Abstract
Purpose
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the incidence of total hip arthroplasty (THA) in patients with Legg-Calve-Perthes disease (LCPD) treated conservatively or surgically and factors influencing the incidence of THA.
Methods
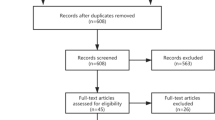
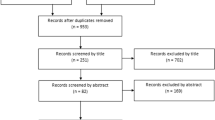
Long-term follow-up studies on the conservative or surgical treatments of LCPD from 1950 to 2021 were conducted using six public databases. Articles were screened by two investigators (PRISMA guidelines), and the quality of the included publications (n = 27) was assessed (MINORS criteria). R version 4.2.1 was used for statistical analysis.
Results
The overall incidences of THA were 6.8% and 5.14% in patients who were treated conservatively and surgically, respectively. At disease onset, the incidences of THA were 6.79% and 6.17% after conservative treatment and surgery in patients aged < seven years, respectively, and 16.97% and 3.61% in patients aged > seven years, respectively. The incidences of THA were 4.91%, 5.19%, and 23.18% in patients who were treated conservatively with ≤ 30, 30–40, and > 40 years of follow-up, respectively, and 3.68%, 3.11%, 9.66%, and 17.92% in patients who were treated surgically with ≤ ten, ten to 20, 20–40, and > 40 years of follow-up, respectively. In patients who received conservative treatment, the incidences of THA were 5.79% and 5.29% in patients with Stulberg I–II and III–V, respectively. In surgically treated patients, the incidence of THA was 0% in Stulberg I-II and 8% in Stulberg III-V.
Conclusion
Patients with LCPD had relatively low incidences of THA. The greater the age at disease onset and longer the follow-up, the higher the incidence of THA; however, the Stulberg classification was not directly associated with the incidence of THA.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are available in a repository upon request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Kim HK (2012) Pathophysiology and new strategies for the treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94:659–669. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.01834
Catterall A (1971) The natural history of Perthes’ disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 53:37–53
Nakashima Y, Kubota H, Yamamoto T, Mawatari T, Motomura G, Iwamoto Y (2011) Transtrochanteric rotational osteotomy for late-onset Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Pediatr Orthop 31:S223–S228. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e318223b4f3
Kelly FB Jr, Canale ST, Jones RR (1980) Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Long-term evaluation of non-containment treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 62:400–407
Aksoy MC, Cankus MC, Alanay A, Yazici M, Caglar O, Alpaslan AM (2005) Radiological outcome of proximal femoral varus osteotomy for the treatment of lateral pillar group-C Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Pediatr Orthop B 14:88–91. https://doi.org/10.1097/01202412-200503000-00005
Beer Y, Smorgick Y, Oron A, Mirovsky Y, Weigl D, Agar G, Shitrit R, Copeliovitch L (2008) Long-term results of proximal femoral osteotomy in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Pediatr Orthop 28:819–824. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e31818e122b
Kamegaya M, Saisu T, Takazawa M, Nakamura J (2008) Arthrographic indicators for decision making about femoral varus osteotomy in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Child Orthop 2:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-008-0120-2
Pecquery R, Laville JM, Salmeron F (2010) Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease treatment by augmentation acetabuloplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 96:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcot.2010.02.007
Stulberg SD, Cooperman DR, Wallensten R (1981) The natural history of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am 63:1095–1108
Kruse RW, Guille JT, Bowen JR (1991) Shelf arthroplasty in patients who have Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. A study of long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Am 73:1338–1347
Gower WE, Johnston RC (1971) Legg-Perthes disease. Long-term follow-up of thirty-six patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 53:759–768
Canavese F, Dimeglio A (2008) Perthes’ disease: prognosis in children under six years of age. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:940–945. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.90B7.20691
Ghanem I, Haddad E, Haidar R, Haddad-Zebouni S, Aoun N, Dagher F, Kharrat K (2010) Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in the treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease: improving mid-term outcome in severely deformed hips. J Child Orthop 4:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-009-0216-3
Kim HK, da Cunha AM, Browne R, Kim HT, Herring JA (2011) How much varus is optimal with proximal femoral osteotomy to preserve the femoral head in Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease? J Bone Joint Surg Am 93:341–347. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.00830
Catterall A (1986) Adolescent hip pain after Perthes’ disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res 209:65–69
McAndrew MP, Weinstein SL (1984) A long-term follow-up of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am 66:860–869. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-198466060-00006
Stančák A, Kautzner J, Chládek P, Adamec O, Havlas V, Trč T (2022) Predictors of radiographic outcomes of conservative and surgical treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Int Orthop 46:2869–2875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05584-x
Onishi E, Ikeda N, Ueo T (2011) Degenerative osteoarthritis after Perthes’ disease: a 36-year follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131:701–707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-011-1264-y
Lecuire F (2002) The long-term outcome of primary osteochondritis of the hip (Legg-Calvé-Perthes’ disease). J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:636–640. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.84b5.12124
Shohat N, Copeliovitch L, Smorgick Y, Atzmon R, Mirovsky Y, Shabshin N, Beer Y, Agar G (2016) The long-term outcome after varus derotational osteotomy for Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease: A mean follow-up of 42 Years. J Bone Joint Surg Am 98:1277–1285. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.15.01349
Shohat N, Gilat R, Shitrit R, Smorgick Y, Beer Y, Agar G (2017) A long-term follow-up study of the clinical and radiographic outcome of distal trochanteric transfer in Legg-Calvé-Perthes’ disease following varus derotational osteotomy. Bone Joint J 99-B:987–992. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.99B7.BJJ-2016-1346.R2
Perpich M, McBeath A, Kruse D (1983) Long-term follow-up of Perthes disease treated with spica casts. J Pediatr Orthop 3:160–165. https://doi.org/10.1097/01241398-198305000-00003
Wiig O, Terjesen T, Svenningsen S (2008) Prognostic factors and outcome of treatment in Perthes’ disease: a prospective study of 368 patients with five-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:1364–1371. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.90B10.20649
Ippolito E, Tudisco C, Farsetti P (1985) Long-term prognosis of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease developing during adolescence. J Pediatr Orthop 5:652–656. https://doi.org/10.1097/01241398-198511000-00004
Larson AN, Sucato DJ, Herring JA, Adolfsen SE, Kelly DM, Martus JE, Lovejoy JF, Browne R, Delarocha A (2012) A prospective multicenter study of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease: functional and radiographic outcomes of nonoperative treatment at a mean follow-up of twenty years. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94:584–592. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.J.01073
De Rosa V, Laurent M, Canavese F, Merlini L (2018) A simple, precocious, and reliable way to assess future clinical outcome in children with Perthes disease and mild femoral head involvement: correlation between MRI with diffusion-weighted and dynamic gadolinium-enhanced subtraction and Catterall and Herring classifications. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumat 28(7):1283–1290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-018-2209-8
Reddy RR, Morin C (2005) Chiari osteotomy in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. J Pediatr Orthop B 14:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/01202412-200501000-00001
Park KS, Cho KJ, Yang HY, Eshnazarov KE, Yoon TR (2017) Long-term results of modified salter innominate osteotomy for Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Clin Orthop Surg 9:397–404. https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.397
Leibold CS, Whitlock P, Schmaranzer F, Ziebarth K, Tannast M, Steppacher SD (2022) Development of acetabular retroversion in LCPD hips-an observational radiographic study from early stage to healing. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-022-04612-0
Wenger DR, Pring ME, Hosalkar HS, Caltoum CB, Lalonde FD, Bastrom TP (2010) Advanced containment methods for Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease: results of triple pelvic osteotomy. J Pediatr Orthop 30:749–757. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181f5a0de
Stepanovich M, Upasani VV, Bomar JD, Wenger DR (2017) Advanced containment with triple innominate osteotomy in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease: A viable option even in severe cases. J Pediatr Orthop 37:563–569. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0000000000000714
Herring JA, Kim HT, Browne R (2004) Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Part II: Prospective multicenter study of the effect of treatment on outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86:2121–2134
Froberg L, Christensen F, Pedersen NW, Overgaard S (2011) The need for total hip arthroplasty in Perthes disease: a long-term study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:1134–1140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1566-3
Shore BJ, Novais EN, Millis MB, Kim YJ (2012) Low early failure rates using a surgical dislocation approach in healed Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:2441–2449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-2187-1
Mosow N, Vettorazzi E, Breyer S, Ridderbusch K, Stücker R, Rupprecht M (2017) Outcome After Combined Pelvic and Femoral Osteotomies in Patients with Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am 99(3):207–213. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.16.00255
Adulkasem N, Phinyo P, Tangadulrat P, Wongcharoenwatana J, Ariyawatkul T, Chotigavanichaya C, Kaewpornsawan K, Eamsobhana P (2022) Comparative effectiveness of treatment modalities in severe Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of observational studies. Int Orthop 46(5):1085–1094. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-022-05352-x
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xinwang Zhi: Data acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data drafting of the manuscript, final approval of the version to be published.
Huimei Wu: Data acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data drafting of the manuscript, final approval of the version to be published.
Chenyu Xiang: Data acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data drafting of the manuscript, final approval of the version to be published.
Jianqun Wang: Analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, final approval of the version to be published.
Yeya Tan: Analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, final approval of the version to be published.
Chun Zeng: Analysis and interpretation of data, critical review, final approval of the version to be published.
Hongwen Xu: Analysis and interpretation of data, critical review, final approval of the version to be published.
Federico Canavese: Study design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript; editing and critical revision of the manuscript, final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This is a meta-analysis, and no ethical approval was required to commence the study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable as this is a meta-analysis.
Consent for publication
All the authors are giving their consent to publish this paper.
The protocol of the meta-analysis was registered in the PRISMA International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (CRD42022352494).
Competing interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, X., Wu, H., Xiang, C. et al. Incidence of total hip arthroplasty in patients with Legg-Calve-Perthes disease after conservative or surgical treatment: a meta-analysis. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 47, 1449–1464 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05770-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-023-05770-5