Abstract
Background
This study was conducted to see if better scar results could be obtained by administering botulinum neurotoxin type A (BoNTA) injection and W-plasty incision for preventing rhytidectomy scar.
Methods
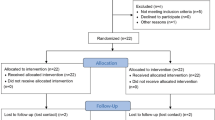
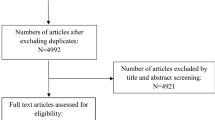
All patients underwent extended deep-plane rhytidectomy in two groups. Group 1 had a straight incision line, and BoNTA was not given. Group 2 was injected with W-plasty and BoNTA. Photos were taken before surgery and twelve months after surgery. Two aesthetic surgeons analyzed the results using MSS, MSRS, and SBSES. Interrater reliability was measured using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
Results
Forty-nine patients were included in the study. Group 1 (Straight incision, No BoNTA) had 26, and Group 2 (W-plasty, BoNTA) had 23 patients. The interrater reliability in Group 1 was excellent for MSS (ICC, 0.957 [0.904–0.981]), and good in two of the interrater reliability measures (ICCs, 0.897 [0.769-0.954] for MSRS, and 0.821 [0.605–0.919] for SBSES). Interrater reliability in Group 2 was good in two out of three measures (ICCs, 0.760 [0.423–0.899] for MSS, 0.746 [0.392–0.893] for MSRS, and 0.851 [0.654–0.937] for SBSES). There was a significant statistical difference between Group 1 and Group 2, showing that Group 2 has superior outcomes (MSS, 6.596 ± 1.569 vs. 5.435 ± 0.590, P = 0.001; MSRS, 4.346 ± 0.967 vs. 3.652 ± 0.510, P = 0.003; SBSES, 3.788 ± 0.695 vs. 4.261 ± 0.541, P = 0.012).
Conclusions
Analyzed by three dedicated scar assessments, better results were obtained through combining W-plasty and BoNTA injections, so it is expected to be a useful method for improving scars.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.




Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Tanna N, Lindsey WH (2007) Review of 1,000 consecutive short-scar rhytidectomies. Dermatol Surg 34(2):196–202. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2007.34037.x.Epub (PMID: 18093201)
Jones BM, Grover R (2004) Reducing complications in cervicofacial rhytidectomy by tumescent infiltration: a comparative trial evaluating 678 consecutive face lifts. Plast Reconstr Surg 113(1):398–403. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000097297.89136.8D (PMID: 14707665)
Griffin JE, Jo C (2007) Complications after superficial plane cervicofacial rhytidectomy: a retrospective analysis of 178 consecutive facelifts and review of the literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65(11):2227–2234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2006.10.075 (PMID: 17954318)
Nouri K, Vidulich K, Rivas MP (2006) Lasers for scars: a review. J Cosmet Dermatol 5:14–22
Yun JS, Choi YJ, Kim WS, Lee GY (2011) Prevention of thyroidectomy scars in Asian adults using a 532-nm potassium titanyl phosphate laser. Dermatol Surg 37(12):1747–1753. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02128.x (Epub 2011 Aug 24 PMID: 21883646)
Min JH, Park KH, Choi HL, Park JS, Lee JH, Kim H, Lee BK, Lee DH, Lee TG (2017) Usefulness of direct W-plasty application to wound debridement for minimizing scar formation in the ED. Am J Emerg Med 35(12):1804–1809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2017.05.055 (Epub 2017 May 29 PMID: 28587949)
Chambers A (2019) Effects of botulinum toxin a observed during early scar formation following rhytidectomy: controlled, double-blinded pilot study. The American J Cosmet Surg 36(2):78–84. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748806818794528
Wilson AM (2006) Use of botulinum toxin type a to prevent widening of facial scars. Plast Reconstr Surg 117(6):1758–1766. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000209944.45949.d1 (PMID: 16651948)
Ziade M, Domergue S, Batifol D, Jreige R, Sebbane M, Goudot P, Yachouh J (2013) Use of botulinum toxin type A to improve treatment of facial wounds: a prospective randomised study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 66(2):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2012.09.012 (Epub 2012 Oct 25 PMID: 23102873)
Chen H, Pan W, Zhang J, Cheng H, Tan Q (2018) The application of W-plasty combined Botox-A injection in treating sunk scar on the face. Medicine (Baltimore) 97(30):e11427. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000011427 (PMID:30045264;PMCID:PMC6078721)
Beausang E, Floyd H, Dunn KW, Orton CI, Ferguson MW (1998) A new quantitative scale for clinical scar assessment. Plast Reconstr Surg 102(6):1954–1961. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199811000-00022 (PMID: 9810991)
Mecott GA, Finnerty CC, Herndon DN, Al-Mousawi AM, Branski LK, Hegde S, Kraft R, Williams FN, Maldonado SA, Rivero HG, Rodriguez-Escobar N, Jeschke MG (2015) Reliable scar scoring system to assess photographs of burn patients. Journal of Surgical Research 199(2):688–697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2014.10.055 (PMID: 26092214; PMCID: PMC4508235)
Singer AJ, Arora B, Dagum A, Valentine S, Hollander JE (2007) Development and validation of a novel scar evaluation scale. Plast Reconstr Surg 120(7):1892–1897. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000287275.15511.10 (PMID: 18090752)
Koo TK, Li MY (2016) A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J Chiropr Med 15(2):155-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Erratum in: J Chiropr Med. 2017 Dec;16(4):346. PMID: 27330520; PMCID: PMC4913118
Jacono AA, Bryant LM, Ahmedli NN (2019) A novel extended deep plane facelift technique for jawline rejuvenation and volumization. Aesthet Surg J 39(12):1265–1281. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjy292 (PMID: 30418482)
Shirakabe Y, Suzuki Y, Lam SM (2003) A new paradigm for the aging Asian face. Aesthetic Plast Surg 27(5):397–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-003-2099-x (Epub 2003 Dec 4 PMID: 14648062)
Shirakabe Y (1988) The Oriental aging face: an evaluation of a decade of experience with the triangular SMAS flap technique in facelifting. Aesthetic Plast Surg 12(1):25–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570381 (PMID: 3376781)
Rodgers BJ, Williams EF, Hove CR (2001) W-plasty and geometric broken line closure. Facial Plast Surg 17(4):239–244. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-18829 (PMID: 11735056)
Tanaka A, Hatoko M, Kuwahara M, Yurugi S, Iioka H, Niitsuma K (2002) Evaluation of scars after harvest of the temporoparietal fascial flap depending on the design of the skin incision. Ann Plast Surg 48(4):376–380. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-200204000-00007 (PMID: 12068219)
Jauregui EJ, Tummala N, Seth R, Arron S, Neuhaus I, Yu S, Grekin R, Knott PD (2016) Comparison of w-plasty vs traditional straight-line techniques for primary paramedian forehead flap donor site closure. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 18(4):258–262. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2016.0099 (PMID: 27031499)
Ratnarathorn M, Petukhova TA, Armstrong AW, Wang AS, King TH, Eisen DB (2016) Perceptions of aesthetic outcome of linear vs multiple z-plasty scars in a national survey. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 18(4):263–267. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2016.0107 (PMID: 27054523)
Shockley WW (2011) Scar revision techniques: z-plasty, w-plasty, and geometric broken line closure. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 19(3):455–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2011.06.002 (PMID: 21856534)
Park SS (1998) Scar Revision Through W-Plasty In: Wang TD, ed. Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America. Vol 6 Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co; 157-161
Gabriel A (2015) Wound Healing and Growth Factors. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/129816-overview. Published 2015. Accessed August 2, 2018
Patrick E S (2016) Skin Wound Healing. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/884594-overview. Published 2016. Accessed August 2, 2018
Sullivan T, Smith J, Kermode J, McIver E, Courtemanche DJ (1990) Rating the burn scar. J Burn Care Rehabil 11(3):256–260. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004630-199005000-00014 (PMID: 2373734)
Yeong EK, Mann R, Engrav LH, Goldberg M, Cain V, Costa B, Moore M, Nakamura D, Lee J (1997) Improved burn scar assessment with use of a new scar-rating scale. J Burn Care Rehabil 18(4):353–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004630-199707000-00014 (PMID: 9261704)
Agrawal K, Shrotriya R, Thakre M, Puri V (2021) W-plasty: an important tool for cross-hatch marks. Indian J Plastic Surg 54(02):246–247. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1729664 (PMCID: PMC8257312)
Goutos I, Yousif AH, Ogawa R (2019) W-plasty in scar revision: geometrical considerations and suggestions for site-specific design modifications. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 7(4):e2179. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002179 (PMID:31321181;PMCID:PMC6554158)
Yue S, Ju M, Su Z (2022) A systematic review and meta-analysis: botulinum toxin a effect on postoperative facial scar prevention. Aesthetic Plast Surg 46(1):395–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02596-7 (Epub 2021 Oct 5 PMID: 34609526)
Qiao Z, Yang H, Jin L, Li S, Wang X (2021) The efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin injections in preventing postoperative scars and improving scar quality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast Surg 45(5):2350–2362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02196-5 (Epub 2021 Mar 5 PMID: 33674930)
WangChen DB (2021) Botulinum toxin type a injection for mammoplasty and abdominoplasty scar management: a split-scar double-blinded randomized controlled study. Aesthetic Plast Surg 45(5):2535–2536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02218-2 (Epub 2021 Mar 17 PMID: 33733332)
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to the reviewers of this article for recommendations that have improved it. Special thanks to my mentor, Dr. Jae-Hyun Park, my brother, Dr. Joel Kulesza, and my son, Mr. Joon Han, for their assistance in finalizing this work.
Funding
The author received no financial support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Ch. Combination of W-plasty and Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A Injection for Preventing Rhytidectomy Scar in Asians. Aesth Plast Surg 47, 181–188 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-02970-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-02970-z