Abstract
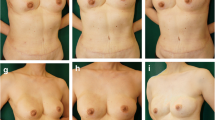
Pectus excavatum is a common type of congenital chest wall abnormality. The defect ranges in severity from mild to severe, and can lead to cardiopulmonary impairment caused by the caved-in chest. The case of a 27-year-old woman with mild pectus excavatum and a diagnosis of scleroderma is reported. Cosmetic correction of pectus excavatum malformation with the use of autologous fat transplantation has never been reported. The individual achievement of relief from the psychological consequences of such disfigurement and the improvement in quality of life are high. Autologous fat transfer could be a new option in the armamentarium of techniques for correction of mild pectus deformities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams AM, Crabbe DC (2003) Pectus deformities of the anterior chest wall. Paediatr Respir Rev 4:237–242
Fox JP, Schnell JL, Adams TA Jr, Hilton WM, Seyfer AE (2007) Pectus excavatum: Comparison of nonprosthetic repairs using multiple techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 119:33e–39e
Pereira LH, Radwanski HN (1996) Fat grafting of the buttocks and lower limbs. Aesth Plast Surg 20:409–416
Onishi K, Maruyama Y (2001) Correction of pectus excavatum using a sternal elevator: Preliminary report. Br J Plast Surg 54:117–124
Horch RE, Stoelben E, Carbon R, Sultan AA, Bach AD, Kneser U (2006) Pectus excavatum breast and chest deformity: Indications for aesthetic plastic surgery versus thoracic surgery in a multicenter experience. Aesth Plast Surg 30:403–411
Margulis A, Sela M, Neuman R, Buller-Sharon A (2006) Reconstruction of pectus excavatum with silicone implants. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:1082–1086. Epub 2006 May 11
Dancey AL, Waters RA (2006) Morphea of the breast: Two case reports and discussion of the literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 59:1114–1117
Chen K, See A, Shumack S (2003) Epidemiology and pathogenesis of scleroderma. Australas J Dermatol 44:1–7
Granel B, Serratrice J, Gaudy C, Weiller-Merli C, Bonerandi JJ, Lepidi H, Coulomb-Marchetti B, Disdier P, Weiller PJ (2001) Localized morphea after silicone-gel-filled breast implant. Dermatology 202:143–144
Torrelo A, Suarez J, Colmenero I, Azorin D, Perera A, Zambrano A (2006) Deep morphea after vaccination in two young children. Pediatr Dermatol 23:484–487
Komocsi A, Tovari E, Kovacs J, Czirjak L (2000) Physical injury as a provoking factor in three patients with scleroderma. Clin Exp Rheumatol 18:622–624
Ghobadi F, Zangeneh M, Massoud BJ (1995) Free fat autotransplantation for the cosmetic treatment of first web space atrophy. Ann Plast Surg 35:197–200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, L.H., Sterodimas, A. Free Fat Transplantation for the Aesthetic Correction of Mild Pectus Excavatum. Aesth Plast Surg 32, 393–396 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-007-9110-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-007-9110-x