Abstract
Background
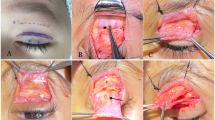
Congenital blepharoptosis is a common pediatric disease. Frontalis muscle flap advancement is an effective surgical technique to treat patients with severe ptosis and poor levator function. However, since eye position changes under general anesthesia, it is necessary to adjust the position of the upper eyelid to achieve a better surgical outcome.
Methods
A total of 162 children with severe congenital blepharoptosis underwent frontalis muscle flap advancement under general anesthesia. Patients were divided into two groups according to the different positions of eyelid suspension. The eyelid position of 82 children (96 eyes) in group A was adjusted to set at the superior limbus under general anesthesia, while the eyelid level of 80 children (94 eyes) in group B was adjusted according to the level labeled before anesthesia or the orthophoria level predicted using Krimsky’s test. Lid level, ptosis recurrence, cosmetic appearance, and complications were evaluated 12 months after surgery.
Results
Excellent functional and cosmetic results were achieved in 61 (63.5 %) children from group A and 85 (90.4 %) from group B. Fewer complications were observed in group B (36.5 vs. 9.6 %).
Conclusion
To achieve better surgical results after frontalis flap advancement for severe ptosis, it is necessary to adjust the eyelid level according to eye position changes that occur when the patient is under general anesthesia.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Finsterer J (2003) Ptosis: causes, presentation, and management. Aesthet Plast Surg 27(3):193–204
Skaat A, Fabian D, Spierer A, Rosen N, Rosner M, Ben Simon GJ (2013) Congenital ptosis repair—surgical, cosmetic, and functional outcome: a report of 162 cases. Can J Ophthalmol 48(2):93–98
Philandrianos C, Galinier P, Salazard B, Bardot J, Magalon G (2010) Congenital ptosis: long-term outcome of frontalis suspension using autogenous temporal fascia or fascia lata in children. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63(5):782–786
Aakalu VK, Setabutr P (2011) Current ptosis management: a national survey of ASOPRS members. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 27(4):270–276
Zhou LY, Chang TS (1988) Frontalis myofascial flap from eyebrow region for the correction of ptosis of the upper eyelid. Eur J Plast Surg 11(2):73–78
Park DH, Choi WS, Yoon SH, Shim JS (2007) Comparison of levator resection and frontalis muscle transfer in the treatment of severe blepharoptosis. Ann Plast Surg 59(4):388–392
Lai CS, Lai CH, Huang SH, Sun I, Chang KP, Lee SS, Lin SD (2010) A new trend for the treatment of blepharoptosis: frontalis-orbicularis oculi muscle flap shortening technique. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63(2):233–239
Cetinkaya A, Brannan PA (2008) Ptosis repair options and algorithm. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 19(5):428–434
Goldey SH, Baylis HI, Goldberg RA, Shorr N (2000) Frontalis muscle flap advancement for correction of blepharoptosis. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 16(2):83–93
Ramirez OM, Peña G (2004) Frontalis muscle advancement: a dynamic structure for the treatment of severe congenital eyelid ptosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 113(6):1841–1849
Ku HC, Lee SY, Lee YC (2005) Change of eye position in patients with orthophoria and horizontal strabismus under general anesthesia. Korean J Ophthalmol 19(1):55–61
Bae HW, Chung SA, Yoon JS, Lee JB (2012) Changes in the interpupillary distance following general anesthesia in children with intermittent exotropia: a predictor of surgical outcomes. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 49(1):49–53
Bernardini FP, Cetinkaya A, Zambelli A (2013) Treatment of unilateral congenital ptosis: putting the debate to rest. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 24(5):484–487
Crawford JS (1977) Repair of ptosis using frontalis muscle and fascia lata: a 20-year review. Ophthalmic Surg 8:31–40
Harvey DJ, Iamphongsai S, Gosain AK (2010) Unilateral congenital blepharoptosis repair by anterior levator advancement and resection: an educational review. Plast Reconstr Surg 126(4):1325–1331
Acknowledgments
Yongan Duan, Rui Jin, and Mingshu Zhong are funded by the National Natural Science Foundation (NSFC 81272129) and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai (STCSM 11ZR1420500).
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has a financial interest in any of the products, devices, or drugs mentioned in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mingshu Zhong and Rui Jin have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, M., Jin, R., Li, Q. et al. Frontalis Muscle Flap Advancement for Correction of Severe Ptosis Under General Anesthesia: Modified Surgical Design with 162 Cases in China. Aesth Plast Surg 38, 503–509 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-014-0297-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-014-0297-3