Abstract
Background
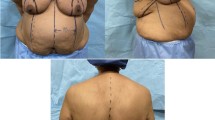
We have developed a dermo-capsular flap mastopexy technique for patients who have experienced massive weight loss after breast reconstruction. The aim of this technique is to lift the inframammary fold, adequately cover the implant, and remove excess skin, elevating the breast and obtaining symmetry with the contralateral breast.
Methods
Between January 2014 and February 2017, we performed this technique on 20 women who were candidates for second-stage breast reconstruction following nipple-sparing mastectomy. All patients had experienced substantial weight loss (> 15 kg) and presented with ptosis after first-stage reconstruction.
Results
There were 8 patients with bilateral reconstruction following bilateral mastectomy (4 with bilateral nipple-sparing mastectomy). There were 12 patients with unilateral mastectomy, all with contralateral breast ptosis treated by augmentation via inverted-T mastopexy (n = 7) or crescent mastopexy (n = 5). The average lift of the nipple-areola complex was 5 cm (range 2–8 cm). The average follow-up was 12 months (range 4–36 months). Two patients had complications, including partial wound dehiscence (in a heavy smoker) and recurrence of breast asymmetry.
Conclusions
Implant breast reconstruction after massive weight loss is still possible even in the setting of thin, ptotic, and anelastic breast tissue. Our inverted-T dermo-capsular flap mastopexy technique for reconstructed breast is safe and effective with good outcomes and high patient satisfaction.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barone M, Cogliandro A, Persichetti P (2017) BREAST-Q following breast reconstruction: analysis of breast perception and sexuality. Plast Reconstr Surg 139:1016–1017
https://asmbs.org/resources/estimate-of-bariatric-surgery-numbers
Persichetti P, Langella M, Filoni A, Cagli B, Tenna S (2013) How to redefine the inframammary fold: the “slingshot” capsular flap. Ann Plast Surg 70:636–638
Gargano F, Ciminello F, Podda S, De Santis G (2009) Salvage of exposed breast implants using capsular flaps. Eplasty 17(9):e41
Brandstetter M, Schoeller T, Pülzl P, Schubert H, Wechselberger G (2010) Capsular flap for coverage of an exposed implant after skin-sparring mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:1388–1390
Gargano F, Moloney D, Arnstein P (2002) Use of a capsular flap to prevent palpable wrinkling of implants. Br J Plast Surg 55:269
Imran D, Javaid M, Lewis D, Attar KH (2005) Capsular flap for correction of contour deformities of the breast. Ann Plast Surg 54:662–663
Hoch J, Stahlenbrecher A (2006) Bottoming out in augmentation mammaplasty-correction and prevention. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir 38:233–239
Bogdanov-Berezovsky A, Silberstein E, Shoham Y, Krieger Y (2013) Capsular flap: new applications. Aesthetic Plast Surg 37:395–397
Bauder AR, Samra F, Kanchwala SK, Serletti JM, Kovach SJ, Wu LC (2017) Autologous breast reconstruction in the postbariatric patient population. Microsurgery 3 [Epub ahead of print]
Dayicioglu D, Tugertimur B, Munzenmaier K, Khan M, Smith P, Murr M, Kumar A, Khakpour N (2016) Outcomes of breast reconstruction after mastectomy using deep inferior epigastric perforator flap after massive weight loss. Ann Plast Surg 76(Suppl 4):S286–S289
Martinez CA, Walters JA III, Sato EA, Hall JJ, Boutros SG (2016) Deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap breast reconstruction in patients with previous bariatric surgery: Is it safe and feasible? Ann Plast Surg 76:216–220
Samra F, Bauder AR, Chin B, Taglienti A, Wes AM, Kanchwala SK, Serletti JM, Wu LC (2015) Autologous breast reconstruction in the post-bariatric patient population. Plast Reconstr Surg 136(4 Suppl):89–90
Acknowledgements
The authors do not have any commercial associations that might pose or create a conflict of interest with information presented in this communication. No intramural or extramural funding supported any aspect of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of our University.
Informed Consent
Each patient provided written informed consent before the participation in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cogliandro, A., Barone, M., Cassotta, G. et al. Mastopexy on Reconstructed Breast Following Massive Weight Loss: An Innovative Technique Using Dermo-Capsular Flaps. Aesth Plast Surg 42, 396–399 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0992-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0992-y