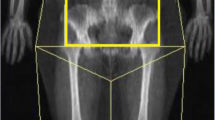
Liposuction is a safe procedure for removal of subcutaneous fat in patients with upper leg lipodystrophy. We present a young woman with lipodystrophy of upper leg who underwent ultrasound-assisted three-dimensional suction lipectomy. The aim of the study was to determine the amount of fat to be removed before liposuction and to evaluate soft tissue composition before and after liposuction. At the initial meeting and four months later, body composition parameters were examined by dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), which produced a precise assessment of regional fat distribution. The baseline DXA measurements revealed excess of fat tissue for the lateral regions of the right and left legs, and for the area from the waist to hip. After liposuction of established amount of tissue, the same measurements revealed a decrease of fat tissue in all three regions, whereas no significant differences were observed for lean mass. We concluded that the suction lipectomy produced decrease in the fat mass of legs without musculature damage. The DXA technique can be useful in predicting fat removal before suction lipectomy and in estimating changes in soft tissue composition after surgical treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maiolo, C., Cervelli, V., Fede, M. et al. Soft Tissue Composition in Upper Leg Lipodystrophy: Application of Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry . Aesth. Plast. Surg. 26, 345–347 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-002-1507-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-002-1507-y