Abstract
Introduction
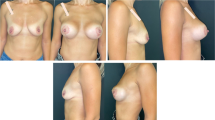
The treatment of breast ptosis using mastopexy associated with the inclusion of a silicone prosthesis in a single surgical procedure is a challenge for surgeons. The aim of this study is to describe the 15-year experience with the placement of silicone breast implants in double, subfascial and submuscular space, in the treatment of patients with breast ptosis, and to analyze the aesthetic results of patients who underwent such surgeries.
Method
During the 15-year period, between 2005 and 2020, 640 mastopexies were performed with the inclusion of silicone breast implants in double space, with high-profile round polyurethane prostheses whose volumes ranged from 135 to 435 ml, in patients with grade 2 and 3 breast ptosis.
Results
The age of the patients ranged from 18 to 55 years and the average age was 34 years. The postoperative follow-up time was 18 months. 400 patients (62.5%) had grade II ptosis, whereas 240 of them (37.5%) had grade III ptosis. The main complications were: 19 cases (3%) of residual sagging skin, 19 cases (3%) of unsightly scars, 12 cases (2%) of partial areola necrosis. There was no case of infection or seroma. There were 330 primary surgeries (52%) and 310 secondary surgeries (48%).
Conclusion
After 15 years of performing mastopexy with prosthesis in double space, both in primary and secondary surgeries, it can be concluded that the technique reached its maturity providing good long-term results with the maintenance of the projection of the upper pole of the breast and low recurrence of ptosis in the lower pole and low rate of complications.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spear SL, Kassan M, Little JW (1990) Guidelines in concentric mastopexy. Plast Reconstr Surg 85(6):961–966. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000072257.66189.3E
Ismail KT, Ismail MT, Ismail TA, Ismail AT, Toth BA (2019) Triple-plane augmentation mastopexy. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 7(8):e2344. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002344
Chiquetti A, Silva ABD (2018) Tratamento das ptoses mamárias com implantes submusculares e pontos de fixação do tecido mamário ao muscular: aspectos técnicos e avaliação de resultado. Rev Soc Bras Cir Plast 33(3):317–323. https://doi.org/10.5935/2177-1235.2018RBCP0144
Khan UD (2010) Muscle-spliting, subglandular, and partial submuscular augmentation mamoplasties: a 12-year retrospective analysis of 2026 primary cases. Aesthet Plast Surg 34(3):290–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-0026-8
Pedroso DB, Daher JC, Amaral JDLG, Cintra Júnior R, Borgatto MS, Câmara Filho JPP (2012) Mastopexia associada a implante de silicone submuscular ou subglandular: sistematização das escolhas e dificuldades. Rev Soc Bras Cir Plast 27(2):294–300
Auersvald A, Auervald LA (2011) Breast augmentation and mastopexy using a pectoral muscle loop. Aesthet Plast Surg 35(3):333–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9
Abramo AC, Scartozzoni M, Luvena TW, Sgarbi RG (2018) High- and extra-high-profile round implants in breast augmentation: guidelines to prevent rippling and implant edge visibility. Aesthet Plast Surg 27:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-018-1264-1
Ono MT, Karner BM (2019) Four-step augmentation mastopexy: lift and augmentation at single time (LAST). Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 7(11):e2523. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002523
Daniel MJB (2005) Inclusão de Prótese de Mama em Duplo Espaço. Rev Soc Bras Cir Plast 20(2):82–87
Daniel MJB (1994) Mamoplastia com Retalho do Músculo Peitoral: uma abordagem dinâmica e definitiva para a ptose mamária. Arq Catarin Med 23(supl 1):37
Daniel MJB (1995) Mammaplasty with pectoral muscle flap. Presented at 64th American annual scientific meeting, Montreal
Graf R, Araujo LRR, Rippel R, Graça Neto L, Pace D, Biggs T (2005) Mamaplastia vertical com retalho da parede torácica. Rev Soc Bras Cir Plást 20(3):148–154
Rehnke RD, Groening RM, Van Buskirk ER, Clarke JM (2018) Anatomy of the superficial fascia system of the breast: a comprehensive theory of breast fascial anatomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 142(5):1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000004948
Graça Neto L, Graf RM (2020) Anatomy of the superficial fascia system of the breast: a comprehensive theory of breast fascial anatomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 145(1):193e–194e
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of in relations of relations to the content of this manuscript.
Ethical Approval
“All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.”
Informed Consents
All patients signed informed consent for surgery, use of photographs and data for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Lincoln Graça Neto and Milton Daniel are active members of Brazilian Soc of Plastic Surgery.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graça Neto, L., Daniel, M. Double Space Augmentation Mastopexy—A Reflection After 15 Years. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 491–497 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-02021-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-02021-5