Abstract
Purpose
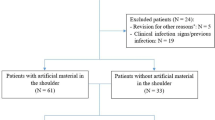
The objective of the study was to compare the functional outcomes and the complication rate of the patients with C. acnes contamination at the end of the primary reverse shoulder arthroplasty (RSA) surgery to those patients without C. acnes contamination.
Method
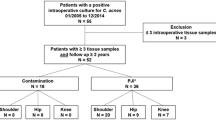
A total of 162 patients were included. In all cases, skin and deep tissue cultures were obtained. A molecular typing characterization of the C. acnes strains was performed. Functional outcomes were assessed with the Constant score at the two and five year follow-up and all complications were also recorded.
Results
A total of 1380 cultures were obtained from the 162 primary RSA surgeries. Of those, 96 turned out to be positive for C. acnes. There were 25 patients with positive cultures for C. acnes. The overall postoperative Constant score was not significantly different between those patients having C. acnes–positive cultures and those with negative cultures at the two and five year follow-up (59.2 vs. 59.6 at two years, p 0.870, and 59.5 vs. 62.4 at five years, p 0.360). Patients with positive cultures presented a higher complication rate (p 0.001) with two infections, one revision surgery, and one dislocation.
Conclusion
Patients ending up with C. acnes–positive cultures after primary shoulder arthroplasty surgery do not have worse clinical outcomes when compared to patients having negative cultures, but a greater number of complications were found in those patients with C. acnes–positive cultures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dodson CC, Craig EV, Cordasco FA et al (2010) Propionibacterium acnes infection after shoulder arthroplasty: a diagnostic challenge. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 19:303–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2009.07.065
Falconer TM, Baba M, Kruse LM et al (2016) Contamination of the surgical field with Propionibacterium acnes in primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 98:1722–1728. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.15.01133
Hsu JE, Matsen FA III, Whitson AJ, Bumgarner RE (2020) Cutibacterium subtype distribution on the skin of primary and revision shoulder arthroplasty patients. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 29:2051–2055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2020.02.0027
Hudek R, Brobeil A, Brüggemann H, Sommer F, Gattenlöhner S, Gohlke F (2021) Cutibacterium acnes is an intracellular and intra-articular commensal of the human shoulder joint. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 30:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2020.04.020
Hudek R, Sommer F, Kerwat M, Abdelkawi AF, Loos F, Gohlke K (2014) Propionibacterium acnes in shoulder surgery: true infection, contamination, or commensal of deep tissue? J Shoulder Elbow Surg 23:1763–1771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2014.05.024
Kajita Y, Iwahori Y, Harada Y, Takahashi R, Deie M (2021) Incidence of Cutibacterium acnes in open shoulder surgery. Nagoya J Med Sci 83:151–157. https://doi.org/10.18999/nagjms.83.1.151
Koh CK, Marsh JP, Drinkovic D, Walker CG, Poon PC (2016) Propionibacterium acnes in primary shoulder arthroplasty: rates of colonization, patient risk factors, and efficacy of perioperative prophylaxis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25:846–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.09.033
Kolakowski L, Lai JK, Duvall GT et al (2018) Benzoyl peroxide effectively decreases preoperative Cutibacterium acnes shoulder burden: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 27:1539–1544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2018.06.012
Levy O, Iyer S, Atoun E et al (2013) Propionibacterium acnes: an underestimated etiology in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis? J Shoulder Elbow Surg 22:505–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2012.07.007
Maccioni CB, Woodbridge AB, Balestro JCY et al (2015) Low rate of Propionibacterium acnes in arthritic shoulders undergoing primary total shoulder replacement surgery using a strict specimen collection technique. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24:1206–1211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2014.12.026
Matsen FA III, Butler-Wu S, Carofino BC, Jette JL, Bertelsen A, Bumgarner R (2013) Origin of Propionibacterium in surgical wounds and evidence-based approach for culturing Propionibacterium from surgical sites. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95:e181(1-7). https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.L.01733
Matsen FA 3rd, Russ SM, Bertelsen A, Butler-Wu S, Pottinger PS (2015) Propionibacterium can be isolated from deep cultures obtained at primary arthroplasty despite intravenous antimicrobial prophylaxis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24:844–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2014.10.016
Mook WR, Klement MR, Green CL, Hazen KC, Garrigues GE (2015) The incidence of Propionibacterium acnes in open shoulder surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am 97:957–963. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.N.00784
Patel A, Calfee RP, Plante M, Fischer SA, Green A (2009) Propionibacterium acnes colonization of the human shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 18:897–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2009.01.023
Phadnis J, Gordon D, Krishnan J, Bain GI (2016) Frequent isolation of Propionibacterium acnes from the shoulder dermis despite skin preparation and prophylactic antibiotics. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.08.002
Torrens C, Marí R, Alier A, Puig L, Santana F, Corvec S (2019) Cutibacterium acnes in primary reverse shoulder arthroplasty: from skin to deep layers. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 28:839–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2018.10.016
Wong JC, Schoch BS, Lee BK et al (2018) Culture positivity in primary total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 27:1422–1428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2018.05.024
Ahsan ZS, Somerson JS, Matsen FA III (2017) Characterizing the Propionibacterium load in revision shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 99:150–154. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.16.00422
Falstie-Jensen T, Lange J, Daugaard H, Sorensen AKB, Ovesen J, Soballe K (2021) Unexpected positive cultures after revision shoulder arthroplasty: does it affect outcome? J Shoulder Elbow Surg 30:1299–1308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2020.12.0164
Foruria AM, Fox TJ, Sperling JW, Cofield RH (2013) Clinical meaning of unexpected positive cultures (UPC) in revision shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 22:620–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2012.07.017
McGoldrick E, McElvany MD, Butler-Wu S, Pottinger PS, Matsen FA III (2015) Substantial cultures of Propionibacterium can be found in apparently aseptic shoulders revised three years or more after index arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 24:31–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2014.05.008
Padegimas EM, Lawrence C, Narzikul AC et al (2017) Future surgery after revision shoulder arthroplasty: the impact of unexpected positive cultures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 26:975–981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2016.10.0123
Pottinger P, Butler-Wu S, Neradilek MB et al (2012) Prognostic factors for bacterial cultures positive for Propionibacterium acnes and other organisms in a large series of revision shoulder arthroplasties performed for stiffness, pain, or loosening. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94:2075–2083. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.K.00861
Topolski MS, Chin PYK, Sperling JW (2006) Cofield RH (2006) Revision shoulder arthroplasty with positive intraoperative cultures: the value of preoperative studies and intraoperative histology. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 15:402–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2005.10.001
Achermann Y, Goldstein EJC, Coenye T, Shirtliff ME (2014) Propionibacterium acnes: from commensal to opportunistic biofilm-associated implant pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 27:419–440. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00092-13
Dagnelie MA, Khammari A, Dréno B, Corvec S (2018) Cutibacterium acnes molecular typing: time to standardize the method. Clin Microbiol Infect 24:114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2018.03.010
Stull JD, Nicholson TA, Davis DE, Namdari S (2020) Addition of 3% hydrogen peroxide to standard skin preparation reduces Cutibacterium acnes-positive culture rate in shoulder surgery: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 29:212–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2019.09.038
Torrens C, Bellosillo B, Gibert J et al (2022) Are Cutibacterium acnes present at the end of primary shoulder prosthetic surgeries responsible for infection? Prospective study. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 41:169–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-021-04348-6
Aubin GG, Lavigne JP, Foucher Y et al (2017) Tropism and virulence of Cutibacterium (formerly Propionibacterium) acnes involved in implant-associated infection. Anaerobe 47:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2017.04.009
Millett PJ, Yen YM, Price CS, Horan MP, van der Meijden OA, Elser F (2011) Propionobacter acnes infection as an occult cause of postoperative shoulder pain. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:2824–2830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1767-4
Zmistowski B, Nicholson TA, Wang WL, Abboud JA, Namdari S (2021) What is the clinical impact of positive cultures at the time of primary total shoulder arthroplasty? J Shoulder Elbow Surg 30:1324–1328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2020.08.032
Constant CR, Murley AH (1987) A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res 214:160–164
Garrigues GE, Zmistowski B, Cooper AM, Green A, ICM Shoulder Group (2019) Proceedings from the 2018 International Consensus Meeting on Orthopedic Infections: the definition of periprosthetic shoulder infection. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 28:S8–S12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2019.04.034
Van Diek FM, Pruijn N, Spijkers KM, Mulder B, Kosse NM, Dorrestijn O (2020) The presence of Cutibacterium acnes on the skin of the shoulder after the use of benzoyl peroxide: a placebo-controlled, double-blinded, randomized trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 29:768–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2019.11.027
Chalmers PN, Beck L, Stertz I, Tashjian RZ (2019) Hydrogen peroxide skin preparation reduces Cutibacterium acnes in shoulder arthroplasty: a prospective, blinded, controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 28:1554–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2019.03.038
SaltzmanMD NGW, Gryzlo SM, Marecek GS, Koh JL (2009) Efficacy of surgical preparation solutions in shoulder surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:1949–1953. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.H.00768
Scheer VM, Jungeström MB, Lerm M, Serrander L, Kalén A (2018) Topical benzoyl peroxide application on the shoulder reduces Propionibacterium acnes: a randomized study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 27:957–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2018.02.038
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Xavier Duran Jordà, MStat, PhD (Methodology and Biostatistics Support Unit, Institute Hospital del Mar for Medical Research (IMIM), Barcelona, Spain) for his work in data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Carlos Torrens, Raquel Marí, Lluís Puig-Verdier, Fernando Santana, Albert Alier, Eva García-Jarabo, Alba Gómez-Sánchez, and Stèphane Corvec. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Carlos Torrens and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the ethical committee with number 2014/5996/I (CEIC-Parc de Salut Mar).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Torrens, C., Marí, R., Puig-Verdier, L. et al. Functional outcomes and complications of patients contaminated with Cutibacterium acnes during primary reverse shoulder arthroplasty: study at two- and five-years of follow-up. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 47, 2827–2833 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05971-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05971-y