online First: 2019/04/23)
Hu Y, Wang Y, Tong Y (2019) Optic perineuritis secondary to hyaluronic acid injections: a case report. BMC Ophthalmol 19(1):241. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-019-1247-2 (Published Online First: 2019/11/30)
Zhang LX, Lai LY, Zhou GW et al (2020) Evaluation of intraarterial thrombolysis in treatment of cosmetic facial filler-related ophthalmic artery occlusion. Plast Reconstr Surg 145(1):42e–50e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000006313 (Published Online First: 2019/12/29)
Zhang L, Luo Z, Li J et al (2021) Endovascular hyaluronidase application through superselective angiography to rescue blindness caused by hyaluronic acid injection. Aesthet Surg J 41(3):344–355. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa036 (Published Online First: 2020/05/14)
Kim BJ, You HJ, Jung I et al (2020) Ophthalmoplegia with skin necrosis after a hyaluronic acid filler injection. J Cosmet Dermatol 19(6):1307–1310. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13403 (Published Online First: 2020/04/14)
Nguyen HH, Tran HTT, Duong QH et al (2021) Significant vision recovery from filler-induced complete blindness with combined intra-arterial injection of hyaluronidase and thrombolytic agents. Aesthet Plast Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02658-w (Published Online First:2021/11/13)
Eldweik L (2021) Orbital infarction syndrome following hyaluronic acid filler rhinoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep 22:101063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajoc.2021.101063 (Published Online First:2021/04/13)
Lee KE, Kim GJ, Sa HS (2021) The clinical spectrum of periorbital vascular complications after facial injection. J Cosmet Dermatol 20(5):1532–1540. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.14019 (Published Online First:2021/02/23)
Wang J, Shen H, Liu T et al (2021) An efficacy and safety study of intra-arterial recanalization of occluded ophthalmic arteries in patients with monocular blindness caused by injection of hyaluronic acid in facial tissues. Aesthet Plast Surg 45(4):1573–1578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02224-4 (Published Online First:2021/03/27)
Xu X, Zhou G, Fu Q et al (2021) Efficacy of intra-arterial thrombolytic therapy for vision loss resulting from hyaluronic acid filler embolization. J Cosmet Dermatol 20(10):3205–3212. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.14111 (Published Online First:2021/04/08)
Davidova P, Muller M, Wenner Y et al (2022) Ophthalmic artery occlusion after glabellar hyaluronic acid filler injection. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep 26:101407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajoc.2022.101407 (Published Online First: 2022/03/05)
Hayreh SS, Kolder HE, Weingeist TA (1980) Central retinal artery occlusion and retinal tolerance time. Ophthalmology 87(1):75–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-6420(80)35283-4 (Published Online First: 1980/01/01)
Kapoor KM, Kapoor P, Heydenrych I et al (2020) Vision loss associated with hyaluronic acid fillers: a systematic review of literature. Aesthet Plast Surg 44(3):929–944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01562-8 (Published Online First: 2019/12/12)
Walker L, Convery C, Davies E et al (2021) Consensus opinion for the management of soft tissue filler induced vision loss. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 14(12):E84-e94 (Published Online First: 2022/02/01)
Goodman GJ, Magnusson MR, Callan P et al (2020) A consensus on minimizing the risk of hyaluronic acid embolic visual loss and suggestions for immediate bedside management. Aesthet Surg J 40(9):1009–1021. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjz312 (Published Online First: 2019/11/07)
Cotofana S, Schenck TL, Trevidic P et al (2015) Midface: clinical anatomy and regional approaches with injectable fillers. Plast Reconstr Surg 136(5 Suppl):219s-s234. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000001837 (Published Online First: 2015/10/07)
Sykes JM, Cotofana S, Trevidic P et al (2015) Upper face: clinical anatomy and regional approaches with injectable fillers. Plast Reconstr Surg 136(5 Suppl):204s-s218. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000001830 (Published Online First: 2015/10/07)
van Loghem J, Sattler S, Casabona G et al (2021) Consensus on the use of hyaluronic acid fillers from the cohesive polydensified matrix range: best practice in specific facial indications. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 14:1175–1199. https://doi.org/10.2147/ccid.S311017 (Published Online First: 2021/09/17)
Jones DH, Fitzgerald R, Cox SE et al (2021) Preventing and treating adverse events of injectable fillers: evidence-based recommendations from the American society for dermatologic surgery multidisciplinary task force. Dermatol Surg 47(2):214–226. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000002921 (Published Online First: 2021/02/06)
DeLorenzi C (2014) Complications of injectable fillers, part 2: vascular complications. Aesthet Surg J 34(4):584–600. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820x14525035 (Published Online First: 2014/04/03)
King M, Convery C, Davies E (2018) This month’s guideline: the use of hyaluronidase in aesthetic practice (v2.4). J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 11(6):E61-e68 (Published Online First: 2018/06/27)
Cavallini M, Gazzola R, Metalla M et al (2013) The role of hyaluronidase in the treatment of complications from hyaluronic acid dermal fillers. Aesthet Surg J 33(8):1167–1174. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820x13511970 (Published Online First: 2013/11/08)
DeLorenzi C (2017) New high dose pulsed hyaluronidase protocol for hyaluronic acid filler vascular adverse events. Aesthet Surg J 37(7):814–825. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjw251 (Published Online First: 2017/03/24)
Li J, Xu Y, Wang Y et al (2019) The role of hyaluronidase for the skin necrosis caused by hyaluronic acid injection-induced embolism: a rabbit auricular model study. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(5):1362–1370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01398-2 (Published Online First: 2019/05/30)
Lee W, Oh W, Oh SM et al (2020) Comparative effectiveness of different interventions of perivascular hyaluronidase. Plast Reconstr Surg 145(4):957–964. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000006639 (Published Online First: 2020/03/30)
Kim DW, Yoon ES, Ji YH et al (2011) Vascular complications of hyaluronic acid fillers and the role of hyaluronidase in management. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 64(12):1590–1595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2011.07.013 (Published Online First: 2011/08/03)
Humzah MD, Ataullah S, Chiang C et al (2019) The treatment of hyaluronic acid aesthetic interventional induced visual loss (AIIVL): a consensus on practical guidance. J Cosmet Dermatol 18(1):71–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12672 (Published Online First: 2018/06/10)
Rauso R, Zerbinati N, Fragola R et al (2021) Transvascular hydrolysis of hyaluronic acid filler with hyaluronidase: an ex vivo study. Dermatol Surg 47(3):370–372. https://doi.org/10.1097/DSS.0000000000002773 (Published Online First: 2020/09/16)
Baley-Spindel I, Villasenor-Villalpando E, Marquez-Espriella C et al (2020) Perivascular hyaluronidase with alteplase as treatment for hyaluronic acid thrombosis. Aesthet Surg J 40(5):551–559. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjz101 (Published Online First: 2019/04/09)
Hurkal O, Sibar S, Cenetoglu S et al (2021) Arterial occlusion after hyaluronic acid injection: treatment with hyaluronidase and streptokinase. Ann Plast Surg 87(6):e137–e144. https://doi.org/10.1097/SAP.0000000000002962 (Published Online First: 2021/08/03)
Chen J, Ruan J, Wang W et al (2021) Superselective arterial hyaluronidase thrombolysis is not an effective treatment for hyaluronic acid-induced retinal artery occlusion: study in a rabbit model. Plast Reconstr Surg 147(1):69–75. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000007449 (Published Online First: 2020/12/29)
Adulkar N, Cheng C, Lee L et al (2019) An in vitro model assessing the penetration of hyaluronidase through optic nerve dura for management of hyaluronic acid facial filler embolism. Plast Reconstr Surg 144(1):43e–47e. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000005714 (Published Online First: 2019/06/28)
Paap MK, Milman T, Ugradar S et al (2019) Assessing retrobulbar hyaluronidase as a treatment for filler-induced blindness in a cadaver model. Plast Reconstr Surg 144(2):315–320. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000005806 (Published Online First: 2019/07/28)
Hwang CJ, Mustak H, Gupta AA et al (2019) Role of retrobulbar hyaluronidase in filler-associated blindness: evaluation of fundus perfusion and electroretinogram readings in an animal model. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 35(1):33–37. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000001132 (Published Online First: 2018/06/08)
Surek CC, Said SA, Perry JD et al (2019) Retrobulbar injection for hyaluronic acid gel filler-induced blindness: a review of efficacy and technique. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(4):1034–1040. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01388-4 (Published Online First:2019/05/09)
Joganathan V, Shah-Desai S (2020) Awareness of management of hyaluronic acid induced visual loss: a British National Survey. Eye (Lond) 34(12):2280–2283. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-020-0810-7 (Published Online First: 2020/02/19)
Carruthers JDA, Fagien S, Rohrich RJ et al (2014) Blindness caused by cosmetic filler injection: a review of cause and therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(6):1197–1201. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000000754 (Published Online First: 2014/11/22)
D’Amico RA, Saltz R, Rohrich RJ et al (2008) Risks and opportunities for plastic surgeons in a widening cosmetic medicine market: future demand, consumer preferences, and trends in practitioners’ services. Plast Reconstr Surg 121(5):1787–1792. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e31816c3c49 (Published Online First: 2008/05/06)
Cotofana S, Velthuis PJ, Alfertshofer M et al (2021) The change of plane of the supratrochlear and supraorbital arteries in the forehead—an ultrasound-based investigation. Aesthet Surg J 41(11):Np1589-np98. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa421 (Published Online First: 2021/03/03)
Velthuis PJ, Jansen O, Schelke LW et al (2021) A guide to doppler ultrasound analysis of the face in cosmetic medicine. Part 1: standard positions. Aesthet Surg J 41(11):Np621-np32. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa410 (Published Online First: 2021/05/07)
Velthuis PJ, Jansen O, Schelke LW et al (2021) A guide to doppler ultrasound analysis of the face in cosmetic medicine. Part 2: vascular mapping. Aesthet Surg J 41(11):Np1633-np44. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjaa411 (Published Online First: 2021/05/07)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights, or Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, H., Kou, W., Yang, Y. et al. Administration Method and Potential Efficacy of Hyaluronidase for Hyaluronic Acid Filler-Related Vision Loss: A Systematic Review. Aesth Plast Surg 48, 709–718 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-03215-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-03215-9