Abstract
Background
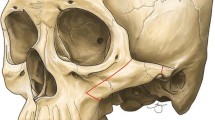
Reduction malarplasty via an intraoral approach for correction of a prominent malar complex is quite popular in the Orient. However, one point of fixation in the anterior zygoma body area, the most widely used method, sometimes is insufficient and likely to result in malunion and cheek drooping. We designed a new assisted fixation technique to strengthen the effect of fixation.
Methods
Two parallel oblique vertical ostectomies were performed on the zygomatic body with a groove left in the inner osteotomy line. The zygomatic arch root was cut obliquely through a small sideburn incision just in front of articular tubercle, medial to lateral and anterior to posterior. The freed malar complex was medially and superiorly repositioned with the zygomatic body wedged in the groove, followed by fixation with one miniplate or wire. Finally, the periosteum in the zygomatic area was pulled and sutured to the deep temporal fascia.
Results
Most patients were satisfied with their results. No inferiorly displaced malunion occurred in the zygomatic body. There were no serious complications such as nonunion or permanent facial nerve injury. Minor complications, including palpable step-off, mild asymmetry, hematoma, and mild cheek drooping, occurred in some cases.
Conclusion
Our assisted fixation method, combined with subperiosteal lifting, can provide ideal effects and sufficient fixation in malar reduction to prevent many complications such as malunion and cheek drooping.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek RM, Lee SW (2009) Face lift with reposition malarplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 123:701–708
Wang T, Gui L, Tang X et al (2009) Reduction malarplasty with a new L-shaped osteotomy through an intraoral approach: retrospective study of 418 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 124:1245–1253
Lee JG, Park YW (2003) Intraoral approach for reduction malarplasty: a simple method. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:453–460
Lee JS, Kang S, Kim YW (2003) Endoscopically assisted malarplasty: one incision and two dissection planes. Plast Reconstr Surg 111:461–467
Sumiya N, Kondo S, Ito Y et al (1997) Reduction malarplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 100:461–467
Lee KC, Ha SU, Park JM et al (2006) Reduction malarplasty by 3-mm percutaneous osteotomy. Aesthet Plast Surg 30:333–341
Nakanishi Y, Nagasao T, Shimizu Y et al (2012) The boomerang osteotomy-a new method of reduction malarplasty. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 65:e111–e120
Mu X (2010) Experience in East Asian facial recontouring: reduction malarplasty and mandibular reshaping. Arch Facial Plast Surg 12:222–229
Lee YH, Lee SW (2009) Zygomatic nonunion after reduction malarplasty. J Craniofac Surg 20:849–852
Baek RM, Kim J, Lee SW (2010) Revision reduction malarplasty with coronal approach. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:2018–2024
Baek RM, Kim J, Kim BK (2012) Three-dimensional assessment of zygomatic malunion using computed tomography in patients with cheek ptosis caused by reduction malarplasty. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 65:448–455
Onizuka T, Watanabe K, Takasu K, Keyama A (1983) Reduction malarplasty. Aesthet Plast Surg 7:121–125
Kim YH, Seul JH (2000) Reduction malarplasty through an intraoral incision: a new method. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:1514–1519
Cho BC (2003) Reduction malarplasty using osteotomy and repositioning of the malar complex: clinical review and comparison of two techniques. J Craniofac Surg 14:383–392
Jin H (2011) Reduction malarplasty using an L-shaped osteotomy through intraoral and sideburns incisions. Aesthet Plast Surg 35:242–244
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, Z., Xie, Y., Yu, B. et al. A New Assisted Fixation Technique to Prevent Zygoma Displacement in Malar Reduction. Aesth Plast Surg 37, 692–696 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-0033-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-0033-9