Abstract
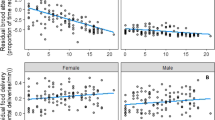
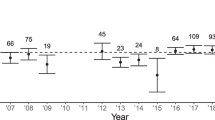
In western bluebirds (Sialia mexicana), most pairs remain together for life and share equally in post-hatching parental care. We removed resident males of socially monogamous pairs during laying and after clutch completion to examine chick-feeding rules used by replacement males and current and future fitness consequences of paternal care. Replacement males were not infanticidal and 7 (47%) fed nestlings. Feeding replacement males and the females they joined fed at rates similar to controls. Females without a feeding replacement male compensated by feeding more themselves so that overall feeding rates were not compromised, but they reduced their brooding time. Unlike assisted females, unassisted females exhibited reduced nesting success and their 14-day-old chicks weighed less than controls. Field metabolic rates of unassisted females were 17% higher than those of control females, but the difference was not statistically significant. Older females were better able to raise young without the male's help than were yearling females. Female condition was not affected by male provisioning and unassisted females were as likely to survive to the next breeding season as assisted females. We found no future benefits of provisioning by replacement males; those that fed were no more likely to breed with the female on her subsequent attempt than were males that did not feed, and subsequent clutch sizes were not reduced for females rearing young without the male's help. These experiments suggest that male parental care increases nesting success in western bluebirds and that replacement males use an all-or-none rule to determine whether or not to feed chicks: if they are present during the fertile period they feed at typical rates; if they are not, they usually do not feed at all. Because chick-feeding by males is tied to opportunity for paternity, influences success in the current nest, and does not affect the male's future breeding success, it appears to be parental rather than mating effort.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 May 1998 / Accepted after revision: 23 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dickinson, J., Weathers, W. Replacement males in the western bluebird: opportunity for paternity, chick-feeding rules, and fitness consequences of male parental care. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 45, 201–209 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650050554
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650050554