Abstract
Background
Fat grafting has been extensively applied as natural filler and has been very promising in restoring volume loss. Lipografting has also been credited to reduce age-related skin changes due to the regenerative potential of adipose derived stem cells. Cell-mediated therapies in plastic surgery are rapidly evolving with growing applications. Nanofat, a bio-regenerative liquid suspension rich in stromal vascular fraction cells without viable adipocytes, has been described as an efficient cutaneous anti-aging therapy. We have published in 2013 a review entitled “stem cell facelift: between reality and fiction.” Available clinical evidence at that time did not substantiate marketing and promotional claims of "stem cell facelift". The same year, the report about nanofat was published demonstrating striking clinical outcome. The current literature search is aimed at reviewing any evidence that has emerged since then regarding clinical efficacy of this modality.
Methods
A thorough PICO tool-based comprehensive literature search of PubMed database for “the efficacy of nanofat cell-mediated anti-aging therapy” was conducted with a time frame from 2013 till present.
Results
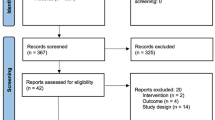
Despite apparent increasing popularity of stem cell rejuvenation, well-controlled clinical studies about this modality are surprisingly very scarce. Only seven papers published after 2013 were identified and were included in this review
Conclusion
Though considered to be a safe procedure, and despite documented histologic improvement and striking clinical outcome in some reports, available evidence can hardly support clinical improvement of skin quality. Before cell-mediated aesthetic rejuvenation applications can be routinely undertaken, more robust evidence with well-defined primary outcome end points and objective outcome measures is required.
Level of Evidence
IV.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu Y, Deng M, Cai Y, Zheng H et al (2020) Cell-free fat extract increases dermal thickness by enhancing angiogenesis and extracellular matrix production in nude mice. Aesthet Surg J 40(8):904–913
Fournier PF (1990) Facial recontouring with fat grafting. Dermatol Clin 8(3):523–537
Coleman SR (1995) Long-Term survival of fat transplants: controlled demonstrations. Aesthet Plast Surg 19(5):421–425
Pourang A, Rockwell H, Karimi K (2020) New frontiers in skin rejuvenation, including stem cells and autologous therapies. Fac Plast Surg Clin 28(1):101–117
Bianchi F, Maioli M, Leonardi E, Olivi E et al (2013) A new nonenzymatic method and device to obtain a fat tissue derivative highly enriched in pericyte-like elements by mild mechanical forces from human lipoaspirates. Cell Transpl 22(11):2063–2077
Rihani J (2019) Microfat and nanofat: when and where these treatments work. Fac Plast Surg Clin 27(3):321–330
Suh A, Pham A, Cress MJ, Pincelli T et al (2019) Adipose-derived cellular and cell-derived regenerative therapies in dermatology and aesthetic rejuvenation. Ageing Res Rev 54:
Stuzin JM (2013) Discussion: nanofat grafting: basic research and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 132(4):1027–1028
Gennai A, Zambelli A, Repaci E, Quarto R et al (2017) Skin rejuvenation and volume enhancement with the micro superficial enhanced fluid fat injection (M-SEFFI) for skin aging of the periocular and perioral regions. Aesthet Surg J 37(1):14–23
van Dongen JA, van Boxtel J, Harmsen MC, Stevens HP (2019) The development of facial lipofilling from a historical point of view. Fac Plast Surg 35(4):358–367
Eto H, Kato H, Suga H, Aoi N et al (2012) The fate of adipocytes after nonvascularized fat grafting: evidence of early death and replacement of adipocytes. Plast Reconstr Surg 129(5):1081–1092
Coleman SR (2020) Long-term survival of fat transplants: controlled demonstrations. Aesthet Plast Surg 44(4):1268–1272
van Dongen JA, Langeveld M, van de Lande LS, Harmsen MC et al (2019) The effects of facial lipografting on skin quality: A systematic review. Plast Reconstr Surg 144(5):784e–797e
Rigotti G, Charles-de-Sá L, Gontijo-de-Amorim NF, Takiya CM et al (2016) Expanded stem cells, stromal-vascular fraction, and platelet-rich plasma enriched fat: comparing results of different facial rejuvenation approaches in a clinical trial. Aesthet Surg J 36(3):261–270
Daumas A, Magalon J, Delaunay F, Abellan M et al (2020) Fat grafting for treatment of facial scleroderma. Clin Plast Surg 47(1):155–163
Brooker JE, Rubin JP, Marra KG (2019) The future of facial fat grafting. J Craniofac Surg 30(3):644–651
Wolf DA, Beeson W, Rachel JD, Keller GS et al (2018) Mesothelial stem cells and stromal vascular fraction for skin rejuvenation. Fac Plast Surg Clin 26(4):513–532
Tremolada C, Colombo V, Ventura C (2016) Adipose tissue and mesenchymal stem cells: state of the art and Lipogems® technology development. Curr Stem Cell Rep 2(3):304–312
Charles-de-Sá L, Gontijo-de-Amorim NF, Rigotti G, Sbarbati A et al (2020) Photoaged skin therapy with adipose-derived stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg 145(6):1037e–1049e
Yang Z, Jin S, He Y, Zhang X et al (2021) Comparison of microfat, nanofat and extracellular matrix/stromal vascular fraction gel for skin rejuvenation: basic research and clinical applications. Aesthet Surg J. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjab033
Tonnard P, Verpaele A, Carvas M (2019) Fat grafting for facial rejuvenation with nanofat grafts. Clin Plast Surg 47(1):53–62
Mashiko T, Wu SH, Feng J, Kanayama K, Yoshimura K et al (2017) Mechanical micronization of lipoaspirates: squeeze and emulsification techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 139(1):79–90
Mashiko T, Wu SH, Feng J, Kanayama K, Yoshimura K et al (2017) Reply: mechanical micronization of lipoaspirates: squeeze and emulsification techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 140(3):509e–510e
Ceserani V, Ferri A, Berenzi A, Benetti A et al (2016) Angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties of micro-fragmented fat tissue and its derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Vasc Cell 8(1):1–12
Charvet HJ, Pu LL (2019) Commentary on: conventional nanofat and SVF/ADSC-concentrated nanofat: a comparative study on improving photoaging of nude mice skin. Aesthet Surg J 39(11):1251–1252
Pak J, Lee JH, Kartolo WA, Lee SH (2016) Cartilage regeneration in human with adipose tissue-derived stem cells: current status in clinical implications. BioMed Res Int 2016:4702674
Tonnard P, Verpaele A, Peeters G, Hamdi M et al (2013) Nanofat grafting: basic research and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 132(4):1017–1026
Chen X, Hong S, Hong F, Yang B et al (2020) Mechanical emulsification of lipoaspirate by different Luer-Lok connector changes the viability of adipose derived stem cells in Nanofat. J Plast Surg Hand Surg 54(6):344–351
Kamat P, Frueh FS, McLuckie M, Sanchez-Macedo N et al (2020) Adipose tissue and the vascularization of biomaterials: stem cells, microvascular fragments and nanofat—a review. Cytotherapy 8:400–411
Friji MT (2014) Nanofat grafting: basic research and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(2):333e–334e
Yao Y, Dong Z, Liao Y, Zhang P et al (2017) Adipose extracellular matrix/stromal vascular fraction gel: a novel adipose tissue-derived injectable for stem cell therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg 139(4):867–879
Banyard DA, Sarantopoulos CN, Borovikova AA, Qiu X et al (2016) Phenotypic analysis of stromal vascular fraction after mechanical shear reveals stress-induced progenitor populations. Plast Reconstr Surg 138(2):237e
Atiyeh BS, Ibrahim AE, Saad DA (2013) Stem cell facelift: between reality and fiction. Aesthet Surg J 33(3):334–338
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097
ASPS Evidence Rating Scales (2011). https://www.plasticsurgery.org/Documents/medical-professionals/health-policy/evidence-practice/ASPS-Rating-Scale-March-2011.pdf. Accessed 6 Mar 2021
Uyulmaz S, Sanchez Macedo N, Rezaeian F, Giovanoli P, Lindenblatt N (2018) Nanofat grafting for scar treatment and skin quality improvement. Aesthet Surg J 38(4):421–428
Uyulmaz S, Sanchez Macedo N, Rezaeian F, Giovanoli P, Lindenblatt N (2018) Nanofat grafting for scar treatment and skin quality improvement. Aesthet Surg J 38(4):421–428
Mailey B, Saba S, Baker J, Tokin C et al (2013) A comparison of cell-enriched fat transfer to conventional fat grafting after aesthetic procedures using a patient satisfaction survey. Ann Plast Surg 70(4):410–415
Charles-de-Sá L, Gontijo-de-Amorim NF, Maeda Takiya C, Borojevic R et al (2015) Antiaging treatment of the facial skin by fat graft and adipose-derived stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg 135(4):999–1009
Menkes S, Luca M, Soldati G, Polla L (2020) Subcutaneous injections of nanofat adipose-derived stem cell grafting in facial rejuvenation. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 8(1):
Liang Z-J, Lu X, Li DQ, Liang YD et al (2018) Precise intradermal injection of nanofat-derived stromal cells combined with platelet-rich fibrin improves the efficacy of facial skin rejuvenation. Cell Physiol Biochem 47(1):316–329
Zarei F, Abbaszadeh A (2019) Application of cell therapy for anti-aging facial skin. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther 14(3):244–248
Wang JV, Schoenberg E, Zaya R, Rohrer T et al (2020) The rise of stem cells in skin rejuvenation: a new frontier. Clin Dermatol 38(4):494–496
Cohen SR, Hewett S, Ross L, Delaunay F et al (2017) Regenerative cells for facial surgery: biofilling and biocontouring. Aesthet Surg J 37(3):S16–S32
Qin F, Zhang W, Zhang M, Long X et al (2021) Adipose-derived stem cells improve the aging skin of nude mice by promoting angiogenesis and reducing local tissue water. Aesthet Surg J. https://doi.org/10.1093/asj/sjab001
Wei H, Gu SX, Liang YD, Liang ZJ et al (2017) Nanofat-derived stem cells with platelet-rich fibrin improve facial contour remodeling and skin rejuvenation after autologous structural fat transplantation. Oncotarget 8(40):68542
Mazini L, Rochette L, Hamdan Y, Malka G (2021) Skin immunomodulation during regeneration: emerging new targets. J Personal Med 11(2):85
Liang J-X, Liao X, Li SH, Jiang X et al (2020) Antiaging properties of exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in photoaged rat skin. BioMed Res Int 2020:6406395
Alharbi Z, Opländer C, Almakadi S, Fritz A et al (2013) Conventional vs. micro-fat harvesting: how fat harvesting technique affects tissue-engineering approaches using adipose tissue-derived stem/stromal cells. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 66(9):1271–1278
van Dongen JA, Tuin AJ, Harmsen MC, Stevens HP, van der Lei B (2019) Enhancement of progenitor cells by two-step centrifugation of emulsified lipoaspirates. Plast Reconstr Surg 143(4):893e–894e
Zheng H, Qiu L, Su Y, Yi C (2019) Conventional nanofat and SVF/ADSC-concentrated nanofat: a comparative study on improving photoaging of nude mice skin. Aesthet Surg J 39(11):1241–1250
Pallua N, Grasys J, Kim B-S (2018) Enhancement of progenitor cells by two-step centrifugation of emulsified lipoaspirates. Plast Reconstr Surg 142(1):99–109
Khouri RK Jr (2018) Discussion: enhancement of progenitor cells by two-step centrifugation of emulsified lipoaspirates. Plast Reconstr Surg 142(1):110–111
van Dongen JA, Stevens HP, Harmsen MC, van der Lei B (2017) Mechanical micronization of lipoaspirates: squeeze and emulsification techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 139(6):1369e–1370e
Charles-de-Sá L, Gontijo-de-Amorim N, Sbarbati A, Benati D et al (2020) Photoaging skin therapy with PRP and ADSC: a comparative study. Stem Cells Int 2020:1–13
Jan SN, Bashir MM, Khan FA, Hidayat Z et al (2019) Unfiltered nanofat injections rejuvenate postburn scars of face. Ann Plast Surg 82(1):28–33
Cohen SR, Womack H, Ghanem A (2020) Fat grafting for facial rejuvenation through injectable tissue replacement and regeneration: a differential, standardized, anatomic approach. Clin Plast Surg 47(1):31–41
Liu W, Shi K, Zhu X, Zhao H et al (2020) Adipose tissue-derived stem cells in plastic and reconstructive surgery: a bibliometric study. Aesthet Plast Surg 45:1–11
Barnes CH, Maas CS (2019) Autologous fat harvest and preparation for optimal predictable outcomes. Fac Plast Surg Clin 27(3):419–423
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atiyeh, B., Ghieh, F. & Oneisi, A. Nanofat Cell-Mediated Anti-Aging Therapy: Evidence-Based Analysis of Efficacy and an Update of Stem Cell Facelift. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 2939–2947 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02353-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-021-02353-w