Abstract
Background
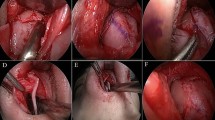
Tip plasty is the most important step of rhinoplasty. To achieve symmetrical cartilages with ideal tip rotation, projection and supratip break many techniques were defined. Besides suture techniques, tip grafts still maintain their importance and widely used among surgeons. However, graft visibility and distortion are the main drawbacks of this technique. In this study double-layered lateral crural perichondrial flap technique was introduced to prevent graft visibility and distortion as a novel technique.
Methods
A total of 16 patients who underwent rhinoplasty with this novel technique were enrolled in this retrospective study. Patient satisfaction was assessed with Rhinoplasty Outcome Evaluation Questionnaire (ROE-Q). Graft visibility and asymmetry of tip defining point as an indicator of graft distortion were evaluated by two independent Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic surgeons. Pre and postoperative photographs were taken and used for evaluation. A three-point Likert scale was used for assessment. Cohen’s Kappa statistic and percent agreement test were used to test inter-rater reliability
Results
The mean follow-up time was 15 months (ranging between 12 and 19 months). According to the ROE-Q score, the mean total preoperative score was 6,25 and the mean total postoperative score was 18,06 (p<0,05). No or minimal evident graft visibility and asymmetry of tip defining point was observed in 12 patients and 10 patients, respectively. Mild evident graft visibility was observed in only 1 patient with thin skin. Severe evident graft visibility or asymmetry of tip defining point was not observed in none of the patients.
Conclusion
The double-layer crural perichondrial flap was an effective and sufficient method for preventing graft visibility and graft distortion. Features like easy and fast flap elevation, no additional comorbidity, being autologous tissue and sufficient flap length and thickness make this technique valuable and useful.
Level of Evidence V
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toriumi DM (2020) Nasal tip contouring: anatomic basis for management. Facial Plast Surg Aesthet Med. 22(1):10–24. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpsam.2019.29006.tor
Xia TY, Punjabi A, Oh JH, Wee C, Guyuron B (2020) Updated dynamics of rhinoplasty: a review of the literature and comprehensive list of the findings. Aesthetic Plast Surg 44(3):904–909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01619-z
Moyer JS (2018) Dissatisfaction with nasal tip shape: secondary tip maneuvers. Facial Plast Surg 34(3):278–286. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1653988
Christophel JJ, Park SS (2012) Structural support and dynamics at the tip. Facial Plast Surg 28(2):145–151. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1313366
Castro-Govea Y, del Campo AF, Chacón-Martínez H, Pérez-Porras S, Vallejo-Estrella RO, Cervantes-Kardasch V (2009) A procedure to prevent cephalic rotation of cartilage grafts in the nasal tip. Aesthet Surg J 29(2):98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asj.2009.01.017
Nitin Chauhan MD, Sardesai Maya G, MD, Andrew E. Burchard, MD, David A. F. Ellis, MD. (2010) Nasal tip refinement: analysis of surgical technique, efficacy, and secondary effect of skin thickness. Aesthetic Surgery Journal 30(1):39–43. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820X09360694
Jang YJ, Kim SH (2018) Tip grafting for the Asian nose. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 26(3):343–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2018.03.008
Cingi C, Bayar Muluk N, Winkler A, Thomas JR (2018) Nasal Tip Grafts. J Craniofac Surg. 29(7):1914–1921. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000005044
Lee M, Guyuron B (2016) Dynamics of the Subdomal Graft. Plast Reconstr Surg 137(6):940e–945e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002225
Sheen JH (1993) Tip graft: a 20-year retrospective. Plast Reconstr Surg 91(1):48–63. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199301000-00007
Peck GC (1983) The onlay graft for nasal tip projection. Plast Reconstr Surg 71(1):27–39. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198301000-00007
Daniel RK (2009) Tip Refinement Grafts: The Designer Tip. Aesthet Surg J 29(6):528–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asj.2009.09.013
Patrocínio TG, Patrocínio LG, Patrocínio JA (2018) The protection of augmented tip (PAT) flap technique for tip camouflage. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 20(4):326–327. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2017.2459
Farrior EH, Ballert JA (2012) Nuances of the nasal tip: rhinoplasty of the thin-skinned nose. Facial Plast Surg 28(2):171–176. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1309296 (Epub 2012 May 6 PMID: 22562566)
Gruber RP, Grover S (1999) The anatomic tip graft for nasal augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 103(6):1744–1758
Gryskiewicz JM (2005) Waste not, want not: the use of AlloDerm in secondary rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 116(7):1999–2004. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000191180.77028.7a
Collawn SS, Fix RJ, Moore JR, Vasconez LO (1997) Nasal cartilage grafts: more than a decade of experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 100(6):1547–1552. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199711000-00027
Lee KH (2016) Infection in the nasal tip caused by acellular dermal matrix. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 3(12):e581. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000000573
Choi JY (2020) Complications of alloplast rhinoplasty and their management: a comprehensive review. Facial Plast Surg 36(5):517–527. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1717082
Heidari MB, Rasti M, Nadri S, Roozbehani A, FarhangFallah A, Mahmoudvand H (2020) Comparison between wrapping dice cartilage with temporal fascia and wrapping in alloderm for dorsal nasal augmentation. World J Plast Surg. 9(2):160–165. https://doi.org/10.29252/wjps.9.2.160
Sherris DA, Oriel BS (2011) Human acellular dermal matrix grafts for rhinoplasty. Aesthet Surg J 31(7 Suppl):95S-100S. https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820X11418200
Gryskiewicz JM (2008) dorsal augmentation with alloderm. Semin Plast Surg 22(2):90–103. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1063568
Gryskiewicz JM, Rohrich RJ, Reagan BJ (2001) The use of alloderm for the correction of nasal contour deformities. Plast Reconstr Surg 107(2):561–571. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-200102000-00040
Karaaltin MV, Batioglu-Karaaltin A, Orhan KS, Demirel T, Guldiken Y (2012) Autologous fascia lata graft for contour restoration and camouflage in tertiary rhinoplasty. J Craniofac Surg 23(3):719–723. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0b013e31824dbb92
Kosins AM (2017) Comprehensive diagnosis and planning for the difficult rhinoplasty patient: applications in ultrasonography and treatment of the soft-tissue envelope. Facial Plast Surg 33(5):509–518. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1606639 (Epub 2017 Sep 29 PMID: 28962057)
Obagi ZE (2014) The Art of Skin Health: Restoration and Rejuvenation, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL
Alsarraf R (2000) Outcomes research in facial plastic surgery: a review and new directions. Aesthetic Plast Surg 24(3):192–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002660010031
McHugh ML (2012) Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 22(3):276–282
Internatıonal survey on aesthetıc/cosmetıc procedures performed ın 2019. https://www.isaps.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Global-Survey-2019.pdf.Last visited May 12th 2021.
Constantian MB (2004) The two essential elements for planning tip surgery in primary and secondary rhinoplasty: observations based on review of 100 consecutive patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(6):1571–1585. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.prs.0000138755.00167.f5
Mao GY, Yang SL, Zheng JH, Liu QY (2008) Aesthetic rhinoplasty of the Asian nasal tip: a brief review. Aesthetic Plast Surg 32(4):632–637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9114-1
Kridel RW, Soliemanzadeh P (2006) Tip grafts in revision rhinoplasty. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 14(4):331–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2006.06.014 (PMID: 17088181)
Jang YJ, Min JY, Lau BC (2011) A multilayer cartilaginous tip-grafting technique for improved nasal tip refinement in Asian rhinoplasty. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 145(2):217–222. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599811406484
Peck GC Jr, Michelson L, Segal J, Peck GC Sr (1998) An 18-year experience with the umbrella graft in rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 102(6):2158–2168. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199811000-00056
Jang YJ, Kim DY (2016) Treatment strategy for revision rhinoplasty in Asians. Facial Plast Surg 32(6):615–619. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1594254
Rohrich RJ, Deuber MA (2002) Nasal tip refinement in primary rhinoplasty: the cephalic trim cap graft. Aesthet Surg J 22(1):39–45. https://doi.org/10.1067/maj.2002.122132
Hodgkinson DJ, Valente PM (2017) The versatile posterior auricular fascia in secondary rhinoplasty procedures. Aesthetic Plast Surg 41(4):893–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0824-0
Courson AM, Adamson PA (2018) The intercrural fascia graft in primary rhinoplasty. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 20(1):76–77. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamafacial.2017.1077
Daniel RK, Palhazi P (2018) The nasal ligaments and tip support in rhinoplasty: an anatomical study. Aesthet Surg J 38(4):357–368. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjx192
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All of the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Pamukkale University Hospital Local Ethical Committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all the patients for enrollment and using photographs in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MOV 11213 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oguzhan, D., Aslı, D. Double Layer Lateral Crural Perichondrial Flap for Coverage and Stabilization of Tip Graft. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 862–870 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02549-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02549-0