Abstract
Background
In certain cases of endoscopic forehead lift without muscle resection, patients were incidentally noted to develop weakness or loss of their ability to frown during the postoperative period despite intact musculature. This finding suggested the possibility of decreasing frown strength using the disinsertion of the relevant muscles. This finding persuaded the authors to try to eliminate or decrease the sensory problems resulting from open or endoscopic frowning muscle resection by disinserting these muscles. We therefore sought to determine the efficacy of a brow/forehead lift that involved disinsertion rather than muscle resection.
Methods
From September 2004 through December 2006, 22 endoscopic forehead lifts (20 females and 2 males) were performed using the conventional corrugator muscle resection technique (group 1). From January 2007 through October 2009, 43 patients (38 females and 5 males) underwent endoscopic forehead lift with a muscle-preserving technique (group 2). In both groups, small scalp incisions were made, and an endoscope was used to elevate the brows and forehead to perform glabellar and forehead muscle resection in group 1 and disinsertion of the frowning muscles in group 2. The skin of the forehead was then reanchored to a more superior location using sutures attached to deep temporal fascia as well as outer table screws and skin staples.
Results
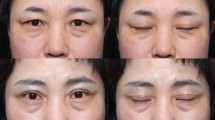
Aesthetically pleasing eyebrow and forehead with reduced power in the frowning muscles were achieved in the majority of patients in both groups. A significant decrease in the depth of vertical and horizontal glabellar creases was obtained in these patients. In group 1, 19 of 22 patients completely lost the ability to frown and 3 patients (13.6%) suffered permanent sensory loss. In group 2, 33 of 43 patients lost their ability to frown but only 2 cases (4.5%) developed minimal unilateral forehead partial sensory deficit after a 12-month follow-up period.
Conclusion
Disinsertion of the corrugator supercilli, procerus, or orbicularis oculi muscles can decrease contractility with less chance of damaging nearby or intermingled sensory nerves than offered by resection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rafaty FM (1981) Elimination of glabellar frown lines. Arch Otolaryngol 107(7):428–430
Knize DM (2000) Muscles that act on glabellar skin: a closer look. Plast Reconstr Surg 105(1):350–361
Presti P, Yalamanchili H, Honrado CP (2006) Rejuvenation of the aging upper third of the face. Facial Plast Surg 22(2):91–96
Abramo AC (1995) Anatomy of the forehead muscles: the basis for the videoendoscopic approach in forehead rhytidoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 95(7):1170–1177
Nemoto M, Uchinuma E, Yamashina S (2002) Three-dimensional analysis of forehead wrinkles. Aesthetic Plast Surg 26(1):10–16
Troilius C (2004) Subperiosteal brow lifts without fixation. Plast Reconstr Surg 114:1595-1603; discussion 1604-5
Core GB, Vasconez LO, Askren C et al (1992) Coronal face-lift with endoscopic techniques. Plast Surg Forum 15:227
Mavrikakis I, DeSousa JL, Malhotra R (2008) Periosteal fixation during subperiosteal brow lift surgery. Dermatol Surg 34(11):1500–1506
Walden JL, Brown CC, Klapper AJ, Chia CT, Aston SJ (2005) An anatomical comparison of transpalpebral, endoscopic, and coronal approaches to demonstrate exposure and extent of brow depressor muscle resection. Plast Reconstr Surg 116(5):1479–1487
Standring S (2004) Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 39th ed. edn. London, Churchill Livingstone, pp 502–503
Nahai F (2005) The Art of Aesthetic Surgery: Principles and Techniques, Vol. 2. Quality Medical Publishing, Inc., St. Louis, p 846
Brand PW (1985) Clinical Mechanics of the Hand. CV Mosby, St. Louis
Brand PW, Beach RB, Thompson DE (1981) Relative tension and potential excursion of muscles in the forearm and hand. J Hand Surg Am 6:209–219
Guyton A, Hall J (2006) Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 72–83
Tabatabai N, Spinelli HM (2007) Limited incision nonendoscopic brow lift. Plast Reconstr Surg 119(5):1563–1570
Caminer DM, Newman MI, Boyd JB (2006) Angular nerve: new insights on innervation of the corrugator supercilii and procerus muscles. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59(4):366–372
Disclosures
F. Hafezi, B. Naghibzadeh, A. Nouhi, and G. Naghibzadeh have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hafezi, F., Naghibzadeh, B., Nouhi, A. et al. Eliminating Frown Lines with an Endoscopic Forehead Lift Procedure (Corrugator Muscle Disinsertion). Aesth Plast Surg 35, 516–521 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9649-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9649-9