Abstract
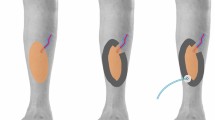
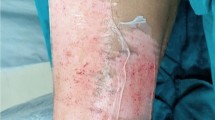
Reconstruction of tissue defects with skin grafts is one of the most used processes in soft tissue defects. While any part of the body can be used as a donor site of split-thickness skin grafts, the posterolateral thigh is the most used one. Pain in the graft donor site may be the primary concern of patients in the postoperative period. Various kinds of donor site dressings and procedures have been described for this purpose. The main goal of this practice is the fast recovery of the donor site. Nevertheless, avoiding infection, decreasing the pain in the donor site, and minimizing the cost should be considered. To minimize pain in the graft donor site, ice pack application, used for its local anesthetic effect, was utilized for patients postoperatively in our clinic. Thirty-six patients were included in this study between June 2001 and May 2002. Patients were divided into two groups, with 18 patients in-group I, to whom ice was applied, and 18 patients in group II, which was specified as the control group. The patients were evaluated according to the pain in the graft donor site. The visual analog scale (VAS) was used to evaluate the pain of the patients. The data were statistically evaluated with the Mann–Whitney U test procedure. In addition to this, infections, recovery periods, and cost benefit effects were also determined. The mean pain scores in the graft donor site were found to be quite low in patients in the group with ice application (p < 0.05). No significant difference was determined between the two groups when their pain scales were compared on the fourth and the fifth days (p > 0.05). Ice can be safely used in patients for whom donor site pain is the primary concern, with advantages such as ease of application, low cost (almost free), and a significant decrease in pain in the donor site.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DL Feldman (1991) ArticleTitleWhich dressing for split thickness skin graft donor sites? Ann Plast Surg 27 288 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2D28%2FotFA%3D Occurrence Handle1952757
SC Brady CFT Snelling G Chow (1980) ArticleTitleComparison of donor site dressing. Ann Plast Surg 5 238 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6D1cvmvVU%3D Occurrence Handle7004320
RM Gemberling TA Miller H Caffee BE Zawacki (1976) ArticleTitleDressing comparison in the healing of donor sites. J Trauma 16 812 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSiD2MzpsFQ%3D Occurrence Handle792464
H Kılınç O Sensoz R Ozdemir et al. (2001) ArticleTitleWhich dressing for split thickness graft donor sites? Ann Plast Surg 46 409 Occurrence Handle11324884
GG Hallock (1999) ArticleTitleThe cosmetic split thickness skin graft donor site. Plast Reconstr Surg 104 2286
RC Hagerty H Warm (1990) ArticleTitlePrimary closure of the split thickness donor site. Plast Reconstr Surg 85 293
S Cenetoğlu S Özmen S Tuncer O Latifoğlu R Yavuzer (2000) ArticleTitleTopical lignocaine gel for split-thickness skin graft donor-site pain management. Plast Reconstr Surg 105 2633
TD Owen D Dye (1990) ArticleTitleThe value of topical lignocaine gel in pain relief on skin graft donor sites. Br J Plast Surg 43 480 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BA28notFI%3D Occurrence Handle2099753
CN Ramaswamy (1991) ArticleTitleTopical lignocaine gel on skin graft donor sites. Br J Plast Surg 44 157 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6B3cflt1w%3D
WT Morris AM Lamb (1990) ArticleTitlePainless split donor sites: A controlled double-blind trial of Opsite, Scarlet Red, and Bupivacaine. Aust N Z J Surg 60 617 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BA2Mfnt1E%3D Occurrence Handle2202283
PE Butler PA Eadie D Lawlor et al. (1993) ArticleTitleBupivacaine and Kaltostat reduces post-operative donor site pain. Br J Plast Surg 46 523 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD3srosVw%3D Occurrence Handle8220862
WT Hyland (1982) ArticleTitleA painless donor site dressing. Plast Reconstr Surg 69 703
ST Tan RH Roberts BG Blake (1993) ArticleTitleComparing Duoderme with Scarlet Red in the treatment of split skin graft donor sites. Br J Plast Surg 46 79 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyC287gsFA%3D Occurrence Handle8431748
ST Tan RH Roberts SW Sinclair (1993) ArticleTitleComparison of Zenoderm with Duoderme in the treatment of split skin graft donor sites. Br J Plast Surg 46 82 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyC287gsFE%3D Occurrence Handle8431749
OM Alvarez PM Mertz WH Eaglestein (1983) ArticleTitleThe effect of occlusive dressings on collogen synthesis and reepithelialization in superficial wounds. J Surg Res 35 142 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXlt1ygsrg%3D Occurrence Handle6887836
MC Varghese AK Balin M Carter D Caldwell (1986) ArticleTitleLocal environment of chronic wounds under synthetic dressings. Arch Dermatol 122 52 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BimC3c3itVY%3D Occurrence Handle3079991
VJ Ablaza AC Berlet ME Manstein (1997) ArticleTitleAn alternative treatment for the split skin graft donor site. Aesth Plast Surg 21 207 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002669900112 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiA2cfhtFM%3D
RJ Wood GL Peltier JA Twomey (1989) ArticleTitleManagement of the difficult split thickness donor site. Ann Plast Surg 22 80 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaC28rhvFM%3D Occurrence Handle2647021
JN Bulmer AC Duckett (1985) ArticleTitleAbsorption of lignocaine through split skin donor sites. Anaesthesia 40 808 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqA3cvns1M%3D Occurrence Handle3898909
IK Cohen MC Crossland A Garrett RF Diegelmann (1995) ArticleTitleTopical application of epidermal growth factor onto partial thickness wounds in human volunteers does not enhance reepithelialization. Plast Reconstr Surg 96 251
GL Brown LB Nanney J Griffen et al. (1989) ArticleTitleEnhancement of wound healing by topical treatment with epidermal growth factor. N Engl J Med 321 76 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaB1c7msFM%3D Occurrence Handle2659995
R Fratianne F Papay I Housini et al. (1993) ArticleTitleKeratinocyte allografts accelerate healing of split thickness donor sites: Applications for improved treatment of burns. J Burn Care Rehab 14 148 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB2sznslU%3D
ML Tenchini C Ranzati M Malcovati (1992) ArticleTitleCulture techniques for human keratinocytes. Burns 18 S11
M De Luca R Cancedda (1992) ArticleTitleCulture of human epithelium. Burns 18 S5
M Akan S Yıldırım A Mısırlıoglu G Ulusoy T Aköz G Avcı (2003) ArticleTitleAn alternative method to minimize pain in the split thickness skin graft donor site. Plast Reconstr Surg 111 2243
E Ernst V Fialka (1994) ArticleTitleIce freezes pain? A review of the clinical effectiveness of analgesic cold therapy. J Pain Symptom Manage 9 56 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuB38zhsVA%3D Occurrence Handle8169463
B Ronald (1975) ArticleTitleThe cooling, analgesic, and rewarming effects of ice massage on localized skin. Phys Ther 55 11 Occurrence Handle1088989
R Clarke R Hellon A Lind (1958) ArticleTitleThe duration of sustained contractions of the human forearm at different muscle temperature. J Physiol 143 454 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CyaD3MjpsFU%3D Occurrence Handle13588567
TK Raymond BS Robert (2001) ArticleTitleEMLA versus ice as a topical anesthetic. Dermatol Surg 27 495 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1524-4725.2001.00343.x Occurrence Handle11359502
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akan, M., Misirlioğlu, A., Yildirim, S. et al. Ice Application to Minimize Pain in the Split-Thickness Skin Graft Donor Site . Aesth. Plast. Surg. 27, 305–307 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-003-3014-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-003-3014-1