Abstract
Background
Dexamethasone and tranexamic acid are used to decrease post-rhinoplasty periorbital edema and ecchymosis. We compared the impact of each medication separately or in combination in this regard.
Methods
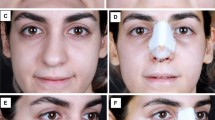
A prospective, randomized triple-blinded study was undertaken on 60 patients who underwent primary open rhinoplasty. They were divided into four groups: Group D (n = 15) received 8 mg dexamethasone, group T (n = 15) received 10 mg/kg tranexamic acid, group DT (n = 15) received both 8 mg dexamethasone and 10 mg/kg tranexamic acid, and group P (n = 15) received neither medication and served as the placebo control group. The medications were given intravenously (IV) 1 h before and three doses every 8 h postoperatively. Digital photographs were taken on the first, third and seventh postoperative days. One expert examiner blinded to the study evaluated the periorbital edema and ecchymosis on a scale of 0–4. Periorbital edema and ecchymosis were examined in all groups.
Results
In group D, group T and group DT, periorbital edema and ecchymosis ratings were significantly lower compared with the control group (p < 0.01). No statistically significant difference was seen in preventing or decreasing both periorbital edema and ecchymosis among group D, group T and group DT.
Conclusion
Tranexamic acid and dexamethasone, separately or in combination, had similar effects in reducing periorbital edema and ecchymosis in open rhinoplasty. Combined application did not show a significantly higher beneficial effect in this regard.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tebbetts JB (2008) Primary Rhinoplasty, 2nd edn. Elsevier, canada
Totonchi A, Guyuron B (2007) A Randomized, controlled comparison between arnica and steroids in the management of postrhinoplasty ecchymosis and edema. Plast Reconstr Surg 120:271–274
Sakallioglu O, Polat C, Soylu E, Duzer S, Orhan I, Akyigit A (2015) The efficacy of tranexamic acid and corticosteroid on edema and ecchymosis in septorhinolasty. Ann Plast Surg 74:392–396
Gutierrez S, Wuesthoff C (2014) Testing the effects of long-acting steroids in edema and ecchymosis after closed rhinoplasty. Plast Surg 22:83–87
Alajmi MA, Al- Abdulhadi KA, AL- Noumas HS, Kavitha G (2009) Results of intravenous steroid injection on reduction of postoperative edema in rhinoplasty. Indian J otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 61:266–269
Ong AA, Farhood Z, kyle AR, Patal KG (2016) Interventions to decrease postoperative edema and ecchymosis after rhinoplasty: a systematic review of the literature. Plast Reconstr Surg 137:1448–1462
Ghassemi A, Prescher A, Hilgers RD, Riediger D, Gerressen M (2011) Effect of the sequence of lateral osteotomy and hump removal on the aesthetic outcome. Aesthetic Plast Surg 35:603–607
Rohrich RJ, Janis JE, Adams WP, Krueger JK (2003) An update on the lateral nasal osteotomy in rhinoplasty: an anatomic endoscopic comparison of the external versus the internal approach. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:2461–2462
Robiony M, Toro C, Costa F, Sembronio S, Polini F, Politi M (2007) Piezosurgery: a new method for osteotomies in rhinoplasty. J Craniofac Surg 18:1098–1100
Ghassemi A, Ayoub A, Modabber A, Bohluli B, Prescher A (2013) Lateral nasal osteotomy: a comparative study between the use of osteotome and a diamond surgical burr—A cadaver study. Head face med 9:41–46
Alzacko SM, Muttalib AA, Al- khayat N, Altakal FS (2010) The effects of single dose dexamethasone on periorbital oedema and ecchymosis after rhinoplasty. J plast reconstr surg 34:147–151
McCormack PL (2012) Tranexamic acid: a review of its use in the treatment of hyperfibrino lysis. Drugs 72:585–617
Langille MA, Chiarella A, Cote DWJ, Mulholland G, Sowerby LJ, Dziegielewski PT, Wright ED (2012) Intravenous tranexamic acid and intraoperative visualization during functional endoscopic sinus surgery: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Int Forum of Allergy Rhinol 3(4):315–318
Gurlek A, Fariz A, Aydogan H, Ersoz-Ozturk A, Eren AT (2006) Effects of different cortico steroids on edema and ecchymosis in open rhinoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 30:150–154
Jalali MM, Moosavi S, Fatemi S, Banan RA (2011) Comparison between dexamethasone and tranexamic acid on postoperative edema and ecchymosis after rhinoplasty operation. J Guilan Univ Med Sci 81:72–76
Owsley JQ, weibel TJ, Adams WA (1996) Does steroid medication reduce facial edema following face lift surgery? A prospective, randomized study of 30 consecutive patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 98:1–6
Da silva EM, Hochman B, Ferreira LM (2014) Perioperative corticosteroids for preventing complications following facial plastic surgery. Sao Paulo Med J 132:316
Berinstein TH, Bane SM, Cupp CL, Demarco JK, Hunsaker DH (1998) Steroid use in rhinoplasty: an objective assessment of postoperative edema. Ear Nose Throat J 77:40–43
Kara CO, Gokalan I (1999) Effects of single dose steroid usage on edema, ecchymosis, and intraoperative bleeding in rhinoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:2213–2218
Hatef DA, Ellsworth WA, Allen JN, Bullocks JM, Hollier LH Jr, Stal S (2011) Perioperative steroids for minimizing edema and ecchymosis after rhinoplasty: a meta- analysis. Aesthet surg j 31:648–657
Hwang SH, Lee JH, kim BG, Kim SW, Kang JM (2015) The efficacy of steroids for edema and ecchymosis after rhinoplasty: a meta- analysis. Laryngoscope 125:92–98
Kargi E, Hosnuter M, Babuccu O, Altunkaya H, Altinyazar C (2003) Effect of steroids on edema, ecchymosis, and intraoperative bleeding. Ann Plast Surg 51:570–574
Tengborn L, Blomback M, Berntorp E (2015) Tranexamic acid- an old drug still going strong and making a revival. Thromb Res 135:231–242
Dunn CJ, Goa KL (1999) Tranexamic acid: a review of its use in surgery and other indications. Drugs 57:1005–1032
Yaniv E, Shvero J, Hadar T (2006) Hemostatic effect of tranexamic acid in elective nasal surgery. Am J Rhinol 20:227–229
Eftekharian HR, Rajabzadeh Z (2015) The efficacy of preoperative oral tranexamic acid on intraoperative bleeding during rhinoplasty: a clinical trial study. J craniofac surg 27:97–100
Ghavimi MA, Taheri Talesh K, Ghoreishizadeh A (2017) Efficacy of tranexamic acid on side effects of rhinoplasty: a randomized double- blind study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 45:897–902
Acknowledgement
The authors express their gratitude to Neda Amani, Ahmad Heidari and Fatemeh Mehravar for technical helps. The authors would like to acknowledge the Clinical Research Development Unit (CRDU) of 5 Azar Hospital at Golestan University of Medical Sciences for consultation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
We have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethics statement/confirmation of patients’ permission
We have no financial interest and we did not have any financial or material support concerning this study. All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehdizadeh, M., Ghassemi, A., Khakzad, M. et al. Comparison of the Effect of Dexamethasone and Tranexamic Acid, Separately or in Combination on Post-Rhinoplasty Edema and Ecchymosis. Aesth Plast Surg 42, 246–252 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0969-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0969-x