Abstract
Background
Capsule formation around breast implants, development of tendon adhesions after tendon repair, intestinal brits after laparatomies, hypertrophic scars in skin incisions all are the results of excessive collagen synthesis to the extracellular matrix by fibroblasts. Any intervention that leads to cessation of collagen synthesis in these clinical situations may help to prevent these untoward results of wound healing. Although 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) is used mainly as a cytotoxic drug in chemotherapy protocols, it decreases cellular metabolism and blocks protein synthesis only at lower concentrations. Findings have shown that 5-FU downregulates fibroblast proliferation and differentiation in vitro. It has been used to treat fibroproliferative disorders of the eye and skin and is thought to inhibit thymidylate synthetase, blocking DNA replication.
Methods
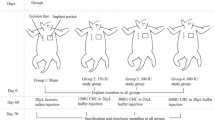
This study used five treatment groups: (1) gelatin only, (2) silicone only, (3) silicone + gelatin, (4) silicone + gelatin containing 1 mg of 5-FU, and (5) silicone + gelatin containing 5 mg of 5-FU. The release kinetics of 5-FU from gelatin have been investigated by means of ultraviolet spectrophotometric analysis. Specimens were obtained on postoperative day 30. Gross evaluation and histopathologic examination were conducted for capsule formation and the development of inflammation.
Results
The silicone group had the most prominent capsule formation among all the groups. The gelatin group was second, and the silicone + gelatin group was third. As compared with the other groups, the 5-FU–containing groups had the least capsule formation. The 5-mg 5-FU–containing group had the most inflammation. The silicone + gelatin group was second in inflammation. Although the silicone, gelatin, and 1-mg 5-FU–containing groups had the same means, the results of the silicone group showed the most divergent data within the group.
Conclusions
Because 5-FU loaded to a gelatin carrier for its slow release seems to prevent capsule formation around silicone blocks, it may be used to prevent capsule formation around silicone breast implants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams WP Jr, Haydon MS, Raniere J Jr, Trott S, Marques M, Feliciano M, Robinson JB Jr, Tang L, Brown SA: A rabbit model for capsular contracture: Development and clinical implications. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1214–1219, 2006
Akali A, Khan U, Khaw PT, McGrouther AD: Decrease in adhesion formation by a single application of 5-fluorouracil after flexor tendon injury. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:151–158, 1999
Baker JL Jr, Chandler ML, LeVier RR: Occurrence and activity of myofibroblasts in human capsular tissue surrounding mammary implants. Plast Reconstr Surg 68:905–912, 1981
Bender RA, Zwelling LA, Doroshow JH, Locker GY, Hande KR, Murinson DS, Cohen M, Myers CE, Chabner BA: Antineoplastic drugs: Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic use. Drugs 16:46–87, 1978
Bucky LP, Ehrlich HP, Sohoni S, May JW Jr: The capsule quality of saline-filled smooth silicone, textured silicone, and polyurethane implants in rabbits: A long-term study. Plast Reconstr Surg 93:1123–1131, 1994
Bulstrode NW, Mudera V, McGrouther DA, Grobbelaar AO, Cambrey AD: 5-fluorouracil selectively inhibits collagen synthesis. Plast Reconstr Surg 116:209–221, 2005
Clugston PA, Perry LC, Hammond DC, Maxwell GP: A rat model for capsular contracture: The effects of surface texturing. Ann Plast Surg 33:595–599, 1994
Coleman DJ, Foo IT, Sharpe DT: Textured or smooth implants for breast augmentation? A prospective controlled trial. Br J Plast Surg 44:444–448, 1991
De Cholnoky T: Augmentation mammaplasty: Survey of complications in 10,941 patients by 265 surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg 45:573–577, 1970
Domanskis E, Owsley JQ Jr: Histological investigation of the etiology of capsule contracture following augmentation mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 58:689–693, 1976
Fitzpatrick RE: Treatment of inflamed hypertrophic scars using intralesional 5-FU. Dermatol Surg 25:224–232, 1999
Frangou J, Kanellaki M: The effect of local application of mitomycin-C on the development of capsule around silicone implants in the breast: An experimental study in mice. Aesth Plast Surg 25:118–128, 2001
Kamel M, Protzner K, Fornasier V, Peters W, Smith D, Ibanez D: The peri-implant breast capsule: An immunophenotypic study of capsules taken at explantation surgery. J Biomed Mater Res 58:88–96, 2001
Khaw PT, Sherwood MB, MacKay SL, Rossi MJ, Schultz G: Five-minute treatments with fluorouracil, floxuridine, and mitomycin have long-term effects on human Tenon’s capsule fibroblasts. Arch Ophthalmol 110:1150–1154, 1992
Lebwohl M: From the literature: Intralesional 5-FU in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids: Clinical experience. J Am Acad Dermatol 42:67, 2000
Manuskiatti W, Fitzpatrick RE: Treatment response of keloidal and hypertrophic sternotomy scars: Comparison among intralesional corticosteroid, 5-fluorouracil, and 585-nm flashlamp-pumped pulsed-dye laser treatments. Arch Dermatol 138:1149–1155, 2002
Moran SL, Ryan CK, Orlando GS, Pratt CE, Michalko KB: Effects of 5-fluorouracil on flexor tendon repair. J Hand Surg Am 25:242–251, 2000
Occleston NL, Daniels JT, Tarnuzzer RW, Sethi KK, Alexander RA, Bhattacharya SS, Schultz GS, Khaw PT: Single exposures to antiproliferatives: Long-term effects on ocular fibroblast wound-healing behavior. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 38:1998–2007, 1997
Ophir A, Ticho U: A randomized study of trabeculectomy and subconjunctival administration of fluorouracil in primary glaucomas. Arch Ophthalmol 110:1072–1075, 1992
Ragoowansi R, Khan U, Brown RA, McGrouther DA: Reduction in matrix metalloproteinase production by tendon and synovial fibroblasts after a single exposure to 5-fluorouracil. Br J Plast Surg 54:283–287, 2001
Rudolph R, Abraham J, Vecchione T, Guber S, Woodward M: Myofibroblasts and free silicon around breast implants. Plast Reconstr Surg 62:185–196, 1978
Soppimath K, Aminabhavi T, Kulkami A, Rudzinzki W: Biodegradable polymericnanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J Control Release 70:1–20, 2001
Vinnik CA: Spherical contracture of fibrous capsules around breast implants: Prevention and treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 58:555–560, 1976
Wilkerson M, Fulcher S, Shields MB, Foulks GN, Hatchell DL, Houston LL: Inhibition of human subconjunctival fibroblast proliferation by immunotoxin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33:2293–2298, 1992
Yamamoto T, Varani J, Soong HK, Lichter PR: Effects of 5-fluorouracil and mitomycin C on cultured rabbit subconjunctival fibroblasts. Ophthalmology 97:1204–1210, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibrahim Canter, H., Konas, E., Bozdogan, O. et al. Effect of Slow-Release 5-Fluorouracil on Capsule Formation Around Silicone Breast Implants: An Experimental Study with Mice. Aesth Plast Surg 31, 674–679 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0172-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-006-0172-y