Abstract
Purpose
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to identify risk factors of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty (THA) in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH).
Methods
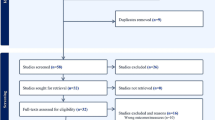
A systematic literature review was performed on 18th August 2022 using Medline, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science electronic databases, and a manual search. The study was conducted according to the PRISMA guidelines and registered with PROSPERO. Statistical analysis includes assessment of heterogeneity and data synthesis using RevMan 5.4.
Results
Review of five studies including 2865 patients and 116 dislocated hips found that lower body mass index (BMI) (SMD = 0.22, p = 0.04, I2 = 0%), Crowe classification type IV versus I, II, and III (OR = 2.70, p = 0.004, I2 = 51%), higher cup inclination (SMD = 0.39 p = 0.0007, I2 = 0%), femoral head size < 28 mm (OR = 5.07, p = 0.003, I2 = 71%), lateral surgical approach (OR = 1.96, p = 0.02, I2 = 0%), and postoperative infection (OR = 6.26, p < 0.0001, I2 = 0%) were significant risk factors. However, age, gender, cup anteversion, femoral osteotomy, vertical (V-COR) centre of rotation, intraoperative fracture, preoperative and postoperative leg length discrepancy (LLD) and previous hip surgery were not found to be significant risk factors.
Conclusion
This study underscores importance of these risk factors in THA planning for DDH patients to reduce dislocation risk. Further research needed to understand mechanisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Gwam CU, Mistry JB, Mohamed NS et al (2017) Current Epidemiology of Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty in the United States: National Inpatient Sample 2009 to 2013. J Arthroplasty 32:2088–2092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2017.02.046
de Palma L, Procaccini R, Soccetti A, Marinelli M (2012) Hospital Cost of Treating Early Dislocation following Hip Arthroplasty. HIP Int 22:62–67. https://doi.org/10.5301/HIP.2012.9059
Kunutsor SK, Barrett MC, Beswick AD et al (2019) Risk factors for dislocation after primary total hip replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 125 studies involving approximately five million hip replacements. Lancet Rheumatol 1:e111–e121. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(19)30045-1
Faldini C, Stefanini N, Fenga D et al (2018) How to prevent dislocation after revision total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review of the risk factors and a focus on treatment options. J Orthop Traumatol 19:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10195-018-0510-2
Falez F, Papalia M, Favetti F et al (2017) Total hip arthroplasty instability in Italy. Int Orthop 41:635–644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3345-6
Fessy MH, Putman S, Viste A et al (2017) What are the risk factors for dislocation in primary total hip arthroplasty? A multicenter case-control study of 128 unstable and 438 stable hips. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 103:663–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2017.05.014
Soong M, Rubash HE, Macaulay W (2004) Dislocation After Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 12:314–321. https://doi.org/10.5435/00124635-200409000-00006
Ullmark G (2016) The unstable total hip arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev 1:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.1.000022
Ravi B, Jenkinson R, Austin PC et al (2014) Relation between surgeon volume and risk of complications after total hip arthroplasty: propensity score matched cohort study. BMJ 348:g3284–g3284. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g3284
Mortazavi SMJ, Ghadimi E, Ardakani MV et al (2022) Risk factors of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip. Int Orthop 46:749–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-021-05294-w
Lo CK-L, Mertz D, Loeb M (2014) Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med Res Methodol 14:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-14-45
Ding Z, Zeng W, Mou P et al (2020) Risk of Dislocation After Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients with Crowe Type IV Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Orthop Surg 12:589–600. https://doi.org/10.1111/os.12665
Wang L, Trousdale RT, Ai S et al (2012) Dislocation After Total Hip Arthroplasty Among Patients With Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. J ARTHROPLASTY 27:764–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2011.08.021
Komiyama K, Fukushi J, Motomura G et al (2019) Does high hip centre affect dislocation after total hip arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip? Int Orthop 43:2057–2063. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4154-x
Yetkin C, Yildirim T, Alpay Y et al (2021) Evaluation of Dislocation Risk Factors With Total Hip Arthroplasty in Developmental Hip Dysplasia Patients: A Multivariate Analysis. J ARTHROPLASTY 36:636–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2020.08.043
Ferguson RJ, Palmer AJ, Taylor A et al (2018) Hip replacement. The Lancet 392:1662–1671. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31777-X
Kuitunen I, Uimonen MM, Haapanen M et al (2022) Incidence of Neonatal Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip and Late Detection Rates Based on Screening Strategy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open 5:e2227638. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.27638
Guo L, Yang Y, An B et al (2017) Risk factors for dislocation after revision total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg 38:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.12.122
Cross MB, Nam D, Mayman DJ (2012) Ideal Femoral Head Size in Total Hip Arthroplasty Balances Stability and Volumetric Wear. HSS J ® 8:270–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-012-9287-7
Cameron HU, Botsford DJ, Park YS (1996) Influence of the crowe rating on the outcome of total hip arthroplasty in congenital hip dysplasia. J Arthroplasty 11:582–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-5403(96)80113-6
Gustke K (2013) The dysplastic hip NOT FOR THE SHALLOW SURGEON. BONE Jt J 95B:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.95B11.32899
Wiznia DH, Buchalter DB, Kirby DJ et al (2021) Applying the hip-spine relationship in total hip arthroplasty. HIP Int 31:144–153. https://doi.org/10.1177/1120700020949837
Romagnoli M, Grassi A, Costa GG et al (2019) The efficacy of dual-mobility cup in preventing dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Int Orthop 43:1071–1082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4062-0
Lan Y, Feng E, Lin B et al (2022) Direct anterior versus posteriorlateral approachs for clinical outcomes after total hip arthroplasty in the treatment of severe DDH. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 23:958. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-022-05759-y
Yang S (2012) Total hip arthroplasty in developmental dysplasia of the hip: Review of anatomy, techniques and outcomes. World J Orthop 3:42. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v3.i5.42
Kosashvili Y, Backstein D, Safir O et al (2011) Dislocation and Infection After Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 26:1170–1175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2011.04.022
Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R et al (1978) Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am 60:217–220
Jolles BM, Zangger P, Leyvraz P-F (2002) Factors predisposing to dislocation after primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 17:282–288. https://doi.org/10.1054/arth.2002.30286
on behalf of the Lundbeck Foundation Centre for Fast-track Hip and Knee Replacement Collaborative Group, Jørgensen CC, Kjaersgaard-Andersen P, et al (2014) Hip dislocations after 2,734 elective unilateral fast-track total hip arthroplasties: incidence, circumstances and predisposing factors. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134:1615–1622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-2051-3
Funding
There is no funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Parmida Shahbazi, Amir Hossein Jalilvand, Amirhossein Ghaseminejad-Raeini and Mehrdad Sheikhvatan. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Parmida Shahbazi, Amir Hossein Jalilvand, Amirhossein Ghaseminejad-Raeini and Ali Ghaderiand all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shahbazi, P., Jalilvand, A.H., Ghaseminejad-Raeini, A. et al. Risk Factors for Dislocation following Total Hip Arthroplasty in Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 47, 3063–3075 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05949-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05949-w