Abstract
Background
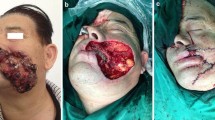
This report aims to describe the technique of using combined flaps for reconstruction of wide-range facial defects.
Methods
Two or more flaps were combined to repair wide-range facial wounds, complying with the principle of facial aesthetic subunits to maintain the inherent structural characteristics of the face, to design incision lines conforming to the natural facial contour lines (e.g., nasolabial fold, sulcus alaris, nasomaxillary suture, palpebral margin, vermilion border, hairline) or wrinkles, and to leave hidden incision lines if possible. There were 18 cases with excessively large facial defects requiring the use of a graft with local flaps.
Results
From April 1996 to May 2008, 124 patients had their wide-range facial defects repaired by combined flaps. The size of the defects ranged in size from 2.5 × 4 to 9 × 10 cm. The healing for all the patients was uneventful, and the flap survived completely without complications. After an average of 6 months (range, 1–48 months), 87 of the patients were available for follow-up evaluation. There was no recurrence of tumor. The repaired tissues were well matched with surrounding tissue in color, texture, and contour. Incision lines were sheltered, and there were no anatomic deformities of the eyelid, upper lip, or nasal ala.
Conclusions
Based on the facial aesthetic subregion principle, combined flaps were used to reconstruct wide-range facial defects effectively, obtaining good color, contour, and texture match with the surrounding skin. All in all, the cosmetic results were satisfactory.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fader DJ, Wang TS, Johnson TM (2002) The Z-plasty transposition flap for reconstruction of the middle cheek. J Am Acad Dermatol 46:738–742
Dobratz EJ, Hilger PA (2009) Cheek defects. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 17:455–467
Yamauchi M, Yotsuyanagi T, Ezoe K et al. (2010) Reverse facial artery flap from the submental region. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 63:58358-8
Benlier E, Top H, Cinar C et al (2007) Reverse-flow retroauricular island flap in facial reconstruction. Dermatol Surg 33:1442–1450
Li JH, Xing X, Li P et al (2007) Transposition movement of V-Y flaps for facial reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 60:1244–1247
Başterzi Y, Sar A, Unal S et al (2007) Versatility of frontal island flaps in the reconstruction of periorbital soft tissue defects. J Craniofac Surg 18:1108–1113
Spence RJ (2008) An algorithm for total and subtotal facial reconstruction using an expanded transposition flap: a 20-year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:795–805
Kaufman AJ (2006) Bilateral vermilion rotation flap. Dermatol Surg 32:721–725
Yenidunya MO, Demirseren ME, Ceran C (2007) Bilobed flap reconstruction in infraorbital skin defects. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:145–150
Murillo WL, Fernandez W, Caycedo DJ et al (2004) Cheek and inferior eyelid reconstruction after skin cancer ablation. Clin Plast Surg 31:49–67
Ninkovic M, di Spilimbergo SS, Ninkovic M (2007) Lower lip reconstruction: introduction of a new procedure using a functioning gracilis muscle free flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:1472–1480
Rohrich RJ, Griffin JR, Ansari M et al (2004) Nasal reconstruction—beyond aesthetic subunits: a 15-year review of 1,334 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 114:1405–1416
Harris GJ, Perez N (2003) Anchored flaps in post-Mohs reconstruction of the lower eyelid, cheek, and lateral canthus: avoiding eyelid distortion. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 19:5–13
Robinson JK (2004) Segmental reconstruction of the face. Dermatol Surg 30:67–74
Chen W, Zeng S, Li J, Yang Z et al (2007) Reconstruction of full-thickness cheek defects with combined temporalis myofacial and facial-cervico-pectoral flaps. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103:e10–e15
Ciatti S, Greenbaum SS (1999) Modified purse-string closure for reconstruction of moderate/large surgical defects of the face. Dermatol Surg 25:215–219
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first two authors contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, CY., Li, L., Guo, LL. et al. Combined Flaps for Reconstructing Wide-Range Facial Defects. Aesth Plast Surg 35, 13–18 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9548-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-010-9548-0