Abstract
Background
Obesity is considered a condition of systemic chronic inflammation. Under this condition, adipose tissue macrophages switch from an M2 (anti-inflammatory) activation pattern to an M1 (proinflammatory) activation pattern.
Objective
The study aimed to verify the profile of skin macrophage activation after bariatric surgery as well as the role of MMP-1 in extracellular tissue remodeling.
Methods
This is a prospective, controlled and comparative study with 20 individuals split into two groups according to their skin condition: post-bariatric and eutrophic patients. Histological and morphometric analyses based on hematoxylin-eosin, picrosirius red (collagen), orcein (elastic fiber systems), and alcian blue (mast cells)-stained sections and immunohistochemical analysis (CD68, iNOS, and mannose receptor) for macrophages and metalloproteinase-1 were performed.
Results
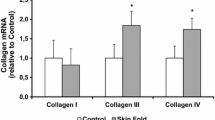
Post-bariatric skin showed an increase in inflammation, angiogenesis, CD68, M1 macrophages (P< 0.001), and mast cells (P< 0.01); a decrease in M2 macrophages (P< 0.01); and a significant decrease in the collagen fiber network (P< 0.001). MMP-1 was increased in the papillary dermis of post-bariatric skin and decreased in the epidermis compared to eutrophic skin (P< 0.05).
Conclusion
This study shows that post-bariatric skin maintains inflammatory characteristics for two years. Mast cells and M1 macrophages maintain and enhance the remodeling of the dermal extracellular matrix initiated during obesity in part due to the presence of MMP-1 in the papillary dermis.
EBM Level IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266 .



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kelly T, Yang W, Chen C-S, Reynolds K, He J (2008) Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes 32:1432–1437. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.102
Johnson AR, Milner JJ, Makowski L (2012) The inflammation highway: metabolism accelerates inflammatory traffic in obesity. Immunol Rev 249:218–238
Lumeng CN, Saltiel AR (2011) Inflammatory links between obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 121:2111–2117
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr (2003) Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 112:1796–1808
Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR (2007) Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest 117:175–184
Padwal R, Klarenbach S, Wiebe N, Birch D, Karmali S, Manns B, Hazel M, Sharma AM, Tonelli M (2011) Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials. Obes Rev 12:602–621
O’Brien PE, Hindle A, Brennan L, Skinner S, Burton P, Smith A, Crosthwaite G, Brown W (2019) Long-term outcomes after bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of weight loss at 10 or more years for all bariatric procedures and a single-centre review of 20-year outcomes after adjustable gastric banding. Obes Surg 29:3–14
Magkos F, Fraterrigo G, Yoshino J, Luecking C, Kirbach K, Kelly SC, Las Fuentes L, He S, Okunade AL, Patterson BW, Samuel Klein S (2016) Effects of moderate and subsequent progressive weight loss on metabolic function and adipose tissue biology in humans with obesity. Cell Metab 23:591–601
Hafida S, Mirshahi T, Nikolajczyk BS (2016) The impact of bariatric surgery on inflammation: quenching the fire of obesity? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 23:373–378
Cancello R, Zulian A, Gentilini D, Mencarelli M, Barba AD, Maffei M, Vitti P, Invitti C, Liuzzi A, Di Blasio AM (2013) Permanence of molecular features of obesity in subcutaneous adipose tissue of ex-obese subjects. Int J Obes 37:867–873
Caslin HL, Bhanot M, Bolus WR, Alyssa H, Hasty AH (2020) Adipose tissue macrophages: unique polarization and bioenergetics in obesity. Immunol Rev 295:101–113
Cummings DE, Overduin J, Foster-Schubert KE (2004) Gastric bypass for obesity: mechanisms of weight loss and diabetes resolution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2608–2615
Cancello R, Henegar C, Viguerie N, Taleb S, Poitou C, Rouault C, Coupaye M, Pelloux V, Hugol D, Bouillot J-L, Bouloumié A, Barbatelli G, Cinti S, Svensson P-A, Barsh GS, Zucker J-D, Basdevant A, Langin D, Clément K (2005) Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes 54:2277–2286
Aron-Wisnewsky J, Tordjman J, Poitou C, Darakhshan F, Hugol D, Basdevant A, Aissat A, Guerre-Millo M, Clément K (2009) Human adipose tissue macrophages: M1 and M2 cell surface markers in subcutaneous and omental depots and after weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4619–4623
Liu Y, Aron-Wisnewsky J, Marcelin G, Genser L, Le Naour G, Torcivia A, Bauvois B, Bouchet S, Pelloux V, Sasso M, Miette V, Tordjman J, Karine Clément K (2016) Accumulation and changes in composition of collagens in subcutaneous adipose tissue after bariatric surgery. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101:293–304
Martinez FO, Sica A, Mantovani A, Locati M (2008) Macrophage activation and polarization. Front Biosci 13:453–461. https://doi.org/10.2741/2692
Gordon S, Martinez FO (2010) Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity 32:593–604
Liu J, Divoux A, Sun J, Zhang J, Clément K, Glickman JN, Sukhova GK, Wolters PJ, Du J, Gorgun CZ, Doria A, Libby P, Blumberg RS, Kahn BB, Hotamisligil GS, Guo-Ping Shi G-P (2009) Genetic deficiency and pharmacological stabilization of mast cells reduce diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Nat Med 15:940–945
Altintas MM, Azad A, Nayer B, Contreras G, Zaias J, Faul C, Reiser J, Ali Nayer A (2011) Mast cells, macrophages, and crown-like structures distinguish subcutaneous from visceral fat in mice. J Lipid Res 52:480–488
Divoux A, Moutel S, Poitou C, Lacasa D, Veyrie N, Aissat A, Arock M, Guerre-Millo M, Clément K (2012) Mast cells in human adipose tissue: link with morbid obesity, inflammatory status, and diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:E1677–E1685. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-1532 (Epub 2012 Jun 28)
Botchkarev VA, Eichmüller S, Peters EM, Pietsch P, Johansson O, Maurer M, Paus R, R, (1997) A simple immunofluorescence technique for simultaneous visualization of mast cells and nerve fibers reveals selectivity and hair cycle-dependent changes in mast cell–nerve fiber contacts in murine Skin. Arch Dermatol Res 289:292–302
Komi DEA, Wöhrl S, Bielory L (2020) Mast cell biology at molecular level: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 58:342–365
Gri G, Frossi B, D’Inca F, Danelli L, Betto E, Mion F, Sibilano R, Pucillo C (2012) Mast cell: an emerging partner in immune interaction. Front Immunol 3:120. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00120
Voss M, Kotrba J, Gaffal E, Katsoulis-Dimitriou K, Dudec A (2021) Mast Cells in the skin: defenders of integrity or offenders in inflammation? Int J Mol Sci 22:4589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094589
Iddamalgoda A, Le QT, Ito K, Tanaka K, Kojima H, Hiroshi Kido H (2008) Mast cell tryptase and photoaging: possible involvement in the degradation of extra cellular matrix and basement membrane proteins. Arch Dermatol Res 300:S69–S76
Di Girolamo N, Wakefield D (2000) In vitro and in vivo expression of interstitial collagenase/MMP-1 by human mast cells. Dev Immunol 7:131–142
Johnson JL, Jackson CL, Angelini GD, George SJ (1998) Activation of matrix-degrading metalloproteinases by mast cell proteases in atherosclerotic plaques. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18:1707–1715
Lijnen HR, Maquoi E, Holvoet P, Mertens A, Lupu F, Morange P, Alessi MC, Juhan-Vague I (2001) Adipose tissue expression of gelatinases in mouse models of obesity. Thromb Haemost 85:1111–1116
Maquoi E, Munaut C, Colige A, Collen D, Lijnen HR (2002) Modulation of adipose tissue expression of murine matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors with obesity. Diabetes 51:1093–1101
Chavey C, Mari B, Monthouel M-N, Bonnafous S, Anglard P, Van Obberghen E, Tartare-Deckert S (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases are differentially expressed in adipose tissue during obesity and modulate adipocyte differentiation. J Biol Chem 278:11888–11896
Bouloumie A, Sengenès C, Portolan G, Galitzky J, Lafontan M, M, (2001) Adipocyte produces matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9: involvement in adipose differentiation. Diabetes 50:2080–2086
Laimer M, Kaser S, Kranebitter M, Sandhofer A, Mühlmann G, Schwelberger H, Weiss H, Patsch JR, Ebenbichler CF (2005) Effect of pronounced weight loss on the nontraditional cardiovascular risk marker matrix metalloproteinase-9 in middle-aged morbidly obese women. Int J Obes 29:498–501
Ress C, Tschoner A, Ciardi C, Laimer MW, Engl JW, Sturm W, Weiss H, Tilg H, Ebenbichler CF, Patsch JR, Kaser S (2010) Influence of significant weight loss on serum matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-7 levels. Eur Cytokine Netw 21:65–70
Lee YJ, Heo Y-S, Park HS, Lee SH, Lee SK, Jang YJ (2014) Serum SPARC and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase-9 concentrations after bariatric surgery in obese adults. Obes Surg 24:604–610
Enser M, Avery NC (1984) Mechanical and chemical properties of the Skin and its collagen from lean and obese hyperglycaemic (ob/ob) mice. Diabetologia 27:44–49
Ibuki A, Akase T, Nagase T, Minematsu T, Nakagami G, Horii M, Sagara H, Komeda T, Kobayashi M, Shimada T, Aburada M, Yoshimura K, Sugama J, Sanada H (2012) Skin fragility in obese diabetic mice: possible involvement of elevated oxidative stress and upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Exp Dermatol 21:178–183
Catalan V, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Rodríguez A, Ramírez B, Silva C, Rotellar F, Gil MJ, Cienfuegos JA, Salvador J, Frühbeck G (2009) Increased adipose tissue expression of lipocalin-2 in obesity is related to inflammation and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase-9 activities in humans. J Mol Med 8:803–813
Makihara H, Hidaka M, Sakai Y, Horie Y, Mitsui H, Ohashi K, Goshima Y, Akase T (2017) Reduction and fragmentation of elastic fibers in the Skin of obese mice is associated with altered mRNA expression levels of fibrillin-1 and neprilysin. Connect Tissue Res 58:479–486
Prist IH, Salles AG, Lima TM, Modolin MLA, Gemperli R, Souza HP (2017) Extracellular matrix remodeling derangement in ex-obese patients. Mol Cell Biochem 425:1–7
Brennan M, Bhatti H, Nerusu K, Bhagavathula N, Kang S, Fisher GJ, Varani J, Voorhees JJ (2003) Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is the major collagenolytic enzyme responsible for collagen damage in UV-irradiated human Skin. Photochem Photobiol 78:43–48
Vaalamo M, Mattila L, Johansson N, Kariniemi AL, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Kähäri VM, Saarialho-Kere U, U, (1997) Distinct populations of stromal cells express collagenase-3 (MMP-13) and collagenase-1(MMP-1) in chronic ulcers but not in normally healing wounds. J Invest Dermatol 109:96–101
Solomonov I, Zehorai E, Talmi-Frank D, Wolf SG, Shainskaya A, Zhuravlev A, Kartvelishvily E, Visse R, Levin Y, Kampf N, Jaitin DA, David E, Amit I, Nagase H, Sagi I (2016) Distinct biological events generated by ECM proteolysis by two homologous collagenases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:10884–10889
Ågren MS, Schnabel R, Christensen LH, Mirastschijski U (2015) Tumor necrosis factor-α-accelerated degradation of type I collagen in human Skin is associated with elevated matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 and MMP-3 ex vivo. Eur J Cell Biol 94:12–21
Xie Y, Mustafa A, Yerzhan A, Merzhakupova D, Yerlan P, Orakov AN, AN, Wang X, Huang Y, Miao L, (2017) Nuclear matrix metalloproteinases: functions resemble the evolution from the intracellular to the extracellular compartment. Cell Death Discov. 3:17036. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2017.36
Si-Tayeb K, Monvoisin A, Mazzocco C, Lepreux S, Decossas M, Cubel G, Taras D, Blanc J-F, Robinson DR, Rosenbaum J (2006) Matrix metalloproteinase 3 is present in the cell nucleus and is involved in apoptosis. Am J Pathol 169:1390–1401
Limb GA, Matter K, Murphy G, Cambrey AD, Bishop PN, Morris GE, Khaw PT (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase-1 associates with intracellular organelles and confers resistance to lamin A/C degradation during apoptosis. Am J Pathol 166:1555–15563
Sami K, Elshahat A, Moussa M, Abbas A, Amr Mahmoud A (2015) Image analyzer study of the skin in patients with morbid obesity and massive weight loss. Eplasty 15(e4):2015
Light D, Arvanitis GM, Abramson D, Glasberg SB (2010) Effect of weight loss after bariatric surgery on skin and the extracellular matrix. Plast Reconstr Surg 125:343–351
Orpheu SC, Coltro PS, Scopel GP, Gomez DS, Rodrigues CJ, Modolin MLA, Faintuch J, Gemperli R, Ferreira MC (2010) Collagen and elastic content of abdominal skin after surgical weight loss. Obes Surg 20:480–486
Rocha RI, Cintra Jr W, Modolin MLA, Takahashi GG, Elia TEG, Caldini ETEG, Gemperli https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33145720/—affiliation-3 R (2021). Skin changes due to massive weight loss: histological changes and the causes of the limited results of contouring surgeries. Obes Surg 31:1505–1513
Veiga DF, Bussolaro RA, Kobayashi EY, Medeiros VP, Martins JRM, Garcia EB, Novo NF, Nader HB, Ferreira LM (2011) Glycosaminoglycans of abdominal skin after massive weight loss in post-bariatric female patients. Obes Surg 21:774–782
Ezure T, Amano S (2009) Increased subcutaneous adipose tissue impairs dermal function in diet-induced obese mice. Exp Dermatol 19:878–882
Mori S, Shiraishi A, Epplen K, Butcher D, Murase D, Yasuda Y, Takatoshi Murase T (2017) Characterization of skin function associated with obesity and specific correlation to local/systemic parameters in American women. Lipids Health Dis 16:214. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-017-0608-1
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM (1993) Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259:87–91
Mihara M, Moriya Y, Ohsugi Y (1996) IL-6-soluble IL-6 receptor complex inhibits the proliferation of dermal fibroblasts. Int J Immunopharmacol 18:89–94
Nettelhoff L, Grimm S, Jacobs C, Walter C, C, Pabst AM, Goldschmitt J, H Wehrbein H, (2016) Influence of mechanical compression on human periodontal ligament fibroblasts and osteoblasts. Clin Oral Investig 20:621–629
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa para o SUS: gestão compartilhada. Grant Number: E-26/110.280/2014 (CMT)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Ethical and Research Committee Board under number 1,884,612 in January 2017. The study adhered to the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki (2013).
Informed Consent
All procedures were performed with adequate understanding and written consent of the subjects.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amaral, C., da Costa, J.R., Costa, M.O. et al. M1 Polarized Macrophages Persist in Skin of Post-Bariatric Patients after 2 Years. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 287–296 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02649-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02649-x