Abstract
Purpose
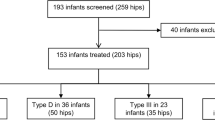
Pavlik harness treatment is the most common treatment in newborns diagnosed with developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). The success rates and predictors for failure have been debated over the last decade. In this study, we explored our treatment failure rate and potential prognostic factors that could predict the failure of Pavlik harness (PH) treatment in patients with DDH.
Methods
Two hundred and sixty-five patients were treated with PH based on the Graf hip types of classification. Age, gender, first born status, family history, foot deformity, plagiocephaly, breech presentation, hip abduction, hip stability, Graf hip type, Galeazzi sign, bilateralism, and femoral nerve palsy were tested as predictors for failure in multivariate logistic regression mode. Success and failure were determined by the normalization of the hip based on the Graf hip classification.
Results
The failure rate of patients treated with Pavlik harness was 16.6% which is within the reported range of failure rate. The mean age of patients who were successfully treated was 6.73 weeks in comparison to 8.84 weeks for those who failed. Age, plagiocephaly, hip instability, Graf classification, and the development of femoral nerve palsy were found to be predictors for failure of PH treatment upon univariate analysis only. However, only the presence of Galeazzi sign, hip instability, high grades of Graf hip classification, and the development of femoral nerve palsy proved to be independent predictors for failed PH treatment upon multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Conclusions
Pavlik harness treatment is a successful treatment with an average success of 83.4%. Several independent predictors for failure of PH treatment have been identified. These include a positive Galeazzi sign, a frankly dislocated hip, Graf types III and IV, and the development of femoral nerve palsy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Anonymous data is available on request.
Code availability
SPSS output data is available on request.
References
Alshryda S, Wright J (2013) A harness for treatment of congenital hip dislocation in infants. In: Classic papers in orthopaedics. Springer Science + Business Media. pp 555–557
Alshryda S, Jones S, Banaszkiewicz PA (2014) Postgraduate paediatric orthopaedics: the candidate’s guide to the FRCS (Tr and Orth) examination. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Thaler M, Biedermann R, Lair J, Krismer M, Landauer F (2011) Cost-effectiveness of universal ultrasound screening compared with clinical examination alone in the diagnosis and treatment of neonatal hip dysplasia in Austria. J Bone Joint Surg British 93-B:1126–1130. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.93b8.25935
Shorter D, Hong T, Osborn DA (2013) Cochrane review: screening programmes for developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborn infants. Evid Based Child Health 8:11–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/ebch.1891
Paton RW (2005) Screening for hip abnormality in the neonate. Early Hum Dev 81:803-806. S0378-3782(05)00184-2 [pii] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2005.09.001
de Hundt M, Vlemmix F, Bais JM, Hutton EK, de Groot CJ, Mol BW, Kok M (2012) Risk factors for developmental dysplasia of the hip: a meta-analysis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 165:8-17. S0301-2115(12)00297-7 [pii] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2012.06.030
Ortiz-Neira CL, Paolucci EO, Donnon T (2011) A meta-analysis of common risk factors associated with the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip in newborns. Eur J Radiol 81:e344-351. S0720-048X(11)00771-6 [pii] https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.11.003
Ömeroglu H (2018) Treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip with the Pavlik harness in children under six months of age: indications, results and failures. J Children’s Orthop 12:308–316. https://doi.org/10.1302/1863-2548.12.180055
Õmeroğlu H (2014) Use of ultrasonography in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Children’s Orthop 8:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-014-0561-8
Gardner ROE, Kelley SK, Alshryda S, Wedge J (2016) Chapter 4: evidence-base for the management of developmental dysplasia of the hip. In: Alshryda H, Banaszkiewicz (ed) Paediatric orthopaedics: an evidence-based approach to clinical questions. Springer. pp 51–75.
Omeroglu H, Kose N, Akceylan A (2015) Success of Pavlik harness treatment decreases in patients >/= 4 months and in ultrasonographically dislocated hips in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-015-4388-5
Al-Essa RS, Aljahdali FH, Alkhilaiwi RM, Philip W, Jawadi AH, Khoshhal KI (2017) Diagnosis and treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a current practice of paediatric orthopaedic surgeons. J Orthop Surg 25:230949901771719. https://doi.org/10.1177/2309499017717197
Swarup I, Penny CL, Dodwell ER (2018) Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Curr Opin Pediatr 30:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/mop.0000000000000574
Ashoor M, Abdulla N, Elgabaly EA, Aldlyami E, Alshryda S (2020) Evidence based treatment for developmental dysplasia of the hip in children under 6 months of age. Syst Rev Exploratory Anal Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surge.2020.02.006
Gulati V (2013) Developmental dysplasia of the hip in the newborn: a systematic review. World J Orthop 4:32. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v4.i2.32
Pavlik A (1953) A harness for treatment of congenital hip dislocation in infants. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech 20:93–100
Pavlik A (1992) The functional method of treatment using a harness with stirrups as the primary method of conservative therapy for infants with congenital dislocation of the hip. 1957. Clin Orthop Relat Res (281):4–10
van der Sluijs JA, De Gier L, Verbeke JI, Witbreuk MM, Pruys JE, van Royen BJ (2009) Prolonged treatment with the Pavlik harness in infants with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91:1090–1093. 91-B/8/1090 [pii] https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.91B8.21692
Nakamura J, Kamegaya M, Saisu T, Someya M, Koizumi W, Moriya H (2007) Treatment for developmental dysplasia of the hip using the Pavlik harness: long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89:230-235. 89-B/2/230 [pii] https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.89B2.18057
Grill F, Bensahel H, Canadell J, Dungl P, Matasovic T, Vizkelety T (1988) The Pavlik harness in the treatment of congenital dislocating hip: report on a multicenter study of the European Paediatric Orthopaedic Society. J Pediatr Orthop 8:1–8
Wilkinson AG, Sherlock DA, Murray GD (2002) The efficacy of the Pavlik harness, the Craig splint and the von Rosen splint in the management of neonatal dysplasia of the hip. A comparative study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:716–719
Cashman JP, Round J, Taylor G, Clarke NM (2002) The natural history of developmental dysplasia of the hip after early supervised treatment in the Pavlik harness. A prospective, longitudinal follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:418–425
Wada I, Sakuma E, Otsuka T, Wakabayashi K, Ito K, Horiuchi O, Asagai Y, Kamegaya M, Goto E, Satsuma S, Kobayashi D, Saito S, Taketa M, Takikawa K, Nakashima Y, Hattori T, Mitani S, Wada A (2013) The Pavlik harness in the treatment of developmentally dislocated hips: results of Japanese multicenter studies in 1994 and 2008. J Orthop Sci 18:749–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-013-0432-z
Westacott DJ, Mackay ND, Waton A, Webb MS, Henman P, Cooke SJ (2013) Staged weaning versus immediate cessation of Pavlik harness treatment for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B 23:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPB.0000000000000025
Murnaghan ML, Browne RH, Sucato DJ, Birch J (2011) Femoral nerve palsy in Pavlik harness treatment for developmental dysplasia of the hip. The Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume 93:493-499. 93/5/493 [pii] https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.01210
Mafalda Santos M, Filipe G (1997) [Treatment of congenital hip dislocation using Pavlik’s harness. Long term results].Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 83:41-50. MDOI-RCO-02-1997-83-1-0035-1040-101019-ART75 [pii]
Filipe G, Carlioz H (1982) Use of the Pavlik harness in treating congenital dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 2:357–362
Atar D, Lehman WB, Tenenbaum Y, Grant AD (1993) Pavlik harness versus Frejka splint in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: bicenter study. J Pediatr Orthop 13:311–313
Czubak J, Piontek T, Niciejewski K, Magnowski P, Majek M, Plonczak M (2004) Retrospective analysis of the non-surgical treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip using Pavlik harness and Frejka pillow: comparison of both methods. OrtopTraumatol Rehabil 6:9-13. 10796 [pii]
Johnson AH, Aadalen RJ, Eilers VE, Winter RB (1981) Treatment of congenital hip dislocation and dysplasia with the Pavlik harness. Clin Orthop Relat Res (155):25–9
Walton MJ, Isaacson Z, McMillan D, Hawkes R, Atherton WG (2010) The success of management with the Pavlik harness for developmental dysplasia of the hip using a United Kingdom screening programme and ultrasound-guided supervision. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92:1013–1016. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.92B7.23513
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gotzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP, Initiative S (2014) The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int J Surg 12:1495–1499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.07.013
Starnes DS, Tabor J, Yates D, Moore DS (2014) The Practice of Statistics. W. H. Freeman
Alshryda S, Howard JJ, Huntley JS, Schoenecker JG (2019) The pediatric and adolescent hip: essentials and evidence. Springer International Publishing
Storer SK, Skaggs DL (2006) Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Am Fam Physician 74:1310–1316
Atalar H, Sayli U, Yavuz OY, Uraş I, Dogruel H (2007) Indicators of successful use of the Pavlik harness in infants with developmental dysplasia of the hip. Int Orthop 31:145–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-006-0097-8
Viere RG, Birch JG, Herring JA, Roach JW, Johnston CE (1990) Use of the Pavlik harness in congenital dislocation of the hip. An analysis of failures of treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72:238–244
Lerman JA, Emans JB, Millis MB, Share J, Zurakowski D, Kasser JR (2001) Early failure of Pavlik harness treatment for developmental hip dysplasia: clinical and ultrasound predictors. J Pediatr Orthop 21:348–353
Jones GT, Schoenecker PL, Dias LS (1992) Developmental hip dysplasia potentiated by inappropriate use of the Pavlik harness. J Pediatr Orthop 12:722–726
Vadillo P, Encinas-Ullan CA, Moraleda L, Albinana J (2015) Results of the Pavlik harness when treating Ortolani-positive hips: predictors of failure and arthrographic findings. J Child Orthop 9:249–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-015-0666-8
Novais EN, Kestel LA, Carry PM, Meyers ML (2016) Higher Pavlik harness treatment failure is seen in Graf type IV ortolani-positive hips in males. Clin Orthop Relat Res 474:1847–1854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-016-4776-5
Borges JL, Kumar SJ, Guille JT (1995) Congenital dislocation of the hip in boys. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:975–984. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-199507000-00001
Lee WC, Gera SK, Mahadev A (2019) Developmental dysplasia of the hip: why are we still operating on them? A plea for institutional newborn clinical screening. Singapore Med J 60:150–153. https://doi.org/10.11622/smedj.2018064
Köse N, Omeroğlu H, Ozyurt B, Akçar N, Ozçelik A, Inan U, Seber S (2006) Our three-year experience with an ultrasonographic hip screening program conducted in infants at 3 to 4 weeks of age. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 40:285–290
White KK, Sucato DJ, Agrawal S, Browne R (2010) Ultrasonographic findings in hips with a positive Ortolani sign and their relationship to Pavlik harness failure. The Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume 92:113-120. 92/1/113 [pii] https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.H.01880
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank our librarians at the above centers for obtaining some of the references that are used in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by Nicholas Heinz, Vasileios Alexopoulos, Ibrar Majid, and Sattar Alshryda. Data cleaning and analysis were performed by Nada Abdulla, Maryam Ashoor, Sattar Alshryda, and Amar Hassan Khamis. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Nada Abdulla and Sattar Alshryda and refined by Ibrar Majid and Emmanouil Morakis, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed consent
Not applicable, as only no identifiable data have been used.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed to publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdulla, N., Ashoor, M., Heinz, N. et al. Prognostic factors for failed Pavlik harness treatment in infants with developmental dysplasia of the hip: a retrospective cohort study. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 47, 2337–2345 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05829-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05829-3