Abstract
Background
An inverted nipple affects not only the aesthetic appearance of the breast but also breastfeeding. Most surgical procedures can cause injury to normal lactiferous ducts and sensory dysfunction. The authors present a simple, safe, and minimally invasive technique for treating inverted nipples.
Methods
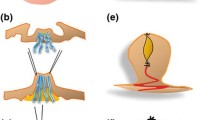
A distracter was made using the distal end of a 5- or 10-ml disposable syringe. The length was 1.3–1.5 cm, and pinholes with a diameter of 1 mm were punctured at 3, 6, 9, and 12 o’clock at the apex of the distracter. The inverted nipple was pulled out, and two steel wires with a diameter of 0.6 mm were crossed through the nipple base and fixed to the external distracter. After surgery, the wires were tightened once per month. According to the severity of the nipple inversion, the distracter was removed after 4–6 months of traction.
Results
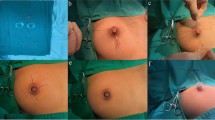
This method was used to correct 604 inverted nipples of 310 patients. The follow-up period ranged from 6 months to 2 years. No complications associated with surgery such as infection, depigmentation, sensory disturbance, or nipple necrosis occurred. The great majority of the patients (95.8 %) were satisfied with the aesthetic results.
Conclusions
The described technique is minimally invasive, simple, safe, reliable, and low in cost. Satisfying aesthetic results can be achieved without destroying breastfeeding function or nipple sensation.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Persichetti P, Poccia I, Pallara T, Delle Femmine PF, Marangi GF (2011) A new simple technique to correct nipple inversion using 2 V-Y advancement flaps. Ann Plast Surg 67:343–345
Ritz M, Silfen R, Morgan D, Southwick G (2005) Simple technique for inverted nipple correction. Aesthet Plast Surg 29:24–27
Wu HL, Huang X, Zheng SS (2008) A new procedure for correction of severe inverted nipple with two triangular areolar dermofibrous flaps. Aesthet Plast Surg 32:641–644
Cabalag MS, Chui CH, Tan BK (2010) Correction of nipple inversion using a micro-knife and transverse to longitudinal skin closure. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 6:e627–e630
Schlenz I, Kuzbari R, Gruber H, Holle J (2000) The sensitivity of the nipple–areola complex: An anatomic study. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:905–909
Jiang HQ, Wei X, Yuan SM, Tang LM (2008) Nipple aspirator: a self-designed instrument for inverted nipple. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:141e–143e
Hyakusoku H, Chin T (2006) Usefulness of the nipple-suspension piercing device after correction of inverted nipples. Aesthet Plast Surg 30:396–398
Teng L, Wu GP, Sun XM, Lu JJ, Ding B, Ren M, Ji Y, Jin XL (2005) Correction of inverted nipple: an alternative method using continuous elastic outside distraction. Ann Plast Surg 54:120–123
Park HS, Yoon CH, Kim HJ (1999) The prevalence of congenital inverted nipple. Aesthet Plast Surg 23:144–146
Shiau JP, Chin CC, Lin MH, Hsiao CW (2011) Correction of severely inverted nipple with telescope method. Aesthet Plast Surg 35:1137–1142
Sapountzis S, Kim JH, Minh P, Hwang YS, Baek RM, Heo CY (2012) Correction of inverted nipple with “arabesque” shape sutures. Aesthet Plast Surg 36:339–342
Ilizarov GA (1989) The tension-stress effect on the genesis and growth of tissue: the influence of stability of fixation and soft-tissue preservation. Clin Orthop 239:264
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, D., Luan, J., Mu, L. et al. A Minimally Invasive Gradual Traction Technique for Inverted Nipple Correction. Aesth Plast Surg 36, 1151–1154 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9959-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9959-1