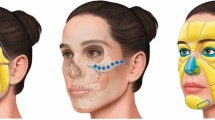
Abstract
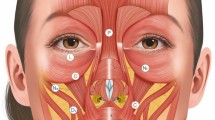
The plunging nasal tip is a challenging condition because, although it is predominantly a dynamic deformity which occurs during smiling, it also indicates a structural problem. When a person smiles, the paired depressor septi nasi muscles pull the tip caudally at the same time as the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscles pull the alar base and lateral lip cephalically. This movement causes straightening of the alar rim. Even though surgical rhinoplasty is the gold standard to restore nasal appearance, the procedure may fail to treat the dynamic cause of the drooping tip. This article outlines the anatomical concepts that lead to a drooping tip and presents a technique that can treat both the dynamic and structural causes of the drooping tip using hyaluronic acid filler. Cases are also presented that illustrate these concepts.
Level of evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Society of Plastic Surgeons (2018) 2018 Plastic Surgery Statistics Report. Available from: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/news/plastic-surgery-statistics
Kontis TC (2017) Nonsurgical rhinoplasty. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 19(5):430–431
Mehta U, Fridirici Z (2019) Advanced techniques in nonsurgical rhinoplasty. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 27(3):355–365
Bayramiçli M, Dogan ZA (2018) Transection of the nasal base muscles for the correction of plunging tip: an outcome analysis. Aesthet Surg J 38(9):951–961
Arregui JS, Elejalde MV, Regalado J, Ezquerra F, Berrazueta M (2000) Dynamic rhinoplasty for the plunging nasal tip: functional unity of the inferior third of the nose. Plast Reconstr Surg 106(7):1624–1629
Kosins AM, Lambros V, Daniel RK (2014) The plunging tip: illusion and reality. Aesthet Surg J 34(1):45–55
Rohrich RJ, Huynh B, Muzaffar AR, Adams WP, Robinson JB (2000) Importance of the depressor septi nasi muscle in rhinoplasty: anatomic study and clinical application. Plast Reconstr Surg 105(1):376–383
Kosins AM, Lambros V, Daniel RK (2015) The plunging tip: analysis and surgical treatment. Aesth Surg J 35(4):367–377
Dayan SH, Kempiners JJ (2005) Treatment of the lower third of the nose and dynamic nasal tip ptosis with botox. Plast Reconstr Surg 115(6):1784–1785
de Maio M (2018) Myomodulation with injectable fillers: an innovative approach to addressing facial muscle movement. Aesth Plast Surg 42(3):798–814
Toriumi DM, Checcone MA (2009) New concepts in nasal tip contouring. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 17(1):55–90
Brown M, Guyuron B (2013) Redefining the ideal nasolabial angle: part 2 expert analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 132(2):221e–225e
Tardy ME, Brown RJ (1990) Surgical anatomy of the nose. Raven Press, New York
Daniel RK, Palhazi P (2018) The nasal ligaments and tip support in rhinoplasty: an anatomical study. Aesthet Surg J 38(4):357–368
Anderson JR (1984) A reasoned approach to nasal base surgery. Arch Otolaryngol 110(6):349–358
Shaw RB, Kahn DM (2007) Aging of the midface bony elements: a three-dimensional computed tomographic study. Plast Reconstr Surg 119(2):675–681
Greene JJ, Sidle DM (2015) The hyaluronic acid fillers: Current understanding of the tissue device interface. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 23(4):423–432
Lee W, Kim J-S, Oh W, Koh I-S, Yang E-J (2019) Nasal dorsum augmentation using soft tissue filler injection. J Cosmet Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13018
Jones D, Tezel A, Borrell M (2010) In vitro resistance to degradation of hyaluronic acid dermal fillers by ovine testicular hyaluronidase. Dermatol Surg 36(s1):804–809
Tanna N, Nguyen KT, Ghavami A, Calvert JW, Guyuron B, Rohrich RJ, Gruber RP (2018) Evidence-based medicine: current practices in rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 141(1):137e–151e
Tardy ME, Becker D, Weinberger M (1995) Illusions in rhinoplasty. Facial Plast Surg 1(3):117–137
Cerrati EW, Dayan SH (2017) Association of increasing nasal tip projection with lip position in primary rhinoplasty. JAMA Facial Plast Surg 19(4):323–326
Signorini M, Liew S, Sundaram H, De Boulle KL, Goodman GJ, Monheit G et al (2016) Global aesthetics consensus: avoidance and management of complications from hyaluronic acid fillers-evidence- and opinion-based review and consensus recommendations. Plast Reconstr Surg 137(6):961e–971e
Wibowo A, Kapoor KM, Philipp-Dormston WG (2019) Reversal of post-filler vision loss and skin ischaemia with high-dose pulsed hyaluronidase injections. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(5):1337–1344
Carruthers J, Fagien S, Dolman P (2015) Retro or peribulbar injection techniques to reverse visual loss after filler injections. Dermatol Surg Off Publ Am Soc Dermatol Surg Al 41(Suppl 1):S354–357
Heydenrych I, Kapoor KM, De Boulle K, Goodman G, Swift A, Kumar N et al (2018) A 10-point plan for avoiding hyaluronic acid dermal filler-related complications during facial aesthetic procedures and algorithms for management. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 23(11):603–611
Jung GS, Chu SG, Lee JW, Chung HY, Yang JD, Cho BC et al (2019) A safer non-surgical filler augmentation rhinoplasty based on the anatomy of the nose. Aesthet Plast Surg 43(2):447–452
de Maio M, Swift A, Signorini M, Fagien S (2017) Aesthetic leaders in facial aesthetics consensus committee. facial assessment and injection guide for botulinum toxin and injectable hyaluronic acid fillers: focus on the upper face. Plast Reconstr Surg 140(2):265e–276e
Van Loghem JA, Fouché JJ, Thuis J (2018) Sensitivity of aspiration as a safety test before injection of soft tissue fillers. J Cosmet Dermatol 17(1):39–46
Wang JV, Hazan E, Hattier G, Torbeck RL, Khorasani H, Saedi N (2020) Utility of preinjection aspiration for hyaluronic fillers: a novel in vivo human evaluation. J Cutan Med Surg. https://doi.org/10.1177/1203475420921387
Mochizuki M, Aoi N, Gonda K, Hirabayashi S, Komuro Y (2018) Evaluation of the in vivo kinetics and biostimulatory effects of subcutaneously injected hyaluronic acid filler. Plast Reconstr Surg 142(1):112–121
Santorelli A, Marlino S (2019) Non-surgical rhinoplasty with hyaluronic acid fillers: predictable results using software for the evaluation of nasal angles. Aesthetic Plast Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-019-01579-z
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Ethical Approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required (retrospective study).
Informed Consent
All patients provided written consent for the use of their images.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MP4 274541 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramos, H.H.A., Bernardino, I.P.L. & de Cássia Capelato Rocha, R. Hyaluronic Acid Filler in the Treatment for Drooping Tip: Anatomical Concepts and Clinical Results. Aesth Plast Surg 44, 2173–2182 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01836-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-01836-6