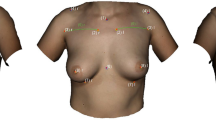
Abstract
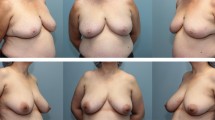
The surgical approach to breast asymmetry depends on several factors, including the surgeon’s experience, the anatomy of the patient, and several methods that may help to choose a technique and define the size of the implant or the amount of breast tissue to be excised. The aim of this study is to assist in evaluation of breast volumes with the Quantra™ software application, intended for use with Hologic™ digital mammography systems. Twenty-eight women were studied with full-field digital mammography (FFDM) with the Quantra™ software application, for use with Hologic™ digital mammography systems preoperatively. The case diagnoses were as follows: breast hypertrophy, ptosis, hypoplasia, and reconstruction, and the surgeries included breast reduction, mastopexy, mastopexy and breast reduction, mastoplasty and breast augmentation, breast augmentation, and immediate or delayed breast reconstruction. Patients were evaluated from 6 to 18 months after surgery. Volumetric mammogram studies help to decide the amount of tissue to be excised, the size of the implants, and the combination of both. The results of this study were evaluated by surgeons and patients and found to be highly satisfactory. The use of full-field digital mammography with adequate software should be considered as another tool to assist in making decisions regarding the correction of breast asymmetries.
Level of Evidence IV This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galdino GM, Nahabedian M, Chiaramonte M, Geng JZ, Klatsky S, Mansonn P (2002) Clinical applications of three-dimensional photography in breast surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:58–70
BodyLogic® (2016) System user guide, Mentor
MENTOR® (2015) Breast implant selection tool for Iphone/Ipad, by Mentor Worldwide LLC
MENTOR® (2015) Breast implant selection tool for android, by Mentor Worldwide LLC
Tebbetts JB, Adams WP Jr (2006) Five critical decisions in breast augmentation using five measurements in 5 minutes: The high five decision support process. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(7S):35S
Edstrom LE, Robson MC, Wright JK (1977) A method for the evaluation of minor degrees of breast asymmetry. Plast Reconstr Surg 60:812–814
Gorney M, Harries T (1974) The preoperative and postoperative consideration of natural facial asymmetry. Plast Reconstr Surg 54:187–191
Chang JB, Small KH, Choi M, Karp NS (2015) Three-dime plastic surgery: practical applications and beyond. Plast Reconstr Surg 135:1295–1304
Tzou CH, Artner NM, Pona I et al (2014) Comparison of three-dimensional surface-imaging systems. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 67:489–497
Kin H, Mun G-H, Wiraatmadja ES et al (2015) Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging-based volumetry for immediate breast reconstruction. Aesth Plast Surg 39:369–376
Hologic Company (2010) R2 Cenova 1.3. DICOM conformance statement. Digital Mammography, pp 40 (private code definition)
Pawluczyk O, Augustine BJ, Yaffe MJ et al (2003) A volumetric method for estimation of breast density on digitized screen-film mammograms. Med Phys 30:352–364
Lokate M, Kallenberg MGJ, Karssemeijer N et al (2010) Volumetric breast density from full-field digital mammograms and its association with breast cancer risk factors: a comparison with a threshold method. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 19:3096
Rohrich RJ, Hartley W, Brown S (2006) Incidence of breast and chest wall asymmetry in breast augmentation: a retrospective analysis of 100 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(7S):7S
Zimman OA (2013) Volumetric mammogram assessment. A helpful tool in the treatment of breast asymmetries. In: Presented at the 17th IPRAS world congress, Santiago, Chile
Jurado J (1976) Plásticas mamárias de redução baseadas em retalho dérmico vertical monopediculado. Anais XII Congresso Brasileiro de Cirurgia Plástica, pp 29
Adams WP Jr, McKee D (2016) Matching the implant to the breast: a systematic review of implant size selection systems for breast augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 138:987–994
Tepper OM, Small KH, Unger JG et al (2009) 3D analysis of breast augmentation defines operative changes and their relationship to implant dimensions. Ann Plast Surg 62:570–575
Liu C, Luan J, Mu L, Ji K (2010) The role of three-dimensional scanning technique in evaluation of breast asymmetry in breast augmentation: a 100-case study. Plast Reconstr Surg 126:2125–2132
Tepper OM, Small K, Rudolph L, Choi M, Karp N (2006) Virtual 3-dimensional modeling as a valuable adjunct to aesthetic and reconstructive breast surgery. Am J Surg 192:548–551
Choi M, Small K, Levovitz C, Lee C, Fadl A, Karp NS (2013) The volumetric analysis of fat graft survival in breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 131:185–191
Donfrancesco A, Montemurro P, Hedén P (2013) Three-dimensional simulated images in breast augmentation surgery: an investigation of patients’ satisfaction and the correlation between prediction and actual outcome. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:810–822
Pallara T, Signoretti M, Cagli B, Cogliandro A, Marangi GF, Persichetti P (2013) The volumetric analysis of fat graft survival in breast reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 132:668e–669e
Baskin B (2015) Invited commentary for “Preoperative magnetic resonance imaging-based volumetry for immediate breast reconstruction”. Aesth Plast Surg 39:377–378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimman, O.A., Butto, C.D., Rostagno, R. et al. Volumetric Mammogram Assessment: A Helpful Tool in the Treatment of Breast Asymmetries. Aesth Plast Surg 41, 1261–1274 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0940-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-017-0940-x