Abstract
Background
We investigated the effect of a combination of pregabalin and dexamethasone, when used as part of a multimodal analgesic regimen, on pain control after rhinoplasty operations.
Methods
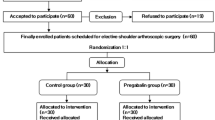
Sixty patients were enrolled in this study. They were randomly assigned into three groups: Group C (placebo + placebo), Group P (pregabalin + placebo), and Group PD (pregabalin + dexamethasone). Patients received either pregabalin 300 mg orally 1 h before surgery, dexamethasone 8 mg intravenously during induction, or placebo according to their allocation. Postoperative pain was treated with intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (tramadol, 20-mg bolus dose, 45-min lockout time). The numeric rating scale (NRS), side effects, and consumption of tramadol, pethidine, and ondansetron were assessed.
Results
The median NRS scores at 0, 1, and 6 h after surgery were significantly higher in Group C than in Group PD (p < 0.001 for all). The 24-h consumption of tramadol and pethidine was significantly reduced in Groups P and PD compared to Group C (p < 0.01 and p < 0.01). The total tramadol consumption was decreased by 54.5 % in Group P and 81.9 % in Group PD compared to Group C (p < 0.001 for both). The incidence of nausea was higher in Group C than in Groups P and PD between the postoperative 0–2 and 0–24-h periods (p < 0.05 for both). The frequency of blurred vision was significantly higher in Groups P and PD than in Group C within the 0–24-h period (p < 0.05 for both).
Conclusion
We found that the addition of a single dose of pregabalin and dexamethasone to multimodal analgesia in rhinoplasty surgeries provided efficient analgesia and thus decreased opioid consumption.
Level of Evidence I
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Menachem E (2004) Pregabalin pharmacology and its relevance to clinical practice. Epilepsia 45(suppl 6):13–18. doi:10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.455003.x
Bigat Z, Boztug N, Hadimioglu N, Cete N, Coskunfirat N, Ertok E (2006) Does dexamethasone improve the quality of intravenous regional anesthesia and analgesia? A randomized, controlled clinical study. Anesth Analg 102:605–609. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000194944.54073.dd
Bisgaard T, Klarskov B, Kehlet H, Rosenberg J (2003) Preoperative dexamethasone improves surgical outcome after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Ann Surg 238:651–660. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000094390.82352.cb
Chizh BA, Gohring M, Troster A, Quartey GK, Schmelz M, Koppert W (2007) Effects of oral pregabalin and aprepitant on pain and central sensitization in the electrical hyperalgesia model in human volunteers. Br J Anaesth 98:246–254. doi:10.1093/bja/ael344
Choi YS, Shim JK, Song JW, Kim JC, Yoo YC, Kwak YL (2013) Combination of pregabalin and dexamethasone for postoperative pain and functional outcome in patients undergoing lumbar spinal surgery: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin J Pain 29:9–14. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e318246d1a9
De Oliveira GS, Castro-Alves LJ Jr, Ahmad S, Kendall MC, McCarthy RJ (2013) Dexamethasone to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesth Analg 116:58–74. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e31826f0a0a
de Sousa SJA, da Silva LC, de Santana ST, Junior LRM, de Assuncao OAC, Brandao JR (2012) Comparative study of tramadol combined with dexamethasone and diclofenac sodium in third-molar surgery. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 40:694–700. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2012.01.001
Dursteler C, Miranda HF, Poveda R, Mases A, Planas E, Puig MM (2007) Synergistic interaction between dexamethasone and tramadol in a murine model of acute visceral pain. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 21:515–520. doi:10.1111/j.1472-8206.2007.00511.x
Gajraj NM (2007) Pregabalin: its pharmacology and use in pain management. Anesth Analg 105:1805–1815. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000287643.13410.5e
Granier M, Dadure C, Bringuier S, Bonnet-Boyer MC, Ryckwaert Y, Loriaux E, Capdevila X (2009) Intranasal lidocaine plus naphazoline nitrate improves surgical conditions and perioperative analgesia in septorhinoplasty surgery. Can J Anaesth 56:102–108. doi:10.1007/s12630-008-9020-7
Grond S, Sablotzki A (2004) Clinical pharmacology of tramadol. Clin Pharmacokinet 43:879–923
Guneli E, Yavasoglu NUK, Apaydin S, Uyar M (2007) Analysis of the antinociceptive effect of systemic administration of tramadol and dexmedetomidine combination on rat models of acute and neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 88:9–17. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2007.06.006
Holte K, Kehlet H (2002) Perioperative single-dose glucocorticoid administration: pathophysiologic effects and clinical implications. J Am Coll Surg 195:694–712
Hong JY, Han SW, Kim WO, Kim EJ, Kil HK (2010) Effect of dexamethasone in combination with caudal analgesia on postoperative pain control in day-case paediatric orchiopexy. Br J Anaesth 105:506–510. doi:10.1093/bja/aeq187
Hval K, Thagaard KS, Schlichting E, Raeder J (2007) The prolonged postoperative analgesic effect when dexamethasone is added to a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug (rofecoxib) before breast surgery. Anesth Analg 105:481–486. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000267261.61444.69
Jokela R, Ahonen J, Tallgren M, Haanpaa M, Korttila K (2008) Premedication with pregabalin 75 or 150 mg with ibuprofen to control pain after day-case gynaecological laparoscopic surgery. Br J Anaesth 100:834–840. doi:10.1093/bja/aen098
Jokela R, Ahonen J, Tallgren M, Haanpaa M, Korttila K (2008) A randomized controlled trial of perioperative administration of pregabalin for pain after laparoscopic hysterectomy. Pain 134:106–112. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2007.04.002
Kavoussi R (2006) Pregabalin: from molecule to medicine. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 16(suppl 2):S128–S133. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2006.04.005
Kehlet H (2007) Glucocorticoids for peri-operative analgesia: how far are we from general recommendations? Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 51:1133–1135. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01459.x
Kehlet H, Dahl JB (1993) The value of “multimodal” or “balanced analgesia” in postoperative pain treatment. Anesth Analg 77:1048–1056
Mathiesen O, Jacobsen LS, Holm HE, Randall S, Adamiec-Malmstroem L, Graungaard BK, Holst PE, Hilsted KL, Dahl JB (2008) Pregabalin and dexamethasone for postoperative pain control: a randomized controlled study in hip arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth 101:535–541. doi:10.1093/bja/aen215
Mathiesen O, Jorgensen DG, Hilsted KL, Trolle W, Stjernholm P, Christiansen H, Hjortso NC, Dahl JB (2011) Pregabalin and dexamethasone improve post-operative pain treatment after tonsillectomy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 55:297–305. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2010.02389.x
Mathiesen O, Rasmussen ML, Dierking G, Lech K, Hilsted KL, Fomsgaard JS, Lose G, Dahl JB (2009) Pregabalin and dexamethasone in combination with paracetamol for postoperative pain control after abdominal hysterectomy. A randomized clinical trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 53:227–235. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2008.01821.x
Meymandi MS, Keyhanfar F (2012) Pregabalin antinociception and its interaction with tramadol in acute model of pain. Pharmacol Rep 64:576–585
Mitra S, Khandelwal P, Sehgal A (2012) Diclofenac-tramadol vs. diclofenac–acetaminophen combinations for pain relief after caesarean section. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 56:706–711. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2012.02663.x
Parrington SJ, O’Donnell D, Chan VW, Brown-Shreves D, Subramanyam R, Qu M, Brull R (2010) Dexamethasone added to mepivacaine prolongs the duration of analgesia after supraclavicular brachial plexus blockade. Reg Anesth Pain Med 35:422–426. doi:10.1097/AAP.0b013e3181e85eb9
Romundstad L, Breivik H, Roald H, Skolleborg K, Haugen T, Narum J, Stubhaug A (2006) Methylprednisolone reduces pain, emesis, and fatigue after breast augmentation surgery: a single-dose, randomized, parallel-group study with methylprednisolone 125 mg, parecoxib 40 mg, and placebo. Anesth Analg 102:418–425. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000194358.46119.e1
Romundstad L, Stubhaug A (2007) Glucocorticoids for acute and persistent postoperative neuropathic pain: what is the evidence? Anesthesiology 107:371–373. doi:10.1097/01.anes.0000279487.27940.5c
Samad I, Stevens HE, Maloney A (1992) The efficacy of nasal septal surgery. J Otolaryngol 21:88–91
Savoia G, Alampi D, Amantea B, Ambrosio F, Arcioni R, Berti M, Bettelli G, Bertini L, Bosco M, Casati A, Castelletti I, Carassiti M, Coluzzi F, Costantini A, Danelli G, Evangelista M, Finco G, Gatti A, Gravino E, Launo C, Loreto M, Mediati R, Mokini Z, Mondello E, Palermo S, Paoletti F, Paolicchi A, Petrini F, Piacevoli Q, Rizza A, Sabato AF, Santangelo E, Troglio E, Mattia C (2010) Postoperative pain treatment SIAARTI recommendations 2010. Short version. Minerva Anestesiol 76:657–667
Sener M, Yilmazer C, Yilmaz I, Caliskan E, Donmez A, Arslan G (2008) Patient-controlled analgesia with lornoxicam vs. dipyrone for acute postoperative pain relief after septorhinoplasty: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Anaesthesiol 25:177–182. doi:10.1017/S0265021507002827
Sommer M, Geurts JW, Stessel B, Kessels AG, Peters ML, Patijn J, van Kleef M, Kremer B, Marcus MA (2009) Prevalence and predictors of postoperative pain after ear, nose, and throat surgery. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135:124–130. doi:10.1001/archoto.2009.3
Szychta P, Antoszewski B (2010) Assessment of early post-operative pain following septorhinoplasty. J Laryngol Otol 124:1194–1199. doi:10.1017/S0022215110001519
Wang JJ, Ho ST, Lee SC, Liu YC, Liu YH, Liao YC (1999) The prophylactic effect of dexamethasone on postoperative nausea and vomiting in women undergoing thyroidectomy: a comparison of droperidol with saline. Anesth Analg 89:200–203
White PF (2005) The changing role of non-opioid analgesic techniques in the management of postoperative pain. Anesth Analg 101:S5–S22
White PF (2008) Multimodal analgesia: its role in preventing postoperative pain. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 9:76–82
Wilder-Smith CH, Hill L, Dyer RA, Torr G, Coetzee E (2003) Postoperative sensitization and pain after cesarean delivery and the effects of single im doses of tramadol and diclofenac alone and in combination. Anesth Analg 97:526–533 (table of contents)
Wittekindt D, Wittekindt C, Schneider G, Meissner W, Guntinas-Lichius O (2012) Postoperative pain assessment after septorhinoplasty. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:1613–1621. doi:10.1007/s00405-011-1854-x
Yilmaz YF, Ozlugedik S, Titiz A, Tuncay A, Ozcan M, Unal A (2008) Comparison of levo-bupivacaine and lidocaine for postoperative analgesia following septoplasty. Rhinology 46:289–291
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demirhan, A., Tekelioglu, U.Y., Akkaya, A. et al. Effect of Pregabalin and Dexamethasone Addition to Multimodal Analgesia on Postoperative Analgesia Following Rhinoplasty Surgery. Aesth Plast Surg 37, 1100–1106 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-013-0207-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-013-0207-0