Abstract
Background
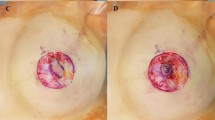
Nipple inversion, which is defined as a nipple located on a plane deeper than the areola, presents both functional and cosmetic problems. Surgical repair of severe cases involves suture or flap techniques. In the present study, an alternative repair technique using two cross dermal areolar flaps to correct challenging inverted nipples is presented. Releasing the inverted nipple is performed by severing the underlying tight fibrous tissue bands and canaliculi.
Methods
This is a retrospective case series. Fifteen patients who had been operated between January 2010 and January 2016 were included in the study. Seven of these had bilateral inverted nipples. Patient age at operation ranged from 26 to 47 years (mean age, 32.5 years). All nipples were congenital, with no previous operations. The follow-up period ranged between 8 and 16 months (mean of 13 months).
Results
There were no complications associated with surgery, including infection, hematoma, permanent sensory disturbance, or nipple necrosis. Unilateral recurrence occurred in one patient on the 26th postoperative day. This patient was reoperated on successfully using the same method. Adequate projection was achieved in all patients. All patients were satisfied with their results.
Conclusions
The authors conclude that their procedure is a reliable, simple, safe, and effective method for correction of inverted nipples. The alignment of the scar with the junction of the nipple and the areola leads to a more aesthetic appearance with no apparent scarring. This technique can be applied to any type of inverted nipple as a primary surgical procedure.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moseley HF, Miller GG. Textbook of Surgery. St. Louis: C. V. Mosby; 1952. p. 269-72.
Regnault P (1975) Nipple Hypertrophy, A physiologic reduction by circumcision. Clin Plast Surg 2(3):391–396
Lee KY, Cho BC (2004) Surgical correction of inverted nipples using the modified Namba or Teimourian technique. Plas Reconstructive Surg. 113(1):328–36
Kim DY, Jeong EC, Eo SR, Kim KS, Lee SY, Cho BH (2003) Correction of inverted nipple: an alternative method using two triangular areolar dermal flaps. Ann Plast Surg 51(6):636–640
Durgun M, Ozakpinar HR, Selcuk CT, Sarici M, Ceran C, Seven E (2014) Inverted nipple correction with dermal flaps and traction. Aesthetic Plast Surg 38(3):533–539
Jeong HS, Lee HK (2015) Correction of inverted nipple using subcutaneous turn-over flaps to create a tent suspension-like effect. PloS one 10(7):e0133588
Kolker AR, Torina PJ (2009) Minimally invasive correction of inverted nipples: a safe and simple technique for reliable, sustainable projection. Ann Plast Surg 62(5):549–553
Han S, Hong YG (1999) The inverted nipple: its grading and surgical correction. Plast reconstructive Surg 104(2):389–95
Hwang K, Kim DH (2013) Half Z-plasty, band release, and cavity filling for correction of inverted nipple. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 47(2):93–96
Teng L, Wu GP, Sun XM, Lu JJ, Ding B, Ren M et al (2005) Correction of inverted nipple: an alternative method using continuous elastic outside distraction. Ann Plast Surg 54(2):120–123
Min KH, Park SS, Heo CY, Min KW (2010) Scar-free technique for inverted-nipple correction. Aesthetic Plast Surg 34(1):116–119
Zhou H, Tan Q, Wu J, Zheng DF, Zhou HR, Xu P et al (2011) Correction of inverted nipple with bilateral areolar rhomboid dermal flaps. J Plast Reconstructive Aesthet Surg JPRAS. 64(6):e159–e161
Yamada N, Kakibuchi M, Kitayoshi H, Kurokawa M, Hosokawa K, Hashimoto K (2004) A method for correcting an inverted nipple with an artificial dermis. Aesthet Plast Surg 28(4):233–238
McGeorge DD (1994) The “Niplette”: an instrument for the non-surgical correction of inverted nipples. Br J Plast Surg 47(1):46–49
Pereira OJ, Bins-Ely J, Granemann AS, Lee KH (2009) Correction of inverted nipples by strong suspension with areola-based dermal flaps. Plast Reconstructive Surg 123(3):1132
Schwager RG, Smith JW, Gray GF, Goulian D Jr (1974) Inversion of the human female nipple, with a simple method of treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 54(5):564–569
Skoog T (1952) An operation for inverted nipples. Br J Plast Surg 5(1):65–69
Spina V (1957) Inverted nipple; contribution to the surgical treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 19(1):63–6
Dessena L, Dast S, Perez S, Mercut R, Herlin C, Sinna R (2018) Inverted nipple treatment and poliglecaprone spacer. Aesthet Plast Surg 42(4):958–963
Mathur B, Loh CYY (2019) Sensation-sparing correction of inverted nipples using the “drawbridge” flap approach. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(2):348–353
Sowa Y, Itsukage S, Morita D, Numajiri T (2017) Inverted nipple correction with selective dissection of lactiferous ducts using an operative microscope and a traction technique. Aesthet Plast Surg 41(5):1045–1048
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Merve Evren for medical illustrations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
This is a retrospective case study and for this type of study formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aysal, B.K., Sever, C. A New Technique in Correction of Nipple Inversion Using Dermal C Flaps. Aesth Plast Surg 46, 101–107 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02521-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02521-y